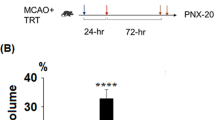
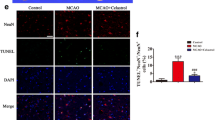
Abstract
CKLF1 is a chemokine with increased expression in ischemic brain, and targeting CKLF1 has shown therapeutic effects in cerebral ischemia model. Microglia/macrophage polarization is a mechanism involved in poststroke injury expansion. Considering the quick and obvious response of CKLF1 and expeditious evolution of stroke lesions, we focused on the effects of CKLF1 on microglial/macrophage polarization at early stage of ischemic stroke (IS). The present study is to investigate the CKLF1-mediated expression of microglia/macrophage phenotypes in vitro and in vivo, discussing the involved pathway. Primary microglia culture was used in vitro, and mice transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model was adopted to mimic IS. CKLF1 was added to the primary microglia for 24 h, and we found that CKLF1 modulated primary microglia skew toward M1 phenotype. In mice transient IS model, CKLF1 was stereotactically microinjected to the lateral ventricle of ischemic hemisphere. CKLF1 aggravated ischemic injury, accompanied by promoting microglia/macrophage toward M1 phenotypic polarization. Increased expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and decreased expression of anti-inflammatory cytokines were observed in mice subjected to cerebral ischemia and administrated with CKLF1. CKLF1−/− mice were used to confirm the effects of CKLF1. CKLF1−/− mice showed lighter cerebral damage and decreased M1 phenotype of microglia/macrophage compared with the WT control subjected to cerebral ischemia. Moreover, NF-κB activation enhancement was detected in CKLF1 treatment group. Our results demonstrated that CKLF1 is an important mediator that skewing microglia/macrophage toward M1 phenotype at early stage of cerebral ischemic injury, which further deteriorates followed inflammatory response, contributing to early expansion of cerebral ischemia injury. Targeting CKLF1 may be a novel way for IS therapy.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekhbat M, Neigh GN (2018) Sex differences in the neuro-immune consequences of stress: focus on depression and anxiety. Brain Behav Immun 67:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.02.006
Chauhan A, Moser H, McCullough LD (2017) Sex differences in ischaemic stroke: potential cellular mechanisms. Clin Sci 131(7):533–552. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20160841
Chen J, Li Z, Hatcher JT, Chen QH, Chen L, Wurster RD, Chan SL, Cheng Z (2017) Deletion of TRPC6 attenuates NMDA receptor-mediated Ca(2+) entry and Ca(2+)-induced neurotoxicity following cerebral ischemia and oxygen-glucose deprivation. Front Neurosci 11:138. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00138
Clemens JA, Stephenson DT, Dixon EP, Smalstig EB, Mincy RE, Rash KS, Little SP (1997) Global cerebral ischemia activates nuclear factor-kappa B prior to evidence of DNA fragmentation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 48(2):187–196
Cramer SC, Wolf SL, Adams HP Jr, Chen D, Dromerick AW, Dunning K, Ellerbe C, Grande A, Janis S, Lansberg MG, Lazar RM, Palesch YY, Richards L, Roth E, Savitz SI, Wechsler LR, Wintermark M, Broderick JP (2017) Stroke recovery and rehabilitation research: issues, opportunities, and the National Institutes of Health StrokeNet. Stroke J Cereb Circ 48(3):813–819. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015501
David S, Kroner A (2011) Repertoire of microglial and macrophage responses after spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Neurosci 12(7):388–399. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3053
Espinosa-Garcia C, Sayeed I, Yousuf S, Atif F, Sergeeva EG, Neigh GN, Stein DG (2017) Stress primes microglial polarization after global ischemia: therapeutic potential of progesterone. Brain Behav Immun 66:177–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2017.06.012
Frangogiannis NG (2007) Chemokines in ischemia and reperfusion. Thrombosis Haemostasis 97(5):738–747
Gibson CL (2013) Cerebral ischemic stroke: is gender important? J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(9):1355–1361. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.2013.102
Han W, Lou Y, Tang J, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Li Y, Gu W, Huang J, Gui L, Tang Y, Li F, Song Q, Di C, Wang L, Shi Q, Sun R, Xia D, Rui M, Tang J, Ma D (2001) Molecular cloning and characterization of chemokine-like factor 1 (CKLF1), a novel human cytokine with unique structure and potential chemotactic activity. Biochem J 357(Pt 1):127–135
Hu X, Li P, Guo Y, Wang H, Leak RK, Chen S, Gao Y, Chen J (2012) Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics reveal novel mechanism of injury expansion after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke J Cereb Circ 43(11):3063–3070. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.659656
Huang M, Cheng G, Tan H, Qin R, Zou Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2017) Capsaicin protects cortical neurons against ischemia/reperfusion injury via down-regulating NMDA receptors. Exp Neurol 295:66–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.05.001
Jin R, Liu L, Zhang S, Nanda A, Li G (2013) Role of inflammation and its mediators in acute ischemic stroke. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 6(5):834–851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-013-9508-6
Jin Q, Cheng J, Liu Y, Wu J, Wang X, Wei S, Zhou X, Qin Z, Jia J, Zhen X (2014) Improvement of functional recovery by chronic metformin treatment is associated with enhanced alternative activation of microglia/macrophages and increased angiogenesis and neurogenesis following experimental stroke. Brain Behav Immun 40:131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2014.03.003
Klein SL, Flanagan KL (2016) Sex differences in immune responses. Nat Rev Immunol 16(10):626–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri.2016.90
Kong LL, Hu JF, Zhang W, Yuan YH, Ma KL, Han N, Chen NH (2011) Expression of chemokine-like factor 1 after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neurosci Lett 505(1):14–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.09.031
Kong LL, Hu JF, Zhang W, Yuan YH, Han N, Chen NH (2012) C19, a C-terminal peptide of chemokine-like factor 1, protects the brain against focal brain ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 508(1):13–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.11.048
Kong LL, Wang ZY, Han N, Zhuang XM, Wang ZZ, Li H, Chen NH (2014) Neutralization of chemokine-like factor 1, a novel C-C chemokine, protects against focal cerebral ischemia by inhibiting neutrophil infiltration via MAPK pathways in rats. J Neuroinflamm 11:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-11-112
Lalancette-Hebert M, Gowing G, Simard A, Weng YC, Kriz J (2007) Selective ablation of proliferating microglial cells exacerbates ischemic injury in the brain. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 27(10):2596–2605. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5360-06.2007
Lan X, Han X, Li Q, Yang QW, Wang J (2017) Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat Rev Neurol 13(7):420–433. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.69
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb perspect Biol 1(6):a001651. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
Li L, Zhi D, Shen Y, Liu K, Li H, Chen J (2016) Effects of CC-chemokine receptor 5 on ROCK2 and P-MLC2 expression after focal cerebral ischaemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Brain Injury 30(4):468–473. https://doi.org/10.3109/02699052.2015.1129557
Li P, Wang L, Zhou Y, Gan Y, Zhu W, Xia Y, Jiang X, Watkins S, Vazquez A, Thomson AW, Chen J, Yu W, Hu X (2017) C-C chemokine receptor type 5 (CCR5)-mediated docking of transferred Tregs protects against early blood–brain barrier disruption after stroke. J Am Heart Assoc 6 (8). https://doi.org/10.1161/jaha.117.006387
Loane DJ, Byrnes KR (2010) Role of microglia in neurotrauma. Neurother J Am Soc Exp Neurother 7(4):366–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2010.07.002
Ma Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang GY (2017) The biphasic function of microglia in ischemic stroke. Prog Neurobiol 157:247–272. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2016.01.005
Mao L, Huang M, Chen SC, Li YN, Xia YP, He QW, Wang MD, Huang Y, Zheng L, Hu B (2014) Endogenous endothelial progenitor cells participate in neovascularization via CXCR4/SDF-1 axis and improve outcome after stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 20(5):460–468. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12238
Mirabelli-Badenier M, Braunersreuther V, Viviani GL, Dallegri F, Quercioli A, Veneselli E, Mach F, Montecucco F (2011) CC and CXC chemokines are pivotal mediators of cerebral injury in ischaemic stroke. Thrombosis Haemostasis 105(3):409–420. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH10-10-0662
Mori M, Matsubara K, Matsubara Y, Uchikura Y, Hashimoto H, Fujioka T, Matsumoto T (2015) Stromal cell-derived factor-1alpha plays a crucial role based on neuroprotective role in neonatal brain injury in rats. Int J Mol Sci 16(8):18018–18032. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms160818018
Murray PJ, Allen JE, Biswas SK, Fisher EA, Gilroy DW, Goerdt S, Gordon S, Hamilton JA, Ivashkiv LB, Lawrence T, Locati M, Mantovani A, Martinez FO, Mege JL, Mosser DM, Natoli G, Saeij JP, Schultze JL, Shirey KA, Sica A, Suttles J, Udalova I, van Ginderachter JA, Vogel SN, Wynn TA (2014) Macrophage activation and polarization: nomenclature and experimental guidelines. Immunity 41(1):14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.008
Nash KM, Schiefer IT, Shah ZA (2018) Development of a reactive oxygen species-sensitive nitric oxide synthase inhibitor for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 115:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.12.027
Pan J, Jin JL, Ge HM, Yin KL, Chen X, Han LJ, Chen Y, Qian L, Li XX, Xu Y (2015) Malibatol A regulates microglia M1/M2 polarization in experimental stroke in a PPARgamma-dependent manner. J Neuroinflamm 12:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0270-3
Parsa R, Lund H, Tosevski I, Zhang XM, Malipiero U, Beckervordersandforth J, Merkler D, Prinz M, Gyllenberg A, James T, Warnecke A, Hillert J, Alfredsson L, Kockum I, Olsson T, Fontana A, Suter T, Harris RA (2016) TGFbeta regulates persistent neuroinflammation by controlling Th1 polarization and ROS production via monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Glia 64(11):1925–1937. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.23033
Shao Y, Deng T, Zhang T, Li P, Wang Y (2015) FAM19A3, a novel secreted protein, modulates the microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics and ameliorates cerebral ischemia. FEBS Lett 589(4):467–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2015.01.003
Shih RH, Wang CY, Yang CM (2015) NF-kappaB signaling pathways in neurological inflammation: a mini review. Front Mol Neurosci 8:77. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2015.00077
Sorce S, Bonnefont J, Julien S, Marq-Lin N, Rodriguez I, Dubois-Dauphin M, Krause KH (2010) Increased brain damage after ischaemic stroke in mice lacking the chemokine receptor CCR5. Br J Pharmacol 160(2):311–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2010.00697.x
Venna VR, Weston G, Benashski SE, Tarabishy S, Liu F, Li J, Conti LH, McCullough LD (2012) NF-kappaB contributes to the detrimental effects of social isolation after experimental stroke. Acta neuropathol 124(3):425–438. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-012-0990-8
Victoria ECG, de Brito Toscano EC, de Sousa Cardoso AC, da Silva DG, de Miranda AS, da Silva Barcelos L, Sugimoto MA, Sousa LP, de Assis Lima IV, de Oliveira ACP, Brant F, Machado FS, Teixeira MM, Teixeira AL, Rachid MA (2017) Knockdown of C-C chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) is protective against cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. Curr Neurovasc Res 14(2):125–131. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567202614666170313113056
Wang L, Zhao H, Zhai ZZ, Qu LX (2018) Protective effect and mechanism of ginsenoside Rg1 in cerebral ischaemia–reperfusion injury in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 99:876–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.136
Won S, Lee JK, Stein DG (2015) Recombinant tissue plasminogen activator promotes, and progesterone attenuates, microglia/macrophage M1 polarization and recruitment of microglia after MCAO stroke in rats. Brain Behav Immun 49:267–279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.06.007
Woo MS, Park JS, Choi IY, Kim WK, Kim HS (2008) Inhibition of MMP-3 or -9 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of proinflammatory cytokines and iNOS in microglia. J Neurochem 106(2):770–780. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2008.05430.x
Xia CY, Zhang S, Gao Y, Wang ZZ, Chen NH (2015) Selective modulation of microglia polarization to M2 phenotype for stroke treatment. Int Immunopharmacol 25(2):377–382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.02.019
Yan YP, Sailor KA, Lang BT, Park SW, Vemuganti R, Dempsey RJ (2007) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 plays a critical role in neuroblast migration after focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab Off J Int Soc Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(6):1213–1224. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600432
Zhou W, Liesz A, Bauer H, Sommer C, Lahrmann B, Valous N, Grabe N, Veltkamp R (2013) Postischemic brain infiltration of leukocyte subpopulations differs among murine permanent and transient focal cerebral ischemia models. Brain Pathol 23(1):34–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1750-3639.2012.00614.x
Zuo W, Zhang W, Chen NH (2013) Sexual dimorphism in cerebral ischemia injury. Eur J Pharmacol 711(1–3):73–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.04.024
Zuo W, Yang PF, Chen J, Zhang Z, Chen NH (2016) Drp-1, a potential therapeutic target for brain ischaemic stroke. Br J Pharmacol 173(10):1665–1677. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13468
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730093, 81730096, 81873026, U1402221); the National Mega-project for Innovative Drugs (2018ZX09711001-002-007, 2018ZX09711001-003-005, 2018ZX09711001-009-013); CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (2016-I2M-1-004); Beijing Key Laboratory of New Drug Mechanisms and Pharmacological Evaluation Study (BZ0150); The State Key Laboratory Fund Open Project (GTZK201610); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M540066); Project of NDRC and State Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine (60011000); Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory for Standardization of Important Chinese Herbal Pieces (BG201701, 4981-0901020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chen Chen, Shi-feng Chu, Zhao Zhang, Nai-hong Chen conceptualized and designed the study; Chen Chen, Qi-di Ai, Fei-Fei Guan, Sha-Sha Wang, Yi-Xiao Dong, Jie-Zhu, Nai-hong Chen acquired and analyzed the data; Chen Chen, Qi-di Ai, Wen-Xuan Jian, Nai-hong Chen drafted the text and prepared the figures. Final approval of the version to be published: All authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Chu, SF., Ai, QD. et al. CKLF1 Aggravates Focal Cerebral Ischemia Injury at Early Stage Partly by Modulating Microglia/Macrophage Toward M1 Polarization Through CCR4. Cell Mol Neurobiol 39, 651–669 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00669-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-019-00669-5