Abstract
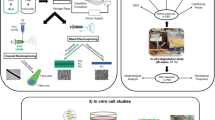
A key aspect of cell replacement therapy in brain injury treatment is construction of a suitable biomaterial scaffold that can effectively carry and transport the therapeutic cells to the target area. In the present study, we created small 3D porous chitosan scaffolds through freeze-drying, and showed that these can support and enhance the differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) to nerve cells in vitro. The DPSCs were collected from the dental pulp of adult human third molars. At a swelling rate of ~84.33 ± 10.92 %, the scaffold displayed high porosity and interconnectivity of pores, as revealed by SEM. Cell counting kit-8 assay established the biocompatibility of the chitosan scaffold, supporting the growth and survival of DPSCs. The successful neural differentiation of DPSCs was assayed by RT-PCR, western blotting, and immunofluorescence. We found that the scaffold-attached DPSCs showed high expression of Nestin that decreased sharply following induction of differentiation. Exposure to the differentiation media also increased the expression of neural molecular markers Microtubule-associated protein 2, glial fibrillary acidic protein, and 2′,3′-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. This study demonstrates that the granular 3D chitosan scaffolds are non-cytotoxic, biocompatible, and provide a conducive and favorable micro-environment for attachment, survival, and neural differentiation of DPSCs. These scaffolds have enormous potential to facilitate future advances in treatment of brain injury.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur A, Rychkov G, Shi S, Koblar SA, Gronthos S (2008) Adult human dental pulp stem cells differentiate toward functionally active neurons under appropriate environmental cues. Stem Cells 26:1787–1795
Arthur A, Shi S, Zannettino AC, Fujii N, Gronthos S, Koblar SA (2009) Implanted adult human dental pulp stem cells induce endogenous axon guidance. Stem Cells 27:2229–2237
Bjorklund A, Lindvall O (2000) Cell replacement therapies for central nervous system disorders. Nat Neurosci 3:537–544
Chai Y, Jiang X, Ito Y, Bringas P Jr, Han J, Rowitch DH, Soriano P, McMahon AP, Sucov HM (2000) Fate of the mammalian cranial neural crest during tooth and mandibular morphogenesis. Development 127:1671–1679
d’Aquino R, De Rosa A, Laino G, Caruso F, Guida L, Rullo R, Checchi V, Laino L, Tirino V, Papaccio G (2009) Human dental pulp stem cells: from biology to clinical applications. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 312B:408–415
Dokmeci MR, Khademhosseini A (2011) Preface to special topic: microfluidics in cell biology and tissue engineering. Biomicrofluidics 5:22101
Feng X, Xing J, Feng G, Sang A, Shen B, Xu Y, Jiang J, Liu S, Tan W, Gu Z, Li L (2013) Age-dependent impaired neurogenic differentiation capacity of dental stem cell is associated with Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33:1023–1031
Fukuda J, Khademhosseini A, Yeo Y, Yang X, Yeh J, Eng G, Blumling J, Wang CF, Kohane DS, Langer R (2006) Micromolding of photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel for spheroid microarray and co-cultures. Biomaterials 27:5259–5267
Gaspar VM, Sousa F, Queiroz JA, Correia IJ (2011) Formulation of chitosan-TPP-pDNA nanocapsules for gene therapy applications. Nanotechnology 22:015101
Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, Robey PG, Shi S (2000) Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13625–13630
Itoh S, Suzuki M, Yamaguchi I, Takakuda K, Kobayashi H, Shinomiya K, Tanaka J (2003a) Development of a nerve scaffold using a tendon chitosan tube. Artif Organs 27:1079–1088
Itoh S, Yamaguchi I, Suzuki M, Ichinose S, Takakuda K, Kobayashi H, Shinomiya K, Tanaka J (2003b) Hydroxyapatite-coated tendon chitosan tubes with adsorbed laminin peptides facilitate nerve regeneration in vivo. Brain Res 993:111–123
Ji C, Khademhosseini A, Dehghani F (2011) Enhancing cell penetration and proliferation in chitosan hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 32:9719–9729
Kas HS (1997) Chitosan: properties, preparations and application to microparticulate systems. J Microencapsul 14:689–711
Kean T, Thanou M (2010) Biodegradation, biodistribution and toxicity of chitosan. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:3–11
Kerkis I, Ambrosio CE, Kerkis A, Martins DS, Zucconi E, Fonseca SA, Cabral RM, Maranduba CM, Gaiad TP, Morini AC, Vieira NM, Brolio MP, Sant’Anna OA, Miglino MA, Zatz M (2008) Early transplantation of human immature dental pulp stem cells from baby teeth to golden retriever muscular dystrophy (GRMD) dogs: local or systemic? J Transl Med 6:35
Kim IY, Seo SJ, Moon HS, Yoo MK, Park IY, Kim BC, Cho CS (2008) Chitosan and its derivatives for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Adv 26:1–21
Kim NR, Lee DH, Chung PH, Yang HC (2009) Distinct differentiation properties of human dental pulp cells on collagen, gelatin, and chitosan scaffolds. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108:e94–e100
Lee M, Wu BM, Dunn JC (2008) Effect of scaffold architecture and pore size on smooth muscle cell growth. J Biomed Mater Res A 87:1010–1016
Li Z, Ramay HR, Hauch KD, Xiao D, Zhang M (2005) Chitosan-alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 26:3919–3928
Li X, Yang Z, Zhang A, Wang T, Chen W (2009) Repair of thoracic spinal cord injury by chitosan tube implantation in adult rats. Biomaterials 30:1121–1132
Muzzarelli RA (2010) Chitins and chitosans as immunoadjuvants and non-allergenic drug carriers. Mar Drugs 8:292–312
Nakashima M, Akamine A (2005) The application of tissue engineering to regeneration of pulp and dentin in endodontics. J Endod 31:711–718
Nosrat IV, Smith CA, Mullally P, Olson L, Nosrat CA (2004) Dental pulp cells provide neurotrophic support for dopaminergic neurons and differentiate into neurons in vitro; implications for tissue engineering and repair in the nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 19:2388–2398
Ribeiro MP, Espiga A, Silva D, Baptista P, Henriques J, Ferreira C, Silva JC, Borges JP, Pires E, Chaves P, Correia IJ (2009) Development of a new chitosan hydrogel for wound dressing. Wound Repair Regen 17:817–824
Sakai K, Yamamoto A, Matsubara K, Nakamura S, Naruse M, Yamagata M, Sakamoto K, Tauchi R, Wakao N, Imagama S, Hibi H, Kadomatsu K, Ishiguro N, Ueda M (2012) Human dental pulp-derived stem cells promote locomotor recovery after complete transection of the rat spinal cord by multiple neuro-regenerative mechanisms. J Clin Invest 122:80–90
Shi W, Nie D, Jin G, Chen W, Xia L, Wu X, Su X, Xu X, Ni L, Zhang X, Chen J (2012) BDNF blended chitosan scaffolds for human umbilical cord MSC transplants in traumatic brain injury therapy. Biomaterials 33:3119–3126
Tamaki Y, Nakahara T, Ishikawa H, Sato S (2013) In vitro analysis of mesenchymal stem cells derived from human teeth and bone marrow. Odontology 101:121–132
Xu Y, Gu Z, Shen B, Xu G, Zhou T, Jiang J, Xing J, Liu S, Li M, Tan W, Feng G, Sang A, Li L (2013) Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in retinal neuron-like differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from nonobese diabetic mice. J Mol Neurosci 49:250–261
Yamagata M, Yamamoto A, Kako E, Kaneko N, Matsubara K, Sakai K, Sawamoto K, Ueda M (2013) Human dental pulp-derived stem cells protect against hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal mice. Stroke 44:551–554
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Graduate Student Innovation of Science and Technology Projects in Jiangsu Province and in Nantong University (Grants No.YKC13084); the “Top Six Types of Talents” Financial Assistance of Jiangsu Province Grant (No. 7 and No. 10); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31171038), Jiangsu Natural Science Foundation (BK2011385); the Grant of Nantong University for Innovation Talent and a project funded by the Priority Academic Program Development (PAPD) of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions. We thank Department of Human Anatomy of Medical College in Nantong University for technical assistance and equipment support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xingmei Feng and Xiaohui Lu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, X., Lu, X., Huang, D. et al. 3D Porous Chitosan Scaffolds Suit Survival and Neural Differentiation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 34, 859–870 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0063-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-014-0063-8