Abstract
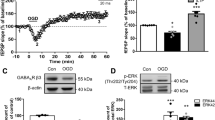
The function of Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a main component of green tea, has been widely investigated, amelioration of synaptic transmission and neuroprotective effects against ischemia-induced brain damage among others. However, the mechanism underlying is still unveiled. We investigated the effects of EGCG on high frequency stimulation-induced long-term potentiation (LTP) in the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse with or without cerebral ischemia injury induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) in vivo to examine the possible relations between EGCG and synaptic transmission. Application of EGCG modulated synaptic transmission and produced a dose-dependent improvement of the induction of LTP. However, relative high-dose EGCG can block the induction of LTP at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse in normal rat in vivo. In addition, the effects of EGCG were observed on the infarct volume and neurological deficit in rats subjected to MCAO; furthermore, the cell viability of primary cultured rat hippocampal and cortical neurons suffered from oxygen–glucose deprivation were evaluated with MTT and LDH assay, which showed significant neuroprotective properties in vitro. Surprisingly, the contents of the glutamate (Glu), glycine (Gly), and gamma-aminobutyric acid amino acids were totally disequilibrated before and after cerebral ischemia injury and could be rebalanced to original level by application of EGCG. Our results suggest that EGCG is able to improve the efficiency of synaptic transmission in cerebral ischemia injury with attenuated effect related to the neuroprotection of EGCG through regulating excitatory and inhibitory amino acid balance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bae JH, Mun KC, Park WK, Lee SR, Suh SI, Baek WK, Yim MB, Kwon TK, Song DK (2002) EGCG attenuates AMPA-induced intracellular calcium increase in hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 290:1506–1512
Bliss TV, Collingridge GL (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361:31–39
Cheng Z, He W, Zhou X, Lv Q, Xu X, Yang S, Zhao C, Guo L (2011) Cordycepin protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro. Eur J Pharmacol 664:20–28
Di Filippo M, Tozzi A, Costa C, Belcastro V, Tantucci M, Picconi B, Calabresi P (2008) Plasticity and repair in the post-ischemic brain. Neuropharmacology 55:353–362
Ginsberg MD, Busto R (1989) Rodent models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 20:1627–1642
Hallenbeck JM, Dutka AJ (1990) Background review and current concepts of reperfusion injury. Arch Neurol 47:1245–1254
He Z, Huang L, Wu Y, Wang J, Wang H, Guo L (2008) DDPH: improving cognitive deficits beyond its alpha 1-adrenoceptor antagonism in chronic cerebral hypoperfused rats. Eur J Pharmacol 588:178–188
He Z, Lu Q, Xu X, Huang L, Chen J, Guo L (2009) DDPH ameliorated oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced injury in rat hippocampal neurons via interrupting Ca2+ overload and glutamate release. Eur J Pharmacol 603:50–55
He W, Cheng Z, Fu G, Xu X, Lu Q, Guo L (2010) ZD7288-induced suppression of long-term potentiation was attenuated by exogenous NMDA at the Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapse in the rat in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 631:10–16
Higdon JV, Frei B (2003) Tea catechins and polyphenols: health effects, metabolism, and antioxidant functions. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 43:89–143
Huang L, Li Q, Li H, He Z, Cheng Z, Chen J, Guo L (2009a) Inhibition of intracellular Ca2+ release by a Rho-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of ischemic damage in primary cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 602:238–244
Huang X, Li Q, Li H, Guo L (2009b) Neuroprotective and antioxidative effect of cactus polysaccharides in vivo and in vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:1211–1221
Jung YD, Ellis LM (2001) Inhibition of tumour invasion and angiogenesis by epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG), a major component of green tea. Int J Exp Pathol 82:309–316
Jung YD, Kim MS, Shin BA, Chay KO, Ahn BW, Liu W, Bucana CD, Gallick GE, Ellis LM (2001) EGCG, a major component of green tea, inhibits tumour growth by inhibiting VEGF induction in human colon carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer 84:844–850
Kang KS, Wen Y, Yamabe N, Fukui M, Bishop SC, Zhu BT (2010) Dual beneficial effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate on levodopa methylation and hippocampal neurodegeneration: in vitro and in vivo studies. PLoS One 5:e11951
Koh JY, Choi DW (1987) Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J Neurosci Methods 20:83–90
Lee JH, Song DK, Jung CH, Shin DH, Park J, Kwon TK, Jang BC, Mun KC, Kim SP, Suh SI, Bae JH (2004) (−)-Epigallocatechin gallate attenuates glutamate-induced cytotoxicity via intracellular Ca modulation in PC12 cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 31:530–536
Li Q, Huang XJ, He W, Ding J, Jia JT, Fu G, Wang HX, Guo LJ (2009) Neuroprotective potential of fasudil mesylate in brain ischemia-reperfusion injury of rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:169–180
Lipton SA, Singel DJ, Stamler JS (1994) Nitric oxide in the central nervous system. Prog Brain Res 103:359–364
Liu J, Kuang P, Wu W, Zhang F, Wan F, Huang Y, Ding A (1998) Radix Salviae miltiorrhizae protects rat hippocampal neuron in culture from anoxic damage. J Tradit Chin Med 18:49–54
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Lyubkin M, Durand DM, Haxhiu MA (1997) Interaction between tetanus long-term potentiation and hypoxia-induced potentiation in the rat hippocampus. J Neurophysiol 78:2475–2482
Macleod MR, Davis SM, Mitchell PJ, Gerraty RP, Fitt G, Hankey GJ, Stewart-Wynne EG, Rosen D, McNeil JJ, Bladin CF, Chambers BR, Herkes GK, Young D, Donnan GA (2005) Results of a multicentre, randomised controlled trial of intra-arterial urokinase in the treatment of acute posterior circulation ischaemic stroke. Cerebrovasc Dis 20:12–17
Mittmann T, Qu M, Zilles K, Luhmann HJ (1998) Long-term cellular dysfunction after focal cerebral ischemia: in vitro analyses. Neuroscience 85:15–27
Mondaca M, Hernandez A, Perez H, Valladares L, Sierralta W, Fernandez V, Soto-Moyano R (2004) Alpha2-adrenoceptor modulation of long-term potentiation elicited in vivo in rat occipital cortex. Brain Res 1021:292–296
Patil CS, Singh VP, Kulkarni SK (2006) Modulatory effect of sildenafil in diabetes and electroconvulsive shock-induced cognitive dysfunction in rats. Pharmacol Rep 58:373–380
Qu M, Mittmann T, Luhmann HJ, Schleicher A, Zilles K (1998) Long-term changes of ionotropic glutamate and GABA receptors after unilateral permanent focal cerebral ischemia in the mouse brain. Neuroscience 85:29–43
Schwartz-Bloom RD, Sah R (2001) gamma-Aminobutyric acid(A) neurotransmission and cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem 77:353–371
Sun HS, Jackson MF, Martin LJ, Jansen K, Teves L, Cui H, Kiyonaka S, Mori Y, Jones M, Forder JP, Golde TE, Orser BA, Macdonald JF, Tymianski M (2009) Suppression of hippocampal TRPM7 protein prevents delayed neuronal death in brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 12:1300–1307
Swanson RA, Shiraishi K, Morton MT, Sharp FR (1990) Methionine sulfoximine reduces cortical infarct size in rats after middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 21:322–327
Thanvi B, Treadwell S, Robinson T (2008) Early neurological deterioration in acute ischaemic stroke: predictors, mechanisms and management. Postgrad Med J 84:412–417
Tseng KY, O’Donnell P (2004) Dopamine-glutamate interactions controlling prefrontal cortical pyramidal cell excitability involve multiple signaling mechanisms. J Neurosci 24:5131–5139
Wang Y, Mei Y, Feng D, Xu L (2006) (−)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate protects mice from concanavalin A-induced hepatitis through suppressing immune-mediated liver injury. Clin Exp Immunol 145:485–492
Xie W, Ramakrishna N, Wieraszko A, Hwang YW (2008) Promotion of neuronal plasticity by (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Neurochem Res 33:776–783
Yamashita K, Suzuki Y, Matsui T, Yoshimaru T, Yamaki M, Suzuki-Karasaki M, Hayakawa S, Shimizu K (2000) Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells: role of tyrosine phosphorylation pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 274:603–608
Yin ST, Tang ML, Su L, Chen L, Hu P, Wang HL, Wang M, Ruan DY (2008) Effects of Epigallocatechin-3-gallate on lead-induced oxidative damage. Toxicology 249:45–54
Yu HN, Yin JJ, Shen SR (2004) Growth inhibition of prostate cancer cells by epigallocatechin gallate in the presence of Cu2+. J Agric Food Chem 52:462–466
Zhang B, Rusciano D, Osborne NN (2008) Orally administered epigallocatechin gallate attenuates retinal neuronal death in vivo and light-induced apoptosis in vitro. Brain Res 1198:141–152
Zhao X, Shoji S, Lau P (2005) Balanced GABAergic and glutamatergic synapse development in hippocampal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 330:1110–1115
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Foundation of Nature and Science of China (No. 81173038) and by the Foundation of Central Authorities of an Institution of Higher Learning of Scientific Research Special Fund (No. 2011TS073).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, J., Fu, G., Zhao, Y. et al. EGCG Ameliorates the Suppression of Long-Term Potentiation Induced by Ischemia at the Schaffer Collateral-CA1 Synapse in the Rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32, 267–277 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9758-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9758-2