Abstract
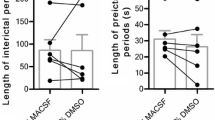
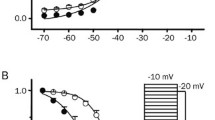
The purpose of this study was to analyze the rapid effects of the antiepileptic drugs valproate, lamotrigine, and levetiracetam on excitability and firing properties of hippocampal neurons. The drug effects on resting potential, action potential, and repetitive firing properties were studied in whole-cell current-clamp recordings of CA1 neurons in rat brain slices. Lamotrigine changed action potential rising slope by −24 ± 38 V/s (mean ± SD), peak amplitude by −6.8 ± 5.0 mV, and maximum firing frequency by −60 ± 13%. Lamotrigine thereto increased the voltage threshold by 4.3 ± 4.2 mV and augmented the action potential attenuation during repetitive firing. All effects were significant (P < 0.01 to P < 0.0002) compared to control cells. Valproate and levetiracetam showed no significant effects on these parameters. None of the tested drugs had a significant effect on the resting potential. The lamotrigine effects are consistent with sodium channel blocking which may explain or contribute to the antiepileptic mode of action. Valproate and levetiracetam did not show these effects and the mechanism of their antiepileptic action need to be different. These findings (valproate) differ in some respects from findings reported in cultured or dissociated neurons. In a slice where the neurons have largely preserved connections, drug effects are likely to be more similar to the therapeutic action in the brain.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albus H, Williamson R (1998) Electrophysiologic analysis of the actions of valproate on pyramidal neurons in the rat hippocampal slice. Epilepsia 39:124–139
Altrup U, Gerlach G, Reith H, Said MN, Speckmann EJ (1992) Effects of valproate in a model nervous system (buccal ganglia of Helix pomatia): I. antiepileptic actions. Epilepsia 33:743–752
Davis R, Peters DH, McTavish D (1994) Valproic acid. A reappraisal of its pharmacological properties and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. Drugs 47:332–372
Englund M, Hyllienmark L, Brismar T (2001) Chemical hypoxia in hippocampal pyramidal cells affects membrane potential differentially depending on resting potential. Neuroscience 106:89–94
Englund M, Bjurling M, Edin F, Hyllienmark L, Brismar T (2004) Hypoxic excitability changes and sodium currents in hippocampus CA1 neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24:685–694
Guven M, Bozdemir H, Gunay I, Sarica Y, Kahraman I, Koc F (2006) The actions of lamotrigine and levetiracetam on the conduction properties of isolated rat sciatic nerve. Eur J Pharmacol 553:129–134
Honack D, Loscher W (1992) Intravenous valproate: onset and duration of anticonvulsant activity against a series of electroconvulsions in comparison with diazepam and phenytoin. Epilepsy Res 13:215–221
Huang CW, Tsai JJ, Huang CC, Wu SN (2009) Experimental and simulation studies on the mechanisms of levetiracetam-mediated inhibition of delayed-rectifier potassium current (KV3.1): contribution to the firing of action potentials. J Physiol Pharmacol 60:37–47
Hyllienmark L, Brismar T (1996) Effect of metabolic inhibition on K+ channels in pyramidal cells of the hippocampal CA1 region in rat brain slices. J Physiol 496:155–164
Kelly KM, Gross RA, Macdonald RL (1990) Valproic acid selectively reduces the low-threshold (T) calcium current in rat nodose neurons. Neurosci Lett 116:233–238
Kuo CC, Lu L (1997) Characterization of lamotrigine inhibition of Na+ channels in rat hippocampal neurones. Br J Pharmacol 121:1231–1238
Loscher W, Honack D (1993) Profile of ucb L059, a novel anticonvulsant drug, in models of partial and generalized epilepsy in mice and rats. Eur J Pharmacol 232:147–158
Loscher W, Vetter M (1985) In vivo effects of aminooxyacetic acid and valproic acid on nerve terminal (synaptosomal) GABA levels in discrete brain areas of the rat. Correlation to pharmacological activities. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1747–1756
Loscher W, Fassbender CP, Nolting B (1991) The role of technical, biological and pharmacological factors in the laboratory evaluation of anticonvulsant drugs. II. Maximal electroshock seizure models. Epilepsy Res 8:79–94
Lynch BA, Lambeng N, Nocka K, Kensel-Hammes P, Bajjalieh SM, Matagne A, Fuks B (2004) The synaptic vesicle protein SV2A is the binding site for the antiepileptic drug levetiracetam. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9861–9866
Madeja M, Margineanu DG, Gorji A, Siep E, Boerrigter P, Klitgaard H, Speckmann EJ (2003) Reduction of voltage-operated potassium currents by levetiracetam: a novel antiepileptic mechanism of action? Neuropharmacology 45:661–671
Margineanu DG, Klitgaard H (2000) Inhibition of neuronal hypersynchrony in vitro differentiates levetiracetam from classical antiepileptic drugs. Pharmacol Res 42:281–285
Martin ED, Pozo MA (2003) Valproate suppresses status epilepticus induced by 4-aminopyridine in CA1 hippocampus region. Epilepsia 44:1375–1379
Niespodziany I, Klitgaard H, Margineanu DG (2001) Levetiracetam inhibits the high-voltage-activated Ca(2+) current in pyramidal neurones of rat hippocampal slices. Neurosci Lett 306:5–8
Niespodziany I, Klitgaard H, Margineanu DG (2004) Is the persistent sodium current a specific target of anti-absence drugs? Neuroreport 15:1049–1052
Patsalos PN (2004) Clinical pharmacokinetics of levetiracetam. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:707–724
Poolos NP, Migliore M, Johnston D (2002) Pharmacological upregulation of h-channels reduces the excitability of pyramidal neuron dendrites. Nat Neurosci 5:767–774
Rogawski MA, Loscher W (2004) The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:553–564
Stefani A, Spadoni F, Siniscalchi A, Bernardi G (1996) Lamotrigine inhibits Ca2+ currents in cortical neurons: functional implications. Eur J Pharmacol 307:113–116
Storm JF (1987) Action potential repolarization and a fast after-hyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 385:733–759
Taverna S, Mantegazza M, Franceschetti S, Avanzini G (1998) Valproate selectively reduces the persistent fraction of Na+ current in neocortical neurons. Epilepsy Res 32:304–308
Van den Berg RJ, Kok P, Voskuyl RA (1993) Valproate and sodium currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Exp Brain Res 93:279–287
Van Dongen AM, Van Erp MG, Voskuyl RA (1986) Valproate reduces excitability by blockage of sodium and potassium conductance. Epilepsia 27:177–182
Vreugdenhil M, Wadman WJ (1999) Modulation of sodium currents in rat CA1 neurons by carbamazepine and valproate after kindling epileptogenesis. Epilepsia 40:1512–1522
Wamil AW, Loscher W, McLean MJ (1997) Trans-2-en-valproic acid limits action potential firing frequency in mouse central neurons in cell culture. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:1349–1356
Xie X, Lancaster B, Peakman T, Garthwaite J (1995) Interaction of the antiepileptic drug lamotrigine with recombinant rat brain type IIA Na+ channels and with native Na+ channels in rat hippocampal neurones. Pflugers Arch 430:437–446
Zeise ML, Kasparow S, Zieglgansberger W (1991) Valproate suppresses N-methyl-d-aspartate- evoked, transient depolarizations in the rat neocortex in vitro. Brain Res 544:345–348
Zona C, Avoli M (1990) Effects induced by the antiepileptic drug valproic acid upon the ionic currents recorded in rat neocortical neurons in cell culture. Exp Brain Res 81:313–317
Zona C, Avoli M (1997) Lamotrigine reduces voltage-gated sodium currents in rat central neurons in culture. Epilepsia 38:522–525
Zona C, Niespodziany I, Marchetti C, Klitgaard H, Bernardi G, Margineanu DG (2001) Levetiracetam does not modulate neuronal voltage-gated Na+ and T-type Ca2+ currents. Seizure 10:279–286
Zona C, Tancredi V, Longone P, D’Arcangelo G, D’Antuono M, Manfredi M, Avoli M (2002) Neocortical potassium currents are enhanced by the antiepileptic drug lamotrigine. Epilepsia 43:685–690
Acknowledgments
The support from Karolinska Institutets Fonder, GlaxoSmithKline (Research Grant in Epilepsy) and Pfizer (Research Grant in Neuroscience) is gratefully acknowledged. The authors wish to thank Orion Pharma, Espoo, Finland (valproate) and UCB Pharma, Braine-L’Alleude, Belgium (levetiracetam) for their kind gift of drugs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Englund, M., Hyllienmark, L. & Brismar, T. Effect of Valproate, Lamotrigine and Levetiracetam on Excitability and Firing Properties of CA1 Neurons in Rat Brain Slices. Cell Mol Neurobiol 31, 645–652 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-011-9660-y