Abstract
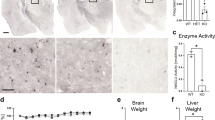
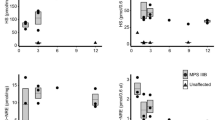
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I is a lysosomal storage disease with alterations in several organs. Little is known about the pathways that lead to the pathology. Evidences point oxidative stress on lysosomal storage diseases and mucopolysaccharidosis type I. The aim of the present study was to evaluate oxidative biomarkers on mucopolysaccharidosis type I mice model. We evaluated antioxidant enzymatic activity, protein damage and lipid peroxidation in the forebrain, cerebellum, heart, lung, diaphragm, liver, kidney and spleen. Superoxide dismutase activity was increased on cerebellum, lung, diaphragm, liver and kidney of mucopolysaccharidosis type I mice. Catalase activity was increased on cerebellum, spleen and lung. There was no alteration on glutathione peroxidase activity on any of the analyzed organs. Mucopolysaccharidosis type I mice showed increased carbonyl groups on cerebellum, heart and spleen. There was a decrease of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances on the cerebellum of mucopolysaccharidosis type I mice. The results indicate a oxidative imbalance in this model. As lysosomes are very susceptible to oxidative damage, leading inclusive to cellular death, and lysosomal storage diseases present several alterations on this organelles, this finding can help to elucidate the cellular damage pathways on mucopolysaccharidosis type I.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- DNPH:
-
Dinitrophenylhydrazine
- GAG:
-
Glycosaminoglycans
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- IDUA:
-
α-L-iduronidase
- LSD:
-
Lysosomal storage diseases
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MPS:
-
Mucopolysaccharidosis
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate diaphorase
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- TBARS:
-
Thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances
- TCA:
-
Trichloroacetic acid
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05016-3
Bannister JV, Calabrese L (1987) Assays for SOD. Methods Biochem Anal 32:279–312. doi:10.1002/9780470110539.ch5
Bascuñan-Castillo EC, Erickson RP, Howison CM, Hunter RJ, Heidenreich RH, Hicks C, Trouard TP, Gillies RJ (2004) Tamoxifen and vitamin E treatments delay symptoms in the mouse model of Niemann-Pick C. J Appl Genet 45:461–467
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86135-I
Evans P, Halliwell B (1999) Free radicals and hearing: cause, consequence, and criteria. Ann NY Acad Sci 884:19–40. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08633.x
Flohé L, Günzler WA (1984) Assays of glutathione peroxidase. Methods Enzymol 105:114–121. doi:10.1016/S0076-6879(84)05015-1
Futerman AH, van Meer G (2004) The cell biology of lysosomal storage disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:554–565. doi:10.1038/nrm1423
German DC, Liang CL, Song T, Yazdani U, Xie C, Dietschy JM (2002) Neurodegeneration in the Niemann-Pick C mouse: glial involvement. Neuroscience 109:437–450. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00517-6
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Hess B, Saftig P, Hartmann D, Coenen R, Lüllmann-Rauch R, Goebel HH, Evers M, von Figura K, D’Hooge R, Nagels G, De Deyn P, Peters C, Gieselmann V (1996) Phenotype of arylsulfatase A-deficient mice: relationship to human metachromatic leukodystrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:14821–14826. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.25.14821
Jeyakumar M, Thomas R, Elliot-Smith E, Smith DA, van der Spoel AC, d’Azzo A, Perry VH, Butters TD, Dwek RA, Platt FM (2003) Central nervous system inflammation is a hallmark of pathogenesis in mouse models of GM1 and GM2 gangliosidosis. Brain 126:974–987. doi:10.1093/brain/awg089
Jeyakumar M, Smith DA, Williams IM, Borja MC, Neville DC, Butters TD, Dwek RA, Platt FM (2004) NSAIDs increase survival in the Sandhoff disease mouse: synergy with N-butyldeoxynojirimycin. Ann Neurol 56:642–649. doi:10.1002/ana.20242
Klegeris A, McGeer PL (1994) Rat brain microglia and peritoneal macrophages show similar responses to respiratory burst stimulants. J Neuroimmunol 53:83–90. doi:10.1016/0165-5728(94)90067-1
Levine RL, Garland D, Oliver CN, Amici A, Climent I, Lenz AG, Ahn BW, Shaltiel S, Stadtman ER (1990) Determination of carbonyl content in oxidatively modified proteins. Methods Enzymol 186:464–478. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(90)86141-H
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Neufeld EF, Muenzer J (1995) The mucopolysaccharidoses. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited diseases. McGraw-Hill, New York
Ohmi K, Greenberg DS, Rajavel KS, Ryazantsev S, Li HH, Neufeld EF (2003) Activated microglia in cortex of mouse models of mucopolysaccharidoses I and IIIB. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:1902–1907. doi:10.1073/pnas.252784899
Pereira VG, Martins AM, Micheletti C, D’Almeida V (2008) Mutational and oxidative stress analysis in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis type I undergoing enzyme replacement therapy. Clin Chim Acta 387:75–79. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2007.09.008
Reolon GK, Braga LM, Camassola M, Luft T, Henriques JA, Nardi NB, Roesler R (2006) Long-term memory for aversive training is impaired in Idua(-/-) mice, a genetic model of mucopolysaccharidosis type I. Brain Res 1076:225–230. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.01.008
Russell C, Hendson G, Jevon G, Matlock T, Yu J, Aklujkar M, Ng KY, Clarke LA (1998) Murine MPS I: insights into the pathogenesis of Hurler syndrome. Clin Genet 53:349–361
Terman A, Kurz T, Gustafsson B, Brunk UT (2006) Lysosomal labilization. IUBMB Life 58:531–539. doi:10.1080/15216540600904885
Villani GR, Gargiulo N, Faraonio R, Castaldo S, Gonzalez Y, Reyero E, Di Natale P (2007) Cytokines, neurotrophins, and oxidative stress in brain disease from mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB. J Neurosci Res 85:612–622. doi:10.1002/jnr.21134
Wu YP, Matsuda J, Kubota A, Suzuki K, Suzuki K (2000) Infiltration of hematogenous lineage cells into the demyelinating central nervous system of twitcher mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:628–639
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Millennium Institute of Gene Therapy (CNPq-MCT grant 420036/2005-9), and grants and fellowships from FAPERGS-RS and CAPES. The authors thank Dr. Elizabeth F. Neufeld for her generous gift of Idua +/− mice.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reolon, G.K., Reinke, A., de Oliveira, M.R. et al. Alterations in Oxidative Markers in the Cerebellum and Peripheral Organs in MPS I Mice. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29, 443–448 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9335-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-008-9335-5