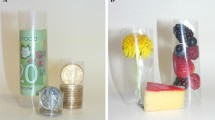Abstract
Bionanocomposite films were fabricated by reinforcing regenerated cellulose (RC) with 3-aminopropyl-functionalized silica nanoparticles (nano-SiO2). The composite films were prepared by dissolving cotton linter RC in a 7% NaOH/12% urea solution followed by the addition of nano-SiO2 and 5% H2SO4 solution. The effects of nano-SiO2 concentration (1–5 wt% with respect to RC) on the morphology, water vapor permeability (WVP), thermal properties, and mechanical properties of the RC/nano-SiO2 composite films were evaluated. Morphological studies indicated uniform dispersions of the low-concentration nano-SiO2 particles in the RC matrix. The tensile strength and modulus were increased by 26% and 15%, respectively, in the presence of 2 wt% of nano-SiO2 relative to the values of neat RC film. The WVP of the RC/nano-SiO2 composite films decreased by 22% after reinforcement with 2 wt% nano-SiO2. The results revealed that there is a potential interaction between RC and nano-SiO2, resulting in improved thermal and mechanical properties of the RC/nano-SiO2 composite films compared to those of neat RC film.
Graphical abstract
Bionanocomposite films were fabricated by reinforcing regenerated cellulose (RC) with 3-amino propyl functionalized silica nanoparticles (nano-SiO2). The effects of nano-SiO2 (1–5 wt% with respect to RC) on the morphology, water vapor permeability (WVP), and thermal and mechanical properties of the RC/nano-SiO2 composite films were evaluated. This study highlights the potential of organically modified nano-SiO2 to enhance the properties of RC owing to the ability of nano-SiO2 to interact with the RC matrix at very low concentrations (2 wt%).








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashok B, Reddy KO, Madhukar K, Cai J, Zhang L, Rajulu AV (2015) Properties of cellulose/Thespesia lampas short fibers bio-composite films. Carbohydr Polym 127:110–115
Bikiaris DN, Vassiliou A, Pavlidou E, Karayannidis GP (2005) Compatibilisation effect of PP-g-MA copolymer on iPP/SiO2 nanocomposites prepared by melt mixing. Eur Polym J 41:1965–1978
Boissiere C, Kummel M, Persin M, Larbot A, Prouzet E (2001) Spherical MSU-mesoporous silica particles tuned for HPLC. Adv Funct Mater 11:129–135
Cai J, Zhang L, Chang C, Cheng G, Chen X, Chu B (2007a) Hydrogen-bond-induced inclusion complex in aqueous cellulose/LiOH/urea solution at low temperature. ChemPhysChem 8:1572–1579
Cai J, Zhang L, Zhou J, Qi H, Chen H, Kondo T, Chen X, Chu B (2007b) Multifilament fibers based on dissolution of cellulose in NaOH/urea aqueous solution: structure and properties. Adv Mater 19:821–825
Cerruti P, Ambrogi V, Postiglione A, Rychly J, Matisová-Rychla L, Carfagna C (2008) Morphological and thermal properties of cellulose–montmorillonite nanocomposites. Biomacromolecules 9:3004–3013
Dai TY, Wang HJ, Cao Y (2015) Preparation, characterization and application of polyaniline/epoxide polysiloxane composite films. Chin J Polym Sci 33:732–742
Delhom CD, White-Ghoorahoo LA, Pang SS (2010) Development and characterization of cellulose/clay nanocomposites. Compos B Eng 41:475–481
Farahani MF, Bedane AH, Pan Y, Xiao H, Eic M, Chibante F (2015) Cellulose/nanoclay composite films with high water vapor resistance and mechanical strength. Cellulose 22:3941–3953
Gennadios A, Weller CL, Goodings CH (1994) Measurement errors in water vapor permeability of high permeable hydrophilic edible films. J Food Eng 21:395–409
Grun M, Lauer I, Unger KK (1997) The synthesis of micrometer- and submicrometer-size spheres of ordered mesoporous oxide MCM-41. Adv Mater 9:254–257
Han D, Yan L, Chen W, Li W, Bangal PR (2011) Cellulose/graphite oxide composite films with improved mechanical properties over a wide range of temperature. Carbohydr Polym 83:966–972
Jayaramudu J, Reddy GSM, Varaprasad K, Sadiku ER, Ray SS, Rajulu AV (2013) Preparation and properties of biodegradable films from Sterculia urens short fiber/cellulose green composites. Carbohydr Polym 93:622–627
Khalil HPS, Abdul AH, Bhat AF, Ireana Y (2012) Green composites from sustainable cellulose nanofibrils: a review. Carbohydr Polym 87:963–979
Kim DH, Park SY, Kim J, Park M (2010) Preparation and properties of the single-walled carbon nanotube/cellulose nanocomposites using N-methylmorpholine-N-oxide monohydrate. J Appl Polym Sci 117:3588–3594
Klemm D, Heublein B, Fink HP, Bohn A (2005) Cellulose: fascinating biopolymer and sustainable raw material. Angew Chem Int Ed 44:3358–3393
Lagaron JM, Catalá R, Gavara R (2004) Structural characteristics defining high barrier polymeric materials. Mater Sci Technol 20:1–7
Lai SM, Hsieh YT (2016) Preparation and properties of polylactic acid (PLA)/silica nanocomposites. J Macromol Sci Part B 55:211–228
Li J, Wei X, Wang Q, Chen J, Chang G, Kong L, Su J, Liu Y (2012) Homogeneous isolation of nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse by high pressure homogenization. Carbohydr Polym 90:1609–1613
Mahmoudian S, Wahit MU, Ismail AF, Yussuf AA (2012) Preparation of regenerated cellulose/montmorillonite nanocomposite films via ionic liquids. Carbohydr Polym 88:1251–1257
Mohammad S, Mat UW, Shaya M, Nurbaiti AH (2013) Regenerated cellulose/halloysite nanotube nanocomposite films prepared with an ionic liquid. Mater Chem Phys 141:936–943
Mohammad S, Mat UW, Abdirahman AY, Al-Saleh MA, Wong TW (2014) Characterization of bio regenerated cellulose/sepiolite nanocomposite films prepared via ionic liquid. Polym Test 33:121–130
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsenf J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994
Nadhan AV, Rajulu AV, Li R, Cai J, Zhang L (2012) Properties of waste silk short fiber/cellulose green composite films. J Compos Mater 46:123–127
Pasternack RM, Sandrine RA, Yves JC (2008) Attachment of 3-(aminopropyl) triethoxysilane on silicon oxide surfaces: dependence on solution temperature. Langmuir 24:12963–12971
Qi H, Chang C, Zhang L (2009) Properties and applications of biodegradable transparent and photoluminescent cellulose films prepared via a green process. Green Chem 11:177–184
Qi H, Liu J, Gao S, Mader E (2013) Multifunctional films composed of carbon nanotubes and cellulose regenerated from alkaline–urea solution. J Mater Chem A 1:2161
Rahatekar SS, Rasheed A, Jain R, Zammarano M, Koziol KK, Windle AH, Gilman JW, Kumar S (2009) Solution spinning of cellulose carbon nanotube composites using room temperature ionic liquids. Polymer 50:4577–4583
Ray S, Bousmina M (2005) Biodegradable polymers and their layered silicate nanocomposites: in greening the 21st century materials world. Prog Mater Sci 50:962–1079
Reddy JP, Rhim JW (2014) Characterization of bionanocomposite films prepared with agar and paper-mulberry pulp nanocellulose. Carbohydr Polym 110:480–488
Rhim JW (2011) Effect of clay contents on mechanical and water vapor barrier properties of agar-based nanocomposite films. Carbohydr Polym 86:691–699
Rhim JW, Wang LF (2013) Mechanical and water barrier properties of agar/-carrageenan/konjac glucomannan ternary blend biohydrogel films. Carbohydr Polym 96:71–81
Saravanan S, Akshay Gowda KM, Ramamurthy PC, Giridhar M (2016) Influence of mesoporous silica and butyral content on the mechanical, water absorption, and permeability properties of in situ synthesized silica/PVB nanocomposite films. Polym Plast Technol Eng 55:1220–1230
Soheilmoghaddam M, Wahit MU, Whye WT, Akos NI, Pour RH, Yussuf AA (2014) Bionanocomposites of regenerated cellulose/zeolite prepared using environmentally benign ionic liquid solvent. Carbohydr Polym 106:326–334
Song H, Zheng L (2013) Nanocomposite films based on cellulose reinforced with nano-SiO2: microstructure, hydrophilicity, thermal stability, and mechanical properties. Cellulose 20:1737–1746
Tang XZ, Kumar P, Alavi S, Sandeep KP (2012) Recent advances in biopolymers and biopolymer-based nanocomposites for food packaging materials. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 52:426–442
Thomas JM, Johnson BFG, Raja R, Sankar G, Midgley PA (2003) High-performance nanocatalysts for single-step hydrogenations. Acc Chem Res 36:20–30
Tsioptsias C, Panayiotou C (2008) Preparation of cellulose–nanohydroxyapatite composite scaffolds from ionic liquid solutions. Carbohydr Polym 74:99–105
Vladimirov V, Betchev C, Vassiliou A, Papageorgiou G, Bikiaris D (2006) Dynamic mechanical and morphological studies of isotactic polypropylene/fumed silica nanocomposites with enhanced gas barrier properties. Compos Sci Technol 66:2935–2944
Yan S, Yin J, Yang Y, Dai Z, Ma J, Chen J (2007) Surface-grafted silica linked with l-lactic acid oligomer: a novel nanofiller to improve the performance of biodegradable poly(l-lactide). Polymer 48:1688–1694
Yang Q, Qi H, Lue A, Hu K, Cheng G, Zhang L (2011) Role of sodium zincate on cellulose dissolution in NaOH/urea aqueous solution at low temperature. Carbohydr Polym 83:1185–1191
Zha J, Lu X, Xin Z (2015) A rational design of double layer mesoporous polysiloxane coatings for broadband antireflection. J Sol Gel Sci Technol 74:677–684
Zhang H, Guo L, Shao H, Hu X (2006) Nano-carbon black filled lyocell fiber as a precursor for carbon fiber. J Appl Polym Sci 99:65–74
Zhang H, Wang ZG, Zhang ZN, Wu J, Zhang J, He JS (2007) Regenerated-cellulose/multiwalled-carbon-nanotube composite fibers with enhanced mechanical properties prepared with the ionic liquid 1-allyl-3-methylimidazolium chloride. Adv Mater 19:698–704
Zhu A, Diao H, Rong Q, Cai A (2010) Preparation and properties of polylactide–silica nanocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 116:2866–2873
Zou H, Wu S, Shen J (2008) Polymer/silica nanocomposites: preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Chem Rev 108:3893–3957
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by both the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIP) [No. 2017R1A2B4011234].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, J.P., Varada Rajulu, A., Rhim, JW. et al. Mechanical, thermal, and water vapor barrier properties of regenerated cellulose/nano-SiO2 composite films. Cellulose 25, 7153–7165 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2059-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-018-2059-x