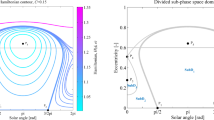
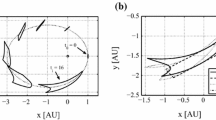
Abstract
This paper introduces and combines for the first time two techniques to allow long-term density propagation in astrodynamics. First, we introduce an efficient method for the propagation of phase space densities based on differential algebra (DA) techniques. Second, this DA density propagator is used in combination with a DA implementation of the averaged orbital dynamics through semi-analytical methods. This approach combines the power of orbit averaging with the efficiency of DA techniques. While the DA-based method for the propagation of densities introduced in this paper is independent of the dynamical system under consideration, the particular combination of DA techniques with averaged equations of motion yields a fast and accurate technique to propagate large clouds of initial conditions and their associated probability density functions very efficiently for long time. This enables the study of the long-term behavior of particles subjected to the given dynamics. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach, the evolution of a cloud of high area-to-mass objects in Medium Earth Orbit is reproduced considering the effects of solar radiation pressure, the Earth’s oblateness and luni-solar perturbations. The method can propagate 10,000 random fragments and their density for 1 year within a few seconds on a common desktop PC.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armellin, R., Di Lizia, P., Bernelli-Zazzera, F., Berz, M.: Asteroid close encounter characterization using differential algebra: the case of aphophis. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 107(4), 451–470 (2010)
Battin, R.: An Introduction to the Mathematics and Methods of Astrodynamics. AIAA Education Series, Reston (1999)
Berz, M.: The method of power series tracking for the mathematical description of beam dynamics. Nucl. Instrum. Methods A 258(3), 431–436 (1987)
Berz, M.: Modern Map Methods in Particle Beam Physics. Academic Press, Cambridge (1999)
Berz, M., Makino, K.: COSY INFINITY version 9 reference manual. Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI 48824. MSU Report MSUHEP060803 (2006)
Broucke, R.A.: Long-term third-body effects via double averaging. J. Guid. Control Dyn. (2003). doi:10.2514/2.5041
Colombo, C.: Long-term evolution of highly-elliptical orbits: luni-solar perturbation effects for stability and re-entry. In: AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Williamsburg, Virginia, AAS-15-395 (2015)
Colombo, C., McInnes, C.R.: Evolution of swarms of smart dust spacecraft. In: New Trends in Astrodynamics and Applications VI, New York (2011)
Colombo, C., Lücking, C., McInnes, C.: Orbital dynamics of high area-to-mass ratio spacecraft with \({J}_2\) and solar radiation pressure for novel earth observation and communication services. Acta Astronaut. 81(1), 137–150 (2012). doi:10.1016/j.actaastro.2012.07.009
Deprit, A.: Canonical transformations depending on a small parameter. Celest. Mech. 1(1), 12–30 (1969). doi:10.1007/BF01230629
Gor’kavyi, N.: A new approach to dynamical evolution of interplanetary dust. Astrophys. J. 474(1), 496–502 (1997). doi:10.1086/303440
Krivov, A.V., Sokolov, L.L., Dikarev, V.V.: Dynamics of Mars-orbiting dust: Effects of light pressure and planetary oblateness. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 63(3), 313–339 (1995). doi:10.1007/bf00692293
Letizia, F., Colombo, C., Lewis, H.G.: Multidimensional extension of the continuity equation method for debris clouds evolution. Adv. Space Res. 57(8), 1624–1640 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.asr.2015.11.035
McInnes, C.R.: An analytical model for the catastrophic production of orbital debris. ESA J. 17(4), 293–305 (1993)
Metris, G., Exertier, P.: Semi-analytical theory of the mean orbital motion. Astron. Astrophys. 294, 278–286 (1994)
Nazarenko, A.I.: Collision of spacecraft with debris particles assessment. In: Proceedings of the 17th ISSFD Symposium. Moscow (2003)
Postnikov, M.M.: Geometry VI: Riemannian Geometry, Encyclopaedia of Mathematical Sciences, vol. 91. Springer, New York (2001)
Rossi, A., Anselmo, L., Cordelli, A., Farinella, P., Pardini, C.: Modelling the evolution of the space debris population. Planet. Space Sci. 46(11–12), 1583–1596 (1998). doi:10.1016/S0032-0633(98)00070-1
Soong, T.: Fundamentals of Probability and Statistics for Engineers. Wiley, Hoboken (2004)
Valli, M., Armellin, R., Di Lizia, P., Lavagna, M.R.: Nonlinear mapping of uncertainties in celestial mechanics. J. Guid. Control Dyn. 36(1), 48–63 (2013). doi:10.2514/1.58068
Wittig, A., Armellin, R., Colombo, C., Di Lizia, P.: Long-term orbital propagation through differential algebra transfer maps and averaging semi-analytical approaches. In: AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, Santa Fe, NM, AAS 14-224 (2014)
Wittig, A., Di Lizia, P., Armellin, R., Makino, K., Bernelli Zazzera, F., Berz, M.: Propagation of large uncertainty sets in orbital dynamics by automatic domain splitting. Celest. Mech. Dyn. Astron. 122(3), 239–261 (2015). doi:10.1007/s10569-015-9618-3
Acknowledgements
A. Wittig gratefully acknowledges the support received from the Marie Curie network PITN-GA 2011-289240 (AstroNet-II); he performed part of this work at the Department of Aerospace Science and Technology, Politecnico di Milano, Italy. C. Colombo acknowledges the support received by the Marie Curie Intra European Fellowship (SpaceDebECM—Space Debris Evolution, Collision risk, and Mitigation—IEF-2011-302270) within the 7th EU Framework Programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wittig, A., Colombo, C. & Armellin, R. Long-term density evolution through semi-analytical and differential algebra techniques. Celest Mech Dyn Astr 128, 435–452 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-017-9756-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10569-017-9756-x