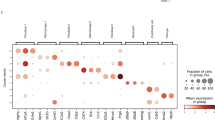
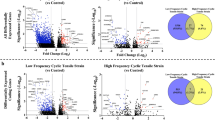
Abstract
Chondrocytes are the major functional elements of articular cartilage. Force has been demonstrated to influence the structure and function of articular cartilage and chondrocytes. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate chondrocytes under different force conditions to gain deep insight into chondrocyte function. Six cartilage tissues from the distal tibia (referred to as the AT group) and five cartilage tissues from the trochlear surface of the talus (referred to as the ATa group) were obtained from 6 donors who had experienced fatal accidents. Single-cell RNA sequencing was used on these samples. A total of 149,816 cells were analyzed. Nine chondrocyte subsets were ultimately identified. Pseudotime analyses, enrichment analyses, cell–cell interaction studies, and single-cell regulatory network inference and clustering were performed for each cell type, and the differences between the AT and ATa groups were analyzed. Immunohistochemical staining was used to verify the existence of each chondrocyte subset and its distribution. The results suggested that reactive oxygen species related processes were active in the force-applied region, while tissue repair processes were common in the force-bearing region. Although the number of prehypertrophic chondrocytes was small, these chondrocytes seemed to play an important role in the ankle.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Raw data for this article will be accessed on online database upon publication.
References
Baker J, Falconer AMD, Wilkinson DJ. Protein kinase D3 modulates MMP1 and MMP13 expression in human chondrocytes. PLoS One. 2018;13(4):e0195864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195864.
Bernardo BC, Belluoccio D, Rowley L, Little CB, Hansen U, Bateman JF. Cartilage intermediate layer protein 2 (CILP-2) is expressed in articular and meniscal cartilage and down-regulated in experimental osteoarthritis. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(43):37758–67. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.248039.
Bhosale AM, Richardson JB. Articular cartilage: Structure, injuries and review of management. Br Med Bull. 2008;87:77–95. https://doi.org/10.1093/bmb/ldn025.
Carballo CB, Nakagawa Y, Sekiya I, Rodeo SA. Basic science of articular cartilage. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36(3):413–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csm.2017.02.001.
Ge Z, Li C, Heng BC, Cao G, Yang Z. Functional biomaterials for cartilage regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(9):2526–36. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.34147.
Goldring SR, Goldring MB. Changes in the osteochondral unit during osteoarthritis: Structure, function and cartilage-bone crosstalk. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016;12(11):632–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2016.148.
Gozar H, Chira A, Nagy R, Derzsi Z. Medical use of finite element modeling of the ankle and foot. J Interdiscip Med. 2018;3(1):34–8.
Huang C, Hales BF. Effects of exposure to a DNA damaging agent on the hypoxia inducible factors in organogenesis stage mouse limbs. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e51937. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0051937.
Jeon OH, Kim C, Laberge RM, Demaria M. Local clearance of senescent cells attenuates the development of post-traumatic osteoarthritis and creates a pro-regenerative environment. Nat Med. 2017;23(6):775–81. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4324.
Ji Q, Zheng Y, Zhang G, Hu Y, Fan X, Hou Y, et al. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis reveals the progression of human osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(1):100–10. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212863.
Kaczmarek M, Cachau RE, Topol IA, Kasprzak KS, Ghio A, Salnikow K. Metal ions-stimulated iron oxidation in hydroxylases facilitates stabilization of HIF-1 alpha protein. Toxicol Sci. 2009;107(2):394–403. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn251.
Kleipool RP, Blankevoort L. The relation between geometry and function of the ankle joint complex: A biomechanical review. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18(5):618–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-010-1088-2.
Morales-Orcajo E, Souza T. R., Bayod, J., & Barbosa de Las Casas, E. Non-linear finite element model to assess the effect of tendon forces on the foot-ankle complex. Med Eng Phys. 2017;49:71–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2017.07.010.
Prein C, Warmbold N, Farkas Z, Schieker M, Aszodi A, Clausen-Schaumann H. Structural and mechanical properties of the proliferative zone of the developing murine growth plate cartilage assessed by atomic force microscopy. Matrix Biol. 2016;50:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2015.10.001.
Quenneville CE, Dunning CE. Development of a finite element model of the tibia for short-duration high-force axial impact loading. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2011;14(2):205–12. https://doi.org/10.1080/10255842.2010.548324.
Radin EL, Paul IL. Response of joints to impact loading. I. In vitro wear. Arthritis Rheum. 1971;14(3):356–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780140306.
Saito T, Fukai A, Mabuchi A, Ikeda T, Yano F, Ohba S, et al. Transcriptional regulation of endochondral ossification by HIF-2alpha during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis development. Nat Med. 2010;16(6):678–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2146.
Smolen C, Quenneville CE. A finite element model of the foot/ankle to evaluate injury risk in various postures. Ann Biomed Eng. 2017;45(8):1993–2008. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-017-1844-2.
St-Jacques B, Hammerschmidt M, McMahon AP. Indian hedgehog signaling regulates proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes and is essential for bone formation. Genes Dev. 1999;13(16):2072–86. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.13.16.2072.
Sun, H., Wen, X., Li, H., Wu, P., Gu, M., Zhao, X., . . . Zhang, Z. Single-cell RNA-seq analysis identifies meniscus progenitors and reveals the progression of meniscus degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79(3), 408-417. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215926
van der Sluijs JA, Geesink RG, van der Linden AJ, Bulstra SK, Kuyer R, Drukker J. The reliability of the Mankin score for osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 1992;10(1):58–61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.1100100107.
Wang T, Wang J, Sun Z, Zhang L, Yu C, Zhao H, et al. Single-cell RNA sequence presents atlas analysis for chondrocytes in the talus and reveals the potential mechanism in coping with mechanical stress. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1047119. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2022.1047119.
Wong DW, Niu W, Wang Y, Zhang M. Finite element analysis of foot and ankle impact injury: Risk evaluation of calcaneus and talus fracture. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0154435. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0154435.
Wong M, Carter DR. Articular cartilage functional histomorphology and mechanobiology: A research perspective. Bone. 2003;33(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/s8756-3282(03)00083-8.
Wright RW. Osteoarthritis classification scales: Interobserver reliability and arthroscopic correlation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(14):1145–51. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.m.00929.
Yao Y, Xiao Z, Wong S, Hsu YC, Cheng T, Chang CC, et al. The effects of oxidative stress on the compressive damage thresholds of C2C12 mouse myoblasts: Implications for deep tissue injury. Ann Biomed Eng. 2015;43(2):287–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-014-1239-6.
Zhu J, Zhu Y, Xiao W, Hu Y, Li Y. Instability and excessive mechanical loading mediate subchondral bone changes to induce osteoarthritis. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(6):350. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2020.02.103.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge all donors and authors contributed to this work
Funding
This work was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (31872310), which supported the scRNA process and IHC methods.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Junjie Wang: analysis and interpretation of the data, drafting of the article, and critical revision of the article for important intellectual content. Zewen Sun: conception and design and critical revision of the article for important intellectual content. Chenghao Yu: provision of study materials or patients, administrative, technical, or logistic support. Haibo Zhao: administrative, technical, or logistic support. Mingyue Yan: administrative, technical, or logistic support. Shenjie Sun: provision of study materials or patients. Xu Han: provision of study materials or patients. Tingting Jiang: administrative, technical, or logistic support, collection and assembly of data. Tianrui Wang: conception and design, final approval of the article, provision of study materials or patients, administrative, technical, or logistic support. Tengbo Yu: conception and design, final approval of the article, provision of study materials or patients, obtaining of funding, administrative, technical, or logistic support. Yingze Zhang: conception and design, final approval of the article, provision of study materials or patients, obtaining of funding, administrative, technical, or logistic support.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the institutional ethics review board of the Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, and the family members of all donors signed written informed consent documents.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information

Fig S1
Interaction possibility of each determined pathway among different cell types. The size of the circle represents the p value, while the color of the circle represents the interaction possibility. (PNG 1963 kb)
Fig S2
Specific TFs identified by SCENIC a to f From left to right, AUC histogram, scatter plot, ridge plots and violin plots, and parts of the motifs for the specific TFs in each cell type. a for FCs; b for HomCs; c to e for preHTCs, and f for SpCs) (PDF 4539 kb)

Fig S3
Heatmap of the differential expression levels for all scored TFs (PNG 481 kb)

Fig S4
PPI network for DEGs between the AT and ATa groups (Fig S4 for the AT group, Fig S5 for the ATa group). Hub genes are marked with red rectangles (PNG 2276 kb)

Fig S5
(PNG 1791 kb)
Table S1
Detailed DEGs of each cell type (XLSX 371 kb)
Table S2
Detailed results for GO enrichment analysis of each cell type (XLSX 147 kb)
Table S3
Detailed results for KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of each cell type (XLSX 68 kb)
Table S4
Gene targets for specific TFs of HomCs, FCs, RegCs and SpCs (XLSX 32 kb)
Table S5
DEGs between the AT and ATa groups, Genes with |log2FC| values greater than 0 were DEGs for the AT group, and genes with |log2FC| values less than 0 were DEGs for the ATa group (XLSX 226 kb)
Table S6
GO enrichment analysis for DEGs for which the |log2FC| was greater than 0.5 in each group (XLSX 31 kb)
Tables S7 and S8
GO enrichment analysis for DEGs with |log2FC| values greater than 0.25 in each cell type in the AT and ATa groups, respectively (XLSX 128 kb)
Table S8
(XLSX 106 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Sun, Z., Yu, C. et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals differences between force application and bearing in ankle cartilage. Cell Biol Toxicol 39, 3235–3253 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-023-09829-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-023-09829-2