Abstract
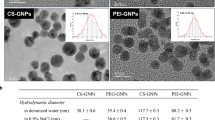
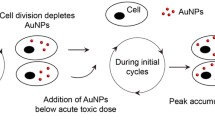
Surface-modified gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) are nanomaterials that hold promise in drug delivery applications. In this study, the cytotoxicity, uptake, intracellular localization, and the exocytosis of citrate-stabilized (Cit-AuNP) and polyethylene glycol (PEG)-modified gold nanoparticles with the carboxyl (COOH) terminal functional group were assessed in human embryonic kidney (HEK 293) and the human caucasian hepatocytes carcinoma (Hep G2) cell systems, representing two major accumulation sites for AuNPs. The zeta (ζ)-potential measurements confirmed the negative surface charge of the AuNPs in water and in cell growth medium. The transmission electron microscopy confirmed the size and morphology of the AuNPs. Both types of AuNPs were shown to induce cytotoxic effects in cells. The Hep G2 cells were more sensitive cell type, with the COOH-PEG-AuNPs inducing the highest toxicity at higher concentrations. Dark field microscopy and TEM images revealed that the AuNPs were internalized in cells, mostly as agglomerates. TEM micrographs further revealed that the AuNPs were confined as agglomerates inside vesicle-like compartments, likely to be endosomal and lysosomal structures as well as in the cytosol, mostly as individual particles. The AuNPs were shown to remain in cellular compartments for up to 3 weeks, but thereafter, clearance of the gold nanoparticles from the cells by exocytosis was evident. The results presented in this study may therefore give an indication on the fate of AuNPs on long-term exposure to cells and may also assist in safety evaluation of AuNPs.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albanese A, Chan WCW. Effects of gold nanoparticle aggregation on cell uptake and toxicity. ACS Nano. 2011;5(7):5478–89.
Aslan K, Luhrs CC, Perez-Luna VH. Controlled and reversible aggregation of biotinlyted gold nanoparticles with Streptavidin. J Phys Chem B. 2004;108:1561–15639.
Atienza JM, Yu N, Kirstein SL, Xi B, Wang X, Xu X, et al. Dynamic and label-free cell-based assays using the real-time cell electronic sensing system. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2006;4:597–607.
Baptista P, Pereira E, Eaton P, Doria G, Miranda A, Gomes I, et al. Gold nanoparticles for the development of clinical diagnostics methods. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2008;391:943–50.
Basiruddin SK, Saha A, Pradhan N. Functionalized gold nanorod solution via reverse micelle based polyacrylate coating. Langmuir. 2010;26:7475–81.
Brandenberger C, Clift MJD, Vanhecke D, Muhfeld C, Stone V, Rothen-Rutishauser B. Intracellular imaging of nanoparticles: is it an elemental mistake to believe what you see? Part Fibre Toxicol. 2010;7(15):1–6.
Brown SD, Native P, Smith J, Stirling D, Edward PR, Venugopal B. Gold nanoparticles for the improved anticancer drug delivery of the active component of oxaliplatin. J Am Chem Soc. 2010;132:4679–89.
Chen PC, Mwakwari SC, Oyelere AK. Gold nanoparticles: from medicine to nanosensing. Nanotechnol Sci Appl. 2008;1:45–66. 2008.
Chithrani BD, Steward A, Allen C, Jaffary DA. Intracellular uptake, transport, and processing of nanostructures in cancer cells. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Medi. 2009;5:8–127. 2009.
Chu Z, Zhang S, Zhang B, Zhang C, Fang CY, Li Q. Unambiguous observation of shape effects on cellular fate of nanoparticles. Sci Rep. 2014;4(4495):1–9.
Connor EE, Mwamuka J, Gole A, Murphy CJ, Wyatt MD. Gold nanoparticles are taken up by human cells but do not cause acute cytotoxicity. Small. 2005;1:325–7.
Donaldson K, Stone V. Current hypothesis on the mechanisms of toxicity of ultrafine particles. Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2003;39(3):405–10.
Fraga S, Faria H, Soares ME, Carmo H. Influence of the surface coating on the cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and uptake of gold nanoparticles in human HepG2 cells. J Appl Toxicol. 2013. doi:10.1002/jat.2865.
Freese C, Uboldi C, Gibson MI, Unger RE, Weksler BB, Romero IA, et al. Uptake and cytotoxicity of citrate-coated gold nanospheres: comparative studies on human endothelial and epithelial cells. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2012;9(3):6–11.
Goodman CM, McCusker CD, Yilmaz T, Rotello VM. Toxicity of gold nanoparticles functionalized with cationic and anionic side chains. Bioconjug Chem. 2004;15:897–900.
Graf C, Gao Q, Schutz I, Noufele CN, Ruan W, Ruhl E. Surface functionalization of silica nanoparticles supports colloidal stability in physiological media and facilitates internalization in cells. Langmuir. 2012;28:7598–613.
Grubbs RB. Roles of polymer ligands in nanoparticle stabilization. Polym Rev. 2007;47(2):197–215.
Gu YJ, Cheng J, Lin CC, Lam YW, Cheng SH, Wong WT. Nuclear penetration of surface functionalized gold nanoparticles. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2009;237:196–204.
Jain PK, Lee KS, El-Sayed IH, El-Sayed MA. Calculated Absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110:7238–48.
Kettler K, Veltman K, Van De Meent D, Van Wzel A, Hendriks AJ. Cellular uptake of nanoparticles as determined by particle properties, experimental conditions and cell type. Environ Toxicol Chem. 2014;33(3):481–92.
Kim CS, Li X, Jiang Y, Yan B, Tonga GY, Ray M, et al. Cellular imaging of endosome entrapped small gold nanoparticles. MethodsX. 2015;2:306–15.
Lacerda SH, Park JJ, Meuse C, Pristinski D, Becker ML, Douglas JF. Interaction of gold nanoparticles with common human blood proteins. ACS Nano. 2010;4(1):365–79.
Levy R, Shaheen U, Cesbron Y, See V. Gold nanoparticle delivery in mammalian live cells: a critical review. Nano Rev. 2010;1:4889–94.
Li JJ, Zou LI, Hartono D, Ong EN, Bay BH, Yung LL. Gold nanoparticles induce oxidative damage in lung fibroblasts: in vitro. Adv Mater. 2005;20:138–42.
Li X, Liu W, Sun L, Aifantis KE, Yu B, Fan Y, et al. Effects of physicochemical properties of nanomaterials on their toxicity. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2015;103A:2499–507.
Liang M, Lin C, Whittaker MR, Minchin RF, Montero MJ, Toth I. Cellular uptake of densely packed polymer coatings on gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2010;4(1):403–13.
Liu X, Huang N, Li H, Jin Q, Ji J. Surface and size effects on cell interaction of gold nanoparticles with both phagocytic and non-phagocytic cells. Langmuir. 2013;29:9138–48.
Maiorano G, Sabella S, Sorce B, Brunetti V, Malvindi MA, Pompa PP. Effects of cell culture media on the dynamic formation of protein-nanoparticle complexes and influence on the cellular response. ACS Nano. 2010;4(12):7481–91.
Nativo P, Prior IA, Brust M. Uptake and intracellular fate of surface-modified gold nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2008;2(8):1639–44.
Navya PN, Daima HK. Rational engineering of physicochemical properties of nanomaterials for biomedical applications with nanotoxicological perspectives. Nano Convergence. 2016;3(1):1–14.
Ng CT, Perumalsamy R, Watt F and Yuan YL. Localizing cellular uptake of nanomaterials in vitro by transmission electron microscopy. Microscopy: Science, technology and education. Formatted. 2010; 316-320.
Oh N, Park J. Endocytosis and exocytosis of nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2014a;9(Suppl I):51–63.
Oh N, Park J. Surface chemistry of Gold nanoparticles mediates their exocytosis in macrophages. ACS Nano. 2014b;8(6):6232–41.
Oh E, Delehanty JB, Medintz IL. Cellular uptake and fate of PEGylated gold nanoparticles is dependent on both cell-penetrating peptides and particle size. ACS Nano. 2011;5(8):6434–48.
Otsuka H, Nagasaki Y, Kataoka K. PEGylated nanoparticles for biological and pharmaceutical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2003;55:403–19.
Patra CR, Bhattacharya R, Mukhopadhyay D, Mukherjee P. Fabrication of gold nanoparticles for targeted therapy in pancreatic cancer. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62:346–61.
Pissuwan D, Cortie CH, Valenzuela SM, Cortie MB. Functionalized gold nanoparticles for controlling pathogenic bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2010;28(4):207–13.
Pissuwan D, Niidome T, Cortie MB. The forthcoming applications of gold nanoparticles in drug and gene delivery systems. J Control Release. 2011;149:65–71.
Rocha A, Zhou Y, Kundu S, Liang H. In vivo observation of gold nanoparticles in the central nervous system of Blaberus discoidalis. J Nanobiotechnol. 2011;9:5.
Rosi AL, Giljohann DA, Thaxton CS, Lytton-Jean AKR, Han MS, Mirkin CA. Oligonucleatide-modified gold nanoparticle for intracellular gene regulation. Science. 2006;312:1027–30.
Sabuncu AC, Grubbs J, Qian S, Beskok A. Probing nanoparticle interactions in cell culture media. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces. 2012;95:96–102.
Sarah B. Breath test to detect cancer may be possible, say scientists. 2010. http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2010/aug/11/breath-test-detect-cancer-scientists
Shenoy D, Fu W, Li J, Crasto C, Jones G, DiMarzio C, et al. Surface Functionalization of Gold nanoparticles using hetero-bifunctional poly (ethylene glycol) spacer for intracellular tracking and delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2006;1:51–7.
Shukla R, Bansal V, Chaudhary M, Basu A, Bhonde RR, Sastry M. Biocompatibility of gold nanoparticles and their endocytotic fate inside the cellular compartment. Langmur. 2006;21:10644–54.
Skebo JE, Grabinski CM, Hussain SM. Assessment of metal nanoparticle agglomeration, uptake, and interaction using high-illuminating system. Int J Toxicol. 2007;29:135–41.
Tiwari PM, Vig K, Dennis VA, Singh SR. Functionalized gold nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomaterials. 2011;1:31–63.
Turkevich J, Stevenson PC, Hillier J. A study of the nucleation and growth processes in the synthesis of colloidal gold. Discuss Faraday Soc. 1951;11:55–75.
Uboldi C, Bonacchi D, Lorenzi G, Hermanns MI, Pohl C, Baldi G, et al. Gold nanoparticles induce cytotoxicity in the alveolar type-II cell lines A549 and NCIH44I. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2009. doi:10.1186/1743-8977-1186-1118.
Ürcan E, Haertel U, Styllou M, Hickel RB, Harry Scherthan H, Reichl FX. Real-time xCELLigence impedance analysis of the cytotoxicity of dental composite components on human gingival fibroblasts. Dent Mater. 2010;26:51–8.
Vetten MA, Tlotleng N, Rascher DT, Skepu A, Keter FK, Gulumian M. Label free in vitro toxicity and uptake assessment of citrate stabilized gold nanoparticles in three cell lines. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2013;10(50):1–15.
Zhang Z, Jia J, Lai Y, Ma Y, Weng J, Sun L. Conjugating folic acid to gold nanoparticles through glutathione for targeting and detecting cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 2010;18:5528–34.
Zhou H, Li X, Lemoh H, Zhang B, Yan B. Structural confirmation and quantification of individual ligands from the surfaces of multi-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Analyst. 2010;135:1210–3.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the South African Department of Science and Technology (DST) and the National Research Foundation (NRF). The authors wish to thank Prof Jim Phillips from the Pathology Department at the National Institute for Occupational Health (NIOH) for the technical advice in preparing samples for TEM for assistance with acquiring the TEM images. We also thank the Immunology and Microbiology Department of the NIOH for sterility testing of the AuNPs.
Authors’ contributions
AuNPs were synthesized by FKK and AS. Characterization of the AuNPs was done by FKK and NT. xCELLigence, CytoViva, and TEM work was performed by NT. NT, MV, RT, and MG were involved in the inception and planning of the project and in the preparation of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tlotleng, N., Vetten, M.A., Keter, F.K. et al. Cytotoxicity, intracellular localization and exocytosis of citrate capped and PEG functionalized gold nanoparticles in human hepatocyte and kidney cells. Cell Biol Toxicol 32, 305–321 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9336-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-016-9336-y