Abstract
Derivatives of (±)-ethyl mandelate are important intermediates in the synthesis of numerous pharmaceuticals. Therefore, efficient routes for the production of these derivatives are highly desirable. The short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase (SDR) is a biocatalyst that could potentially be applied to the synthesis of (±)-ethyl mandelate; however, this enzyme requires the reduced form of the cofactor nicotine adenine dinucleotide (phosphate) (NAD(P)H), which is expensive. In this study, we developed a co-immobilization strategy to overcome the issue of NADPH demand in the SDR catalytic process. The SDR from Thermus thermophilus HB8 and the NAD(P)-dependent glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from Thermoplasma acidophilum DSM 1728 were co-immobilized on silica gel. The properties and the catalytic abilities of this dual-enzyme system were evaluated. A final yield of 1.17 mM (±)-ethyl mandelate was obtained from the catalytic conversion of ethyl benzoylformate, with a conversion rate of ethyl benzoylformate to (S)-(+)-mandelate of 71.86% and in an enantiomeric excess of > 99% after 1.5 h. This system offers an efficient route for the biosynthesis of (±)-ethyl mandelate.
Graphical Abstract
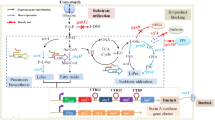
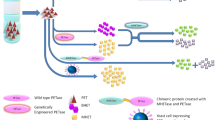
In this study, we developed a co-immobilization strategy to overcome the issue of NADPH demand in the SDR catalytic process. The SDR from Thermus thermophilus HB8 and the NAD(P)-dependent glucose dehydrogenase (GDH) from Thermoplasma acidophilum DSM 1728 were co-immobilized on silica gel. Results showed that, this dual-system offers an efficient route for the biosynthesis of (±)-ethyl mandelate.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kasprzak J, Rauter M, Denter S et al (2016) J Mol Catal B 133:176–186
Poterała M, Dranka M, Borowiecki P (2017) Eur J Org Chem 16:2290–2304
Zhang XH, Liu ZQ, Xue YP et al (2018) Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184: 1024–1035
Martínková L, Křen V (2018) Appl Biochem Biotechnol 102: 3893–3900
Lima RN, Porto AL (2017) Catal Commun 100:157–163
Kallberg Y, Oppermann U, Persson B (2010) FEBS J 277:2375–2386
Persson B, Kallberg Y (2013) Chem Bio Interact 202:111–115
Sonawane PD, Heinig U, Panda S et al (2018) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:5419–5428
Müller M, Roth S, Kilgore M et al (2018) ChemBioChem 19:1849–1852
Riegert AS, Thoden JB, Schoenhofen IC et al (2017) Biochemistry 56:6030–6040
Ferri S, Kojima K, Sode K (2011) J Diabetes Sci Technol 5:1068–1076
Asada Y, Endo S, Inoue Y et al (2009) Chem Biol Interact 178:117–126
Budgen N, Danson MJ (1986) FEBS Lett 196:207–210
Smith L, Budgen N, Bungard S et al (1989) Biochem J 261:973–977
Ohshima T, Ito Y, Sakuraba H al (2003) J Mol Catal B-Enzym 2:281–289
Kanoh K, Uehara S, Iwata H et al (2014) Acta Crystallogr D 70:1271–1280
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (2000) Q Rev Biol 186:182–183
Sachadyn P, Jedrzejczak R, Milewski S et al (2000) Protein Expres Purif 19:343–349
Deng MD, Severson DK, Grund AD et al (2005) Metab Eng 7:201–214
Kruger NJ (1998) Methods Mol Biol 32:9–15
Zhou S, Zhang SC, Lai DY et al (2013) Biotechnol Lett 35:359–365
Pennacchio A, Giordano A, Pucci B et al (2010) Extremophiles 14:193–204
Pennacchio A, Pucci B, Secundo F et al (2008) Appl Environ Microb 74:3949–3958
Acknowledgements
The authors are supported by the National Natural Science Foundation cultivation project of Jining medical university (Grant No. JYP201704), the Supporting Fund for Teachers’ research of Jining Medical University (Grant No. JYFC2018KJ031), the Startup Fund of Jining Medical University (Grant No. 6001/600557001), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21376215). The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from the one mentioned above. We thank Hayden Peacock, PhD, from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Editing China (http://www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Xh., Du, X., Feng, Jr. et al. Co-immobilization of Short-Chain Dehydrogenase/Reductase and Glucose Dehydrogenase for the Efficient Production of (±)-Ethyl Mandelate. Catal Lett 149, 1710–1720 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02727-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10562-019-02727-5