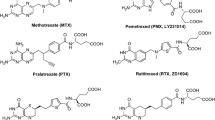
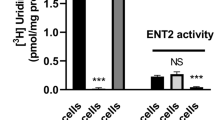
Abstract
Nucleoside analogs are important components of treatment regimens for various malignancies. Nucleoside-specific membrane transporters mediate plasma membrane permeation of physiologic nucleosides and most nucleoside analogs, for which the initial event is cellular conversion of nucleosides to active agents. Understanding of the roles of nucleoside transporters in nucleoside drug toxicity and resistance will provide opportunities for potentiating anticancer efficacy and avoiding resistance. Because transportability is a possible determinant of toxicity and resistance of many nucleoside analogs, nucleoside transporter abundance might be a prognostic marker to assess drug resistance. Elucidation of the structural determinants of nucleoside analogs for interaction with transporter proteins as well as the structural features of transporter proteins required for permeant interaction and translocation will lead to “transportability guidelines” for the rational design and therapeutic application of nucleoside analogs as anticancer drugs. It should eventually be possible to develop clinical assays that predict sensitivity and/or resistance to nucleoside anti-cancer drugs and thus to identify those patient populations that will most likely benefit from optimal nucleoside analog treatments. This review discusses recent results from structure/function studies of human nucleoside transporters, the role of nucleoside transport processes in the cytotoxicity and resistance of several anticancer nucleoside analogs and strategies to improve the nucleoside transporter-related anticancer effects of nucleoside analogs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Belle, H. (1993). Nucleoside transport inhibition: A therapeutic approach to cardioprotection via adenosine? Cardiovascular Research, 27, 68–76.
Baldwin, S. A., Mackey, J. R., Cass, C. E., & Young, J. D. (1999). Nucleoside transporters: Molecular biology and implications for therapeutic development. Molecular Medicine Today, 5, 216–224.
Vickers, M. F., Young, J. D., Baldwin, S. A., & Cass, C. E. (2000). Nucleoside transporter proteins: Emerging target for drug discovery. Emerging Therapeutic Targets, 4, 515–539.
Galmarini, C. M., Mackey, J. R., & Dumontet, C. (2002). Nucleoside analogues and nucleobases in cancer treatment. Lancet Oncology, 3, 415–424.
Kong, W., Engel, K., & Wang, J. (2004). Mammalian nucleoside transporters. Current Drug Metabolism, 5, 63–84.
Clarke, M. L., Mackey, J. R., Baldwin, S. A., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2002). The role of membrane transporters in cellular resistance to anticancer nucleoside drugs. Cancer Treatment and Research, 112, 27–47.
Mackey, J. R., Jennings, L. L., Clarke, M. L., Santos, C. L., Dabbagh, L., Vsianska, M., et al. (2002). Immunohistochemical variation of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 protein in primary breast cancers. Clinical Cancer Research, 8, 110–116.
Mackey, J. R., Baldwin, S. A., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (1998). Nucleoside transport and its significance for anticancer drug resistance. Drug Resistance Updates, 1, 310–324.
Landfear, S. M. (2001). Molecular genetics of nucleoside transporters in Leishmania and African trypanosomes. Biochemical Pharmacology, 62, 149–155.
Damaraju, V. L., Damaraju, S., Young, J. D., Baldwin, S. A., Mackey, J., Sawyer, M. B., et al. (2003). Nucleoside anticancer drugs: The role of nucleoside transporters in resistance to cancer chemotherapy. Oncogene, 22, 7524–7536.
de Koning, H. P., Bridges, D. J., & Burchmore, R. J. (2005). Purine and pyrimidine transport in pathogenic protozoa: From biology to therapy. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 29, 987–1020.
Pastor-Anglada, M., Cano-Soldado, P., Molina-Arcas, M., Lostao, M. P., Larrayoz, I., Martinez-Picado, J., et al. (2005). Cell entry and export of nucleoside analogues. Virus Research, 107, 151–164.
Griffiths, M., Beaumont, N., Yao, S. Y., Sundaram, M., Boumah, C. E., Davies, A., et al. (1997) Cloning of a human nucleoside transporter implicated in the cellular uptake of adenosine and chemotherapeutic drugs [see comments]. Nat Med, 3, 89–93.
Griffiths, M., Yao, S. Y., Abidi, F., Phillips, S. E., Cass, C. E., Young, J. D., et al. (1997). Molecular cloning and characterization of a nitrobenzylthioinosine-insensitive (ei) equilibrative nucleoside transporter from human placenta. Biochemical Journal, 328, 739–743.
Baldwin, S. A., Yao, S. Y., Hyde, R. J., Ng, A. M., Foppolo, S., Barnes, K., et al. (2005). Functional characterisation of novel human and mouse equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT3 and mENT3) located in intracellular membranes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 15880–15887.
Baldwin, S. A., Beal, P. R., Yao, S. Y., King, A. E., Cass, C. E., & Young, J. D. (2004). The equilibrative nucleoside transporter family, SLC29. Pflugers Archiv, 447, 735–743.
Ritzel, M. W., Yao, S. Y., Huang, M. Y., Elliott, J. F., Cass, C. E., & Young, J. D. (1997). Molecular cloning and functional expression of cDNAs encoding a human Na+-nucleoside cotransporter (hCNT1). American Journal of Physiology, 272, C707–C714.
Ritzel, M. W., Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Mackey, J. R., Cass, C. E., & Young, J. D. (1998). Molecular cloning, functional expression and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding a human Na+/nucleoside cotransporter (hCNT2) selective for purine nucleosides and uridine. Molecular Membrane Biology, 15, 203–211.
Ritzel, M. W. L., Ng, A. M., Yao, S. Y. M., Graham, K., Loewen, S. K., Smith, K. M., et al. (2001). Molecularidentification and characterization of novel human and mouse concentrative Na+-nucleoside cotransporter proteins (hCNT3 and mCNT3) broadly selective for purine and pyrimidinnNucleosides (system cib). Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 2914–2927.
Crawford, C. R., Patel, D. H., Naeve, C., & Belt, J. A. (1998). Cloning of the human equilibrative, nitrobenzylmercaptopurine riboside (NBMPR)-insensitive nucleoside transporter ei by functional expression in a transport-deficient cell line. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 5288–5293.
Visser, F., Vickers, M. F., Ng, A. M., Baldwin, S. A., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2002). Mutation of residue 33 of human equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 2 alters sensitivity to inhibition of transport by dilazep and dipyridamole. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 395–401.
Visser, F., Baldwin, S. A., Isaac, R. E., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2005). Identification and mutational analysis of amino acid residues involved in dipyridamole interactions with human and caenorhabditis elegans equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 11025–11034.
Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Vickers, M. F., Sundaram, M., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (2002). Functional and molecular characterization of nucleobase transport by recombinant human and rat equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 2. Chimeric constructs reveal a role for the ENT2 helix 5–6 region in nucleobase translocation. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 24938–24948.
Acimovic, Y., & Coe, I. R. (2002). Molecular evolution of the equilibrative nucleoside transporter family: Identification of novel family members in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 19, 2199–2210.
Hyde, R. J., Abidi, F., Griffiths, M., Yao, S. Y. M., Sundaram, M., Phillips, S. E. V., et al. (2000). Probing the structure/function relationships of human equilibrative nucleoside transporters using site-directed mutagenesis. Drug Development Research, 50, 38.
Engel, K., Zhou, M., & Wang, J. (2004). Identification and characterization of a novel monoamine transporter in the human brain. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 50042–50049.
Barnes, K., Dobrzynski, H., Foppolo, S., Beal, P. R., Ismat, F., Scullion, E. R., et al. (2006). Distribution and functional characterization of equilibrative nucleoside transporter-4, a novel cardiac adenosine transporter activated at acidic pH. Circulation Research, 99, 510–519.
Smith, K. M., Slugoski, M. D., Loewen, S. K., Ng, A. M., Yao, S. Y., Chen, X. Z., et al. (2005). The broadly selective human Na+/nucleoside cotransporter (hCNT3) exhibits novel cation-coupled nucleoside transport characteristics. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 25436–25449.
Wang, J., Su, S. F., Dresser, M. J., Schaner, M. E., Washington, C. B., & Giacomini, K. M. (1997). Na+-dependent purine nucleoside transporter from human kidney: Cloning and functional characterization. American Journal of Physiology, 273, F1058–F1065.
Wang, J., Schaner, M. E., Thomassen, S., Su, S. F., Piquette-Miller, M., & Giacomini, K. M. (1997). Functional and molecular characteristics of Na(+)-dependent nucleoside transporters. Pharmaceutical Research, 14, 1524–1532.
Griffith, D. A., & Jarvis, S. M. (1996). Nucleoside and nucleobase transport systems of mammalian cells. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1286, 153–181.
Lu, X., Gong, S., Monks, A., Zaharevitz, D., & Moscow, J. A. (2002). Correlation of nucleoside and nucleobase transporter gene expression with antimetabolite drug cytotoxicity. Journal of Experimental Therapeutics & Oncology, 2, 200–212.
Pennycooke, M., Chaudary, N., Shuralyova, I., Zhang, Y., & Coe, I. R. (2001). Differential expression of human nucleoside transporters in normal and tumor tissue. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 280, 951–959.
Molina-Arcas, M., Bellosillo, B., Casado, F. J., Montserrat, E., Gil, J., Colomer, D., et al. (2003). Fludarabine uptake mechanisms in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood, 101, 2328–2334.
Hamilton, S. R., Yao, S. Y., Ingram, J. C., Hadden, D. A., Ritzel, M. W., Gallagher, M. P., et al. (2001). Subcellular distribution and membrane topology of the mammalian concentrative Na+-nucleoside cotransporter rCNT1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 27981–27988.
Pastor-Anglada, M., Casado, F. J., Valdes, R., Mata, J., Garcia-Manteiga, J., & Molina, M. (2001). Complex regulation of nucleoside transporter expression in epithelial and immune system cells. Molecular Membrane Biology, 18, 81–85.
Felipe, A., Valdes, R., Santo, B., Lloberas, J., Casado, J., & Pastor-Anglada, M. (1998). Na+-dependent nucleoside transport in liver: Two different isoforms from the same gene family are expressed in liver cells. Biochemical Journal, 330, 997–1001.
Pisoni, R. L., & Thoene, J. G. (1991). The transport systems of mammalian lysosomes. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1071, 351–373.
Mani, R. S., Hammond, J. R., Marjan, J. M., Graham, K. A., Young, J. D., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (1998). Demonstration of equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT1 and hENT2) in nuclear envelopes of cultured human choriocarcinoma (BeWo) cells by functional reconstitution in proteoliposomes. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 30818–30825.
Lai, Y., Tse, C. M., & Unadkat, J. D. (2004). Mitochondrial expression of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) results in enhanced mitochondrial toxicity of antiviral drugs. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 279, 4490–4497.
Mackey, J. R., Galmarini, C. M., Graham, K. A., Joy, A. A., Delmer, A., Dabbagh, L., et al. (2005). Quantitative analysis of nucleoside transporter and metabolism gene expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL): Identification of fludarabine-sensitive and -insensitive populations. Blood, 105, 767–774.
Choi, D. S., Cascini, M. G., Mailliard, W., Young, H., Paredes, P., McMahon, T., et al. (2004). The type 1 equilibrative nucleoside transporter regulates ethanol intoxication and preference. Nature Neuroscience, 7, 855–861.
Lang, T. T., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2004). Interactions of nucleoside analogs, caffeine, and nicotine with human concentrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 2 stably produced in a transport-defective human cell line. Molecular Pharmacology, 65, 925–933.
Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Loewen, S. K., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., & Young, J. D. (2002). An ancient prevertebrate Na+-nucleoside cotransporter (hfCNT) from the Pacific hagfish (Eptatretus stouti). American Journal of Physiology Cell Physiology, 283, C155–C168.
Ritzel, M. W., Ng, A. M., Yao, S. Y., Graham, K., Loewen, S. K., Smith, K. M., et al. (2001). Recent molecular advances in studies of the concentrative Na+-dependent nucleoside transporter (CNT) family: Identification and characterization of novel human and mouse proteins (hCNT3 and mCNT3) broadly selective for purine and pyrimidine nucleosides (system cib). Molecular Membrane Biology, 18, 65–72.
Zhang, J., Visser, F., Vickers, M. F., Lang, T., Robins, M. J., Nielsen, L. P., et al. (2003). Uridine binding motifs of human concentrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 3 produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molecular Pharmacology, 64, 1512–1520.
Zhang, J., Smith, K. M., Tackaberry, T., Visser, F., Robins, M. J., Nielsen, L. P., et al. (2005). Uridine binding and transportability determinants of human concentrative nucleoside transporters. Molecular Pharmacology, 68, 830–839.
Visser, F., Zhang, J., Raborn, R. T., Baldwin, S. A., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2005). Residue 33 of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 2 is a functionally important component of both the dipyridamole and nucleoside binding sites. Molecular Pharmacology, 67, 1291–1298.
Ward, J. L., Sherali, A., Mo, Z. P., & Tse, C. M. (2000). Kinetic and pharmacological properties of cloned human equilibrative nucleoside transporters, ENT1 and ENT2, stably expressed in nucleoside transporter-deficient PK15 cells. Ent2 exhibits a low affinity for guanosine and cytidine but a high affinity for inosine [In Process Citation]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 8375–8381.
Mackey, J. R., Mani, R. S., Selner, M., Mowles, D., Young, J. D., Belt, J. A., et al. (1998). Functional nucleoside transporters are required for gemcitabine influx and manifestation of toxicity in cancer cell lines. Cancer Research, 58, 4349–4357.
Galmarini, C. M., Thomas, X., Calvo, F., Rousselot, P., Rabilloud, M., El Jaffari, A., et al. (2002). In vivo mechanisms of resistance to cytarabine in acute myeloid leukaemia. British Journal of Haematology, 117, 860–868.
Clarke, M. L., Damaraju, V. L., Zhang, J., Mowles, D., Tackaberry, T., Lang, T., et al. (2006). Uptake of 4′-thio-β-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine and β-d-arabinosylcytosine by human nucleoside transporters. Molecular Pharmacology, 70, 301–310.
Gati, W. P., Paterson, A. R., Belch, A. R., Chlumecky, V., Larratt, L. M., Mant, M. J., et al. (1998). Es nucleoside transporter content of acute leukemia cells: Role in cell sensitivity to cytarabine (araC). Leukemia and Lymphoma, 32, 45–54.
Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Sundaram, M., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., & Young, J. D. (2001). Transport of antiviral 3′-deoxy-nucleoside drugs by recombinant human and rat equilibrative, nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-insensitive (ENT2) nucleoside transporter proteins produced in Xenopus oocytes. Molecular Membrane Biology, 18, 161–167.
Mackey, J. R., Yao, S. Y., Smith, K. M., Karpinski, E., Baldwin, S. A., Cass, C. E., et al. (1999). Gemcitabine transport in xenopus oocytes expressing recombinant plasma membrane mammalian nucleoside transporters. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 91, 1876–1881.
Lostao, M. P., Mata, J. F., Larrayoz, I. M., Inzillo, S. M., Casado, F. J., & Pastor-Anglada, M. (2000). Electrogenic uptake of nucleosides and nucleoside-derived drugs by the human nucleoside transporter 1 (hCNT1) expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. FEBS Letters, 481, 137–140.
Graham, K. A., Leithoff, J., Coe, I. R., Mowles, D., Mackey, J. R., Young, J. D., et al. (2000). Differential transport of cytosine-containing nucleosides by recombinant human concentrative nucleoside transporter protein hCNT1. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 19, 415–434.
Mata, J. F., Garcia-Manteiga, J. M., Lostao, M. P., Fernandez-Veledo, S., Guillen-Gomez, E., Larrayoz, I. M., et al. (2001). Role of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter (hCNT1) in the cytotoxic action of 5[Prime]-deoxy-5-fluorouridine, an active intermediate metabolite of capecitabine, a novel oral anticancer drug. Molecular Pharmacology, 59, 1542–1548.
Li, J. Y., Boado, R. J., & Pardridge, W. M. (2001). Differential kinetics of transport of 2′,3′-dideoxyinosine and adenosine via concentrative Na+ nucleoside transporter CNT2 cloned from rat blood-brain barrier. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 299, 735–740.
Gerstin, K. M., Dresser, M. J., & Giacomini, K. M. (2002). Specificity of human and rat orthologs of the concentrative nucleoside transporter, SPNT. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 283, F344–F349.
Sundaram, M., Yao, S. Y. M., Ingram, J. C., Berry, Z. A., Abidi, F., Cass, C. E., et al. (2001). Topology of a human nucleoside transporter implicated in cellular uptake of adenosine and anti-cancer drugs. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276, 45270–45275.
Ward, J. L., Leung, G. P., Toan, S. V., & Tse, C. M. (2003). Functional analysis of site-directed glycosylation mutants of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-2. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 411, 19–26.
Vickers, M. F., Mani, R. S., Sundaram, M., Hogue, D. L., Young, J. D., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (1999). Functional production and reconstitution of the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter (hENT1) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Interaction of inhibitors of nucleoside transport with recombinant hENT1 and a glycosylation-defective derivative (hENT1/N48Q). Biochemical Journal, 339, 21–32.
Huang, Q. Q., Yao, S. Y., Ritzel, M. W., Paterson, A. R., Cass, C. E., & Young, J. D. (1994). Cloning and functional expression of a complementary DNA encoding a mammalian nucleoside transport protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 269, 17757–17760.
Craig, J. E., Zhang, Y., & Gallagher, M. P. (1994). Cloning of the nupC gene of Escherichia coli encoding a nucleoside transport system, and identification of an adjacent insertion element, IS 186. Molecular Microbiology, 11, 1159–1168.
Toan, S. V., To, K. K., Leung, G. P., de Souza, M. O., Ward, J. L., & Tse, C. M. (2003). Genomic organization and functional characterization of the human concentrative nucleoside transporter-3 isoform (hCNT3) expressed in mammalian cells. Pflugers Archiv, 447, 195–204.
Mangravite, L. M., & Giacomini, K. M. (2003) Sorting of rat SPNT in renal epithelium is independent of N-glycosylation. Pharmaceutical Research, 20, 319–323.
Huang, Y., Lemieux, M. J., Song, J., Auer, M., & Wang, D. N. (2003). Structure and mechanism of the glycerol-3-phosphate transporter from Escherichia coli. Science, 301, 616-620.
Abramson, J., Smirnova, I., Kasho, V., Verner, G., Kaback, H. R., & Iwata, S. (2003). Structure and mechanism of the lactose permease of Escherichia coli. Science, 301, 610–615.
Yernool, D., Boudker, O., Jin, Y., & Gouaux, E. (2004). Structure of a glutamate transporter homologue from Pyrococcus horikoshii. Nature, 431, 811–818.
Widdas, W. F. (1952). Inability of diffusion to account for placental glucose transfer in the sheep and consideration of the kinetics of a possible carrier transfer. Journal of Physiology, 118, 23–39.
DeFelice, L. J. (2004). Transporter structure and mechanism. Trends in Neurosciences, 27, 352–359.
Locher, K. P., Bass, R. B., & Rees, D. C. (2003). Structural biology. Breaching the barrier. Science, 301, 603–604.
Agbanyo, F. R., Cass, C. E., & Paterson, A. R. (1988). External location of sites on pig erythrocyte membranes that bind nitrobenzylthioinosine. Molecular Pharmacology, 33, 332–337.
Damaraju, S., Zhang, J., Visser, F., Tackaberry, T., Dufour, J., Smith, K. M., et al. (2005). Identification and functional characterization of variants in human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3, hCNT3 (SLC28A3), arising from single nucleotide polymorphisms in coding regions of the hCNT3 gene. Pharmacogenet Genomics, 15, 173–182.
Mohlmann, T., Mezher, Z., Schwerdtfeger, G., & Neuhaus, H. E. (2001). Characterisation of a concentrative type of adenosine transporter from Arabidopsis thaliana (ENT1,At). FEBS Letters, 509, 370–374.
Xiao, G., Wang, J., Tangen, T., & Giacomini, K. M. (2001). A novel proton-dependent nucleoside transporter, CeCNT3, from Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular Pharmacology, 59, 339–348.
Wormit, A., Traub, M., Florchinger, M., Neuhaus, H. E., & Mohlmann, T. (2004). Characterization of three novel members of the Arabidopsis thaliana equilibrative nucleoside transporter (ENT) family. Biochemical Journal, 383, 19–26.
Landfear, S. M., Ullman, B., Carter, N. S., & Sanchez, M. A. (2004). Nucleoside and nucleobase transporters in parasitic protozoa. Eukaryot Cell, 3, 245–254.
Li, G., Liu, K., Baldwin, S. A., & Wang, D. (2003). Equilibrative nucleoside transporters of Arabidopsis thaliana. cDNA cloning, expression pattern, and analysis of transport activities. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 35732–35742.
Smith, K. M., Ng, A. M., Yao, S. Y., Labedz, K. A., Knaus, E. E., Wiebe, L. I., et al. (2004). Electrophysiological characterization of a recombinant human Na+-coupled nucleoside transporter (hCNT1) produced in Xenopus oocytes. Journal of Physiology, 558, 807–823.
Jauch, P., Petersen, O. H., & Lauger, P. (1986). Electrogenic properties of the sodium-alanine cotransporter in pancreatic acinar cells. I. Tight-seal whole-cell recordings. Journal of Membrane Biology, 94, 99–115.
Mackenzie, B., Loo, D. D., Panayotova-Heiermann, M., & Wright, E. M. (1996). Biophysical characteristics of the pig kidney Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT2 reveal a common mechanism for SGLT1 and SGLT2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 32678–32683.
Grewer, C., & Rauen, T. (2005). Electrogenic glutamate transporters in the CNS: Molecular mechanism, pre-steady-state kinetics, and their impact on synaptic signaling. Journal of Membrane Biology, 203, 1–20.
Sundaram, M., Yao, S. Y. M., Ng, A. M. L., Griffiths, M., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (1998). Chimeric constructs between human and rat equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT1 and rENT1) reveal hENT1 structural domains interacting with coronary vasoactive drugs. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 21519–21525.
Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Muzyka, W. R., Griffiths, M., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (1997). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-sensitive (es) and NBMPR-insensitive (ei) equilibrative nucleoside transporter proteins (rENT1 and rENT2) from rat tissues. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 28423–28430.
Sundaram, M., Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., & Young, J. D. (2001). Equilibrative nucleoside transporters: Mapping regions of interaction for the substrate analogue nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR) using rat chimeric proteins. Biochemistry, 40, 8146–8151.
Yao, S. M., Sundaram, M., Chomey, E. G., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., & Young, J. D. (2001). Identification of Cys140 in helix 4 as an exofacial cysteine residue within the substrate-translocation channel of rat equilibrative nitrobenzylthioinosine (NBMPR)-insensitive nucleoside transporter rENT2. Biochemical Journal, 353, 387–393.
SenGupta, D. J., Lum, P. Y., Lai, Y., Shubochkina, E., Bakken, A. H., Schneider, G., et al. (2002). A single glycine mutation in the equilibrative nucleoside transporter gene, hENT1, alters nucleoside transport activity and sensitivity to nitrobenzylthioinosine. Biochemistry, 41, 1512–1519.
Appleford, P. J., Griffiths, M., Yao, S. Y., Ng, A. M., Chomey, E. G., Isaac, R. E., et al. (2004). Functional redundancy of two nucleoside transporters of the ENT family (CeENT1, CeENT2) required for development of Caenorhabditis elegans. Molecular Membrane Biology, 21, 247–259.
Lemmon, M. A., Flanagan, J. M., Hunt, J. F., Adair, B. D., Bormann, B. J., Dempsey, C. E., et al. (1992). Glycophorin A dimerization is driven by specific interactions between transmembrane alpha-helices. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 7683–7689.
Endres, C. J., & Unadkat, J. D. (2005). Residues Met89 and Ser160 in the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 affect its affinity for adenosine, guanosine, S6-(4-Nitrobenzyl)-mercaptopurine riboside, and dipyridamole. Molecular Pharmacology, 67, 837–844.
Vasudevan, G., Ullman, B., & Landfear, S. M. (2001). Point mutations in a nucleoside transporter gene from Leishmania donovani confer drug resistance and alter substrate selectivity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 6092–6097.
Valdes, R., Vasudevan, G., Conklin, D., & Landfear, S. M. (2004). Transmembrane domain 5 of the LdNT1.1 nucleoside transporter is an amphipathic helix that forms part of the nucleoside translocation pathway. Biochemistry, 43, 6793–6802.
Arastu-Kapur, S., Ford, E., Ullman, B., & Carter, N. S. (2003). Functional analysis of an inosine-guanosine transporter from Leishmania donovani. The role of conserved residues, aspartate 389 and arginine 393. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 33327–33333.
Visser, F. (2005). Identification and characterization of molecular determinants of inhibitor interactions with equilibrative nucleoside transporters. Oncology, pp. 176. Edmonton: University of Alberta.
Lai, Y., Lee, E. W., Ton, C. C., Vijay, S., Zhang, H., & Unadkat, J. D. (2005). Conserved residues F316 and G476 in the concentrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hCNT1) affect guanosine sensitivity and membrane expression, respectively. American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology, 288, C39–C45.
Flanagan, S. A., & Meckling-Gill, K. A. (1997). Characterization of a novel Na+-dependent, guanosine-specific, nitrobenzylthioinosine-sensitive transporter in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 18026–18032.
Wang, J., & Giacomini, K. M. (1997). Molecular determinants of substrate selectivity in Na+-dependent nucleoside transporters. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 28845–28848.
Loewen, S. K., Ng, A. M., Yao, S. Y., Cass, C. E., Baldwin, S. A., & Young, J. D. (1999). Identification of amino acid residues responsible for the pyrimidine and purine nucleoside specificities of human concentrative Na(+) nucleoside cotransporters hCNT1 and hCNT2. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 24475–24484.
Zhang, J., Tackaberry, T., Ritzel, M. W., Raborn, T., Barron, G., Baldwin, S. A., et al. (2006). Cysteine-accessibility analysis of transmembrane domains 11–13 of human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3. Biochemical Journal, 394, 389–398.
Lang, T. T., Selner, M., Young, J. D., & Cass, C. E. (2001). Acquisition of human concentrative nucleoside transporter 2 (hcnt2) activity by gene transfer confers sensitivity to fluoropyrimidine nucleosides in drug-resistant leukemia cells. Molecular Pharmacology, 60, 1143–1152.
Chang, C., Swaan, P. W., Ngo, L. Y., Lum, P. Y., Patil, S. D., & Unadkat, J. D. (2004). Molecular requirements of the human nucleoside transporters hCNT1, hCNT2, and hENT1. Molecular Pharmacology, 65, 558–570.
Patil, S. D., Ngo, L. Y., & Unadkat, J. D. (2000). Structure-inhibitory profiles of nucleosides for the human intestinal N1 and N2 Na+-nucleoside transporters. Cancer Chemotheraphy and Pharmacology, 46, 394–402.
Vickers, M. F., Zhang, J., Visser, F., Tackaberry, T., Robins, M. J., Nielsen, L. P., et al. (2004). Uridine recognition motifs of human equilibrative nucleoside transporters 1 and 2 produced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 23, 361–373.
Damaraju, V. L., Visser, F., Zhang, J., Mowles, D., Ng, A. M., Young, J. D., et al. (2005). Role of human nucleoside transporters in the cellular uptake of two inhibitors of IMP dehydrogenase, tiazofurin and benzamide riboside. Molecular Pharmacology, 67, 273–279.
Guida, L., Bruzzone, S., Sturla, L., Franco, L., Zocchi, E., & De Flora, A. (2002). Equilibrative and Concentrative Nucleoside Transporters Mediate Influx of Extracellular Cyclic ADP-Ribose into 3T3 Murine Fibroblasts. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 47097–47105.
Huang, M., Wang, Y., Collins, M., Gu, J. J., Mitchell, B. S., & Graves, L. M. (2002). Inhibition of nucleoside transport by p38 MAPK inhibitors. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 28364–28367.
Huang, M., Wang, Y., Cogut, S. B., Mitchell, B. S., & Graves, L. M. (2003). Inhibition of nucleoside transport by protein kinase inhibitors. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 304, 753–760.
Leabman, M. K., Huang, C. C., DeYoung, J., Carlson, E. J., Taylor, T. R., de la Cruz, M., et al. (2003). Natural variation in human membrane transporter genes reveals evolutionary and functional constraints. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 5896–5901.
Osato, D. H., Huang, C. C., Kawamoto, M., Johns, S. J., Stryke, D., Wang, J., et al. (2003). Functional characterization in yeast of genetic variants in the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter, ENT1. Pharmacogenetics, 13, 297–301.
Owen, R. P., Lagpacan, L. L., Taylor, T. R., De La Cruz, M., Huang, C. C., Kawamoto, M., et al. (2006). Functional characterization and haplotype analysis of polymorphisms in the human equilibrative nucleoside transporter, ENT2. Drug Metabolism and Disposition, 34, 12–15.
Badagnani, I., Chan, W., Castro, R. A., Brett, C. M., Huang, C. C., Stryke, D., et al. (2005). Functional analysis of genetic variants in the human concentrative nucleoside transporter 3 (CNT3; SLC28A3). Pharmacogenomics Journal, 5, 157–165.
Gray, J. H., Mangravite, L. M., Owen, R. P., Urban, T. J., Chan, W., Carlson, E. J., et al. (2004). Functional and genetic diversity in the concentrative nucleoside transporter, CNT1, in human populations. Molecular Pharmacology, 65, 512–519.
Owen, R. P., Gray, J. H., Taylor, T. R., Carlson, E. J., Huang, C. C., Kawamoto, M., et al. (2005). Genetic analysis and functional characterization of polymorphisms in the human concentrative nucleoside transporter, CNT2. Pharmacogenet Genomics, 15, 83–90.
Lai, Y., Bakken, A. H., & Unadkat, J. D. (2002). Simultaneous expression of hCNT1-CFP and hENT1-YFP in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Localization and vectorial transport studies. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 37711–37717.
Mangravite, L. M., Lipshutz, J. H., Mostov, K. E., Giacomini, K. M. (2001). Localization of GFP-tagged concentrative nucleoside transporters in a renal polarized epithelial cell line. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 280, F879–F885.
Mangravite, L. M., Xiao, G., & Giacomini, K. M. (2003). Localization of human equilibrative nucleoside transporters, hENT1 and hENT2, in renal epithelial cells. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology, 284, F902–F910.
Galmarini, C. M., Mackey, J. R., & Dumontet, C. (2001). Nucleoside analogues: Mechanisms of drug resistance and reversal strategies. Leukemia, 15, 875–890.
Gourdeau, H., Clarke, M. L., Ouellet, F., Mowles, D., Selner, M., Richard, A., et al. (2001). Mechanisms of uptake and resistance to troxacitabine, a novel deoxycytidine nucleoside analogue, in human leukemic and solid tumor cell lines. Cancer Research, 61, 7217–7224.
Stam, R. W., den Boer, M. L., Meijerink, J. P., Ebus, M. E., Peters, G. J., Noordhuis, P., et al. (2003). Differential mRNA expression of Ara-C-metabolizing enzymes explains Ara-C sensitivity in MLL gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood, 101, 1270–1276.
Huang, Y., Anderle, P., Bussey, K. J., Barbacioru, C., Shankavaram, U., Dai, Z., et al. (2004). Membrane transporters and channels: Role of the transportome in cancer chemosensitivity and chemoresistance. Cancer Research, 64, 4294–4301.
Spratlin, J., Sangha, R., Glubrecht, D., Dabbagh, L., Young, J. D., Dumontet, C., et al. (2004). The absence of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 is associated with reduced survival in patients with gemcitabine-treated pancreas adenocarcinoma. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 6956–6961.
Galmarini, C. M., Clarke, M. L., Jordheim, L., Santos, C. L., Cros, E., Mackey, J. R., et al. (2004). Resistance to gemcitabine in a human follicular lymphoma cell line is due to partial deletion of the deoxycytidine kinase gene. BMC Pharmacology, 4, 8.
Jordheim, L. P., Cros, E., Gouy, M. H., Galmarini, C. M., Peyrottes, S., Mackey, J., et al. (2004). Characterization of a gemcitabine-resistant murine leukemic cell line: reversion of in vitro resistance by a mononucleotide prodrug. Clinical Cancer Research, 10, 5614–5621.
Chow, L., Lai, R., Dabbagh, L., Belch, A., Young, J. D., Cass, C. E., et al. (2005). Analysis of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (hENT1) protein in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma by immunohistochemistry. Modern Pathology, 18, 558–564.
Robak, T. (2005). Therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukaemia with purine nucleoside analogues: facts and controversies. Drugs Aging, 22, 983–1012.
Grever, M. R., Kopecky, K. J., Coltman, C. A., Files, J. C., Greenberg, B. R., Hutton, J. J., et al. (1988). Fludarabine monophosphate: A potentially useful agent in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Nouvelle Revue Francaise d’hematologie, 30, 457–459.
Ross, S. R., McTavish, D., & Faulds, D. (1993). Fludarabine. A review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic potential in malignancy. Drugs, 45, 737–759.
Beutler, E. (1992). Cladribine (2-chlorodeoxyadenosine). Lancet, 340, 952–956.
Robak, T., Korycka, A., Kasznicki, M., Wrzesien-Kus, A., & Smolewski, P. (2005). Purine nucleoside analogues for the treatment of hematological malignancies: pharmacology and clinical applications. Current Cancer Drug Targets, 5, 421–444.
Plunkett, W., & Saunders, P. P. (1991). Metabolism and action of purine nucleoside analogs. Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 49, 239–268.
Wang, L., Karlsson, A., Arner, E. S., & Eriksson, S. (1993). Substrate specificity of mitochondrial 2′-deoxyguanosine kinase. Efficient phosphorylation of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 268, 22847–22852.
Pettitt, A. R., Sherrington, P. D., & Cawley, J. C. (2000). Role of poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in the killing of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by purine analogues. Cancer Research, 60, 4187–4193.
Huang, P., & Plunkett, W. (1991). Action of 9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl-2-fluoroadenine on RNA metabolism. Molecular Pharmacology, 39, 449–455.
Huang, P., Sandoval, A., Van Den Neste, E., Keating, M. J., & Plunkett, W. (2000). Inhibition of RNA transcription: A biochemical mechanism of action against chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by fludarabine. Leukemia, 14, 1405–1413.
Genini, D., Adachi, S., Chao, Q., Rose, D. W., Carrera, C. J., Cottam, H. B., et al. (2000). Deoxyadenosine analogs induce programmed cell death in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells by damaging the DNA and by directly affecting the mitochondria. Blood, 96, 3537–3543.
Montgomery, J. A., Shortnacy-Fowler, A. T., Clayton, S. D., Riordan, J. M., & Secrist, J. A., (1992). 3rd synthesis and biologic activity of 2′-fluoro-2-halo derivatives of 9-beta-d-arabinofuranosyladenine. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 35, 397–401.
Xie, K. C., & Plunkett, W. (1996). Deoxynucleotide pool depletion and sustained inhibition of ribonucleotide reductase and DNA synthesis after treatment of human lymphoblastoid cells with 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl) adenine. Cancer Research, 56, 3030–3037.
Waud, W. R., Schmid, S. M., Montgomery, J. A., & Secrist, J. A. (2000). 3rd preclinical antitumor activity of 2-chloro-9-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-beta-d- arabinofuranosyl)adenine (Cl-F-ara-A). Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids, 19, 447-460.
Kantarjian, H. M., Gandhi, V., Kozuch, P., Faderl, S., Giles, F., Cortes, J., et al. (2003). Phase I clinical and pharmacology study of clofarabine in patients with solid and hematologic cancers. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 21, 1167–1173.
Kantarjian, H., Gandhi, V., Cortes, J., Verstovsek, S., Du, M., Garcia-Manero, G., et al. (2003). Phase 2 clinical and pharmacologic study of clofarabine in patients with refractory or relapsed acute leukemia. Blood, 102, 2379–2386.
Jeha, S., Gandhi, V., Chan, K. W., McDonald, L., Ramirez, I., Madden, R., et al. (2004). Clofarabine, a novel nucleoside analog, is active in pediatric patients with advanced leukemia. Blood, 103, 784–789.
Faderl, S., Gandhi, V., Keating, M. J., Jeha, S., Plunkett, W., & Kantarjian, H. M. (2005). The role of clofarabine in hematologic and solid malignancies—Development of a next-generation nucleoside analog. Cancer, 103, 1985–1995.
Molina-Arcas, M., Marce, S., Villamor, N., Huber-Ruano, I., Casado, F. J., Bellosillo, B., et al. (2005). Equilibrative nucleoside transporter-2 (hENT2) protein expression correlates with ex vivo sensitivity to fludarabine in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells. Leukemia, 19, 64–68.
King, K. M., Damaraju, V. L., Vickers, M. F., Yao, S. Y., Lang, T., Tackaberry, T. E., et al. (2006). A comparison of the transportability, and its role in cytotoxicity, of clofarabine, cladribine, and fludarabine by recombinant human nucleoside transporters produced in three model expression systems. Molecular Pharmacology, 69, 346–353.
King, K. M., & Cass, C. E. (1994). Membrane transport of 2-chloro-2′-deoxyadenosine and 2-chloro-2′-arabinofluoro-2′-deoxyadenosine is required for cytotoxicity. Proceedings of the American Association for Cancer Research, 35, A3436.
Schaner, M. E., Wang, J., Zevin, S., Gerstin, K. M., & Giacomini, K. M. (1997). Transient expression of a purine-selective nucleoside transporter (SPNTint) in a human cell line (HeLa). Pharmaceutical Research, 14, 1316–1321.
Avery, T. L., Rehg, J. E., Lumm, W. C., Harwood, F. C., Santana, V. M., & Blakley, R. L. (1989). Biochemical pharmacology of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine in malignant human hematopoietic cell lines and therapeutic effects of 2-bromodeoxyadenosine in drug combinations in mice. Cancer Research, 49, 4972-4978.
Ellison, R. R., Holland, J. F., Weil, M., Jacquillat, C., Boiron, M., Bernard, J., et al. (1968). Arabinosyl cytosine: A useful agent in the treatment of acute leukemia in adults. Blood, 32, 507–523.
Grant, S. (1998). Ara-C: Cellular and molecular pharmacology. Advances in Cancer Research, 72, 197–233.
Plunkett, W., Liliemark, J. O., Estey, E., & Keating, M. J. (1987). Saturation of ara-CTP accumulation during high-dose ara-C therapy: pharmacologic rationale for intermediate-dose ara-C. Seminars in Oncology, 14, 159–166.
Laliberte, J., & Momparler, R. L. (1994). Human cytidine deaminase: Purification of enzyme, cloning, and expression of its complementary DNA. Cancer Research, 54, 5401–5407.
Amici, A., Emanuelli, M., Magni, G., Raffaelli, N., & Ruggieri, S. (1997). Pyrimidine nucleotidases from human erythrocyte possess phosphotransferase activities specific for pyrimidine nucleotides. FEBS Letters, 419, 263–267.
Mancini, W. R., & Cheng, Y. C. (1983). Human deoxycytidylate deaminase. Substrate and regulator specificities and their chemotherapeutic implications. Molecular Pharmacology, 23, 159–164.
Ho, D. H., & Frei, E., 3rd (1971). Clinical pharmacology of 1-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl cytosine. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 12, 944-954.
Wiley, J. S., Jones, S. P., Sawyer, W. H., & Paterson, A. R. (1982). Cytosine arabinoside influx and nucleoside transport sites in acute leukemia. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 69, 479–489.
Wiley, J. S., Woodruff, R. K., Jamieson, G. P., Firkin, F. C., & Sawyer, W. H. (1987). Cytosine arabinoside in the treatment of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine, 17, 379–386.
Hubeek, I., Stam, R. W., Peters, G. J., Broekhuizen, R., Meijerink, J. P., van Wering, E. R., et al. (2005). The human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 mediates in vitro cytarabine sensitivity in childhood acute myeloid leukaemia. British Journal of Cancer, 93, 1388–1394.
Takagaki, K., Katsuma, S., Kaminishi, Y., Horio, T., Nakagawa, S., Tanaka, T., et al. (2004). Gene-expression profiling reveals down-regulation of equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 (ENT1) in ara-C-resistant CCRF-CEM-derived cells. Journal of Biochemistry (Tokyo), 136, 733–740.
Wiley, J. S., Brocklebank, A. M., Snook, M. B., Jamieson, G. P., Sawyer, W. H., Craik, J. D., et al. (1991). A new fluorescent probe for the equilibrative inhibitor-sensitive nucleoside transporter. 5′-S-(2-aminoethyl)-N6-(4-nitrobenzyl)-5′- thioadenosine (SAENTA)-chi 2-fluorescein. Biochemical Journal, 273, 667–672.
Wright, A. M., Paterson, A. R., Sowa, B., Akabutu, J. J., Grundy, P. E., & Gati, W. P. (2002). Cytotoxicity of 2-chlorodeoxyadenosine and arabinosylcytosine in leukaemic lymphoblasts from paediatric patients: significance of cellular nucleoside transporter content. British Journal of Haematology, 116, 528–537.
Capizzi, R. L., Yang, J. L., Cheng, E., Bjornsson, T., Sahasrabudhe, D., Tan, R. S., et al. (1983). Alteration of the pharmacokinetics of high-dose ara-C by its metabolite, high ara-U in patients with acute leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 1, 763–771.
Ravindranath, Y., Chang, M., Steuber, C. P., Becton, D., Dahl, G., Civin, C., et al. (2005). Pediatric Oncology Group (POG) studies of acute myeloid leukemia (AML): A review of four consecutive childhood AML trials conducted between 1981 and 2000. Leukemia, 19, 2101–2116.
Bohm, A., Piribauer, M., Wimazal, F., Geissler, K., Gisslinger, H., Knobl, P., et al. (2005). High dose intermittent ARA-C (HiDAC) for consolidation of patients with de novo AML: A single center experience. Leukemia Research, 29, 609–615.
Friberg, G., & Kindler, H. L. (2005). Chemotherapy for advanced pancreatic cancer: Past, present, and future. Current Oncology Reports, 7, 186–195.
Patel, S. R., Gandhi, V., Jenkins, J., Papadopolous, N., Burgess, M. A., Plager, C., et al. (2001). Phase II clinical investigation of gemcitabine in advanced soft tissue sarcomas and window evaluation of dose rate on gemcitabine triphosphate accumulation. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 19, 3483–3489.
Kose, M. F., Meydanli, M. M., & Tulunay, G. (2006). Gemcitabine plus carboplatin in platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian carcinoma. Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy, 6, 437–443.
Saha, A., & Rudd, R. (2006). Gemcitabine and carboplatin: Is this the best combination for non-small cell lung cancer? Expert Review of Anticancer Therapy, 6, 165–173.
Poveda, A. (2005). Gemcitabine in patients with ovarian cancer. Cancer Treatment Reviews, 31(4), S29–S37.
Yardley, D. A. (2005). Gemcitabine plus paclitaxel in breast cancer. Seminars in Oncology, 32, S14–S21.
Plunkett, W., Huang, P., Xu, Y. Z., Heinemann, V., Grunewald, R., & Gandhi, V. (1995). Gemcitabine: Metabolism, mechanisms of action, and self-potentiation. Seminars in Oncology, 22, 3–10.
Baker, C. H., Banzon, J., Bollinger, J. M., Stubbe, J., Samano, V., Robins, M. J., et al. (1991). 2′-Deoxy-2′-methylenecytidine and 2′-deoxy-2′,2′-difluorocytidine 5′-diphosphates: Potent mechanism-based inhibitors of ribonucleotide reductase. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 34, 1879–1884.
Heinemann, V., Xu, Y. Z., Chubb, S., Sen, A., Hertel, L. W., Grindey, G. B., et al. (1992). Cellular elimination of 2′,2′-difluorodeoxycytidine 5′-triphosphate: A mechanism of self-potentiation. Cancer Research, 52, 533–539.
Heinemann, V., Schulz, L., Issels, R. D., & Plunkett, W. (1995). Gemcitabine: A modulator of intracellular nucleotide and deoxynucleotide metabolism. Seminars in Oncology, 22, 11–18.
Plunkett, W., Huang, P., Searcy, C. E., & Gandhi, V. (1996). Gemcitabine: Preclinical pharmacology and mechanisms of action. Seminars in Oncology, 23, 3–15.
Achiwa, H., Oguri, T., Sato, S., Maeda, H., Niimi, T., & Ueda, R. (2004). Determinants of sensitivity and resistance to gemcitabine: The roles of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter 1 and deoxycytidine kinase in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Science, 95, 753–757.
Burke, T., Lee, S., Ferguson, P. J., & Hammond, J. R. (1998). Interaction of 2′,2′-difluorodeoxycytidine (gemcitabine) and formycin B with the Na+-dependent and -independent nucleoside transporters of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 286, 1333–1340.
Garcia-Manteiga, J., Molina-Arcas, M., Casado, F. J., Mazo, A., & Pastor-Anglada, M. (2003). Nucleoside transporter profiles in human pancreatic cancer cells: Role of hCNT1 in 2′,2′-difluorodeoxycytidine-induced cytotoxicity. Clinical Cancer Research, 9, 5000–5008.
Giovannetti, E., Del Tacca, M., Mey, V., Funel, N., Nannizzi, S., Ricci, S., et al. (2006). Transcription analysis of human equilibrative nucleoside transporter-1 predicts survival in pancreas cancer patients treated with gemcitabine. Cancer Research, 66, 3928–3935.
Alexander, R. L., Greene, B. T., Torti, S. V., & Kucera, G. L. (2005). A novel phospholipid gemcitabine conjugate is able to bypass three drug-resistance mechanisms. Cancer Chemotheraphy and Pharmacology, 56, 15–21.
Whistler, R. L., Doner, L. W., & Nayak, U. G. (1971). 4-thio-d-arabinofuranosylpyrimidine nucleosides. Journal of Organic Chemistry, 36, 108-110.
Miura, S., Yoshimura, Y., Endo, M., Satoh, H., Machida, H., & Sasaki, T. (1999). Comparison of 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-4-thio-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)cytosine with gemcitabine in its antitumor activity. Cancer Letter, 144, 177–182.
Miura, S., Yoshimura, Y., Endo, M., Machida, H., Matsuda, A., Tanaka, M., et al. (1998). Antitumor activity of a novel orally effective nucleoside, 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-4-thio-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl)cytosine. Cancer Letter, 129, 103–110.
Miller, D. S. (2001). Nucleoside phosphonate interactions with multiple organic anion transporters in renal proximal tubule. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 299, 567–574.
Zajchowski, D. A., Biroc, S. L., Liu, H. L., Chesney, S. K., Hoffmann, J., Bauman, J., et al. (2005). Anti-tumor efficacy of the nucleoside analog 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-4-thio-beta-d-arabinofuranosyl) cytosine (4′-thio-FAC) in human pancreatic and ovarian tumor xenograft models. International Journal of Cancer, 114, 1002–1009.
Parker, W. B., Shaddix, S. C., Rose, L. M., Waud, W. R., Shewach, D. S., Tiwari, K. N., et al. (2000). Metabolism of 4′-thio-beta-d-arabinofuranosylcytosine in CEM cells. Biochemical Pharmacology, 60, 1925–1932.
Someya, H., Waud, W. R., & Parker, W. B. (2005). Long intracellular retention of 4′-thio-arabinofuranosylcytosine 5′-triphosphate as a critical factor for the anti-solid tumor activity of 4′-thio-arabinofuranosylcytosine. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 1–9.
Richardson, F., Black, C., Richardson, K., Franks, A., Wells, E., Karimi, S., et al. (2005). Incorporation of OSI-7836 into DNA of Calu-6 and H460 xenograft tumors. Cancer Chemotheraphy and Pharmacology, 55, 213–221.
Richardson, K. A., Vega, T. P., Richardson, F. C., Moore, C. L., Rohloff, J. C., Tomkinson, B., et al. (2004). Polymerization of the triphosphates of AraC, 2′,2′-difluorodeoxycytidine (dFdC) and OSI-7836 (T-araC) by human DNA polymerase alpha and DNA primase. Biochemical Pharmacology, 68, 2337–2346.
Grove, K. L., Guo, X., Liu, S. H., Gao, Z., Chu, C. K., & Cheng, Y. C. (1995). Anticancer activity of beta-L-dioxolane-cytidine, a novel nucleoside analogue with the unnatural L configuration. Cancer Research, 55, 3008–3011.
Gourdeau, H., Genne, P., Kadhim, S., Bibeau, L., Duchamp, O., Ouellet, F., et al. (2002). Antitumor activity of troxacitabine (Troxatyl) against anthracycline-resistant human xenografts. Cancer Chemotheraphy and Pharmacology, 50, 490–496.
Giles, F. J., Cortes, J. E., Baker, S. D., Thomas, D. A., O’Brien, S., Smith, T. L., et al. (2001). Troxacitabine, a novel dioxolane nucleoside analog, has activity in patients with advanced leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 19, 762–771.
Giles, F. J., Garcia-Manero, G., Cortes, J. E., Baker, S. D., Miller, C. B., O’Brien, S. M., et al. (2002). Phase II study of troxacitabine, a novel dioxolane nucleoside analog, in patients with refractory leukemia. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 20, 656–664.
Townsley, C. A., Chi, K., Ernst, D. S., Belanger, K., Tannock, I., Bjarnason, G. A., et al. (2003). Phase II study of troxacitabine (BCH-4556) in patients with advanced and/or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: A trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada-Clinical Trials Group. Journal of Clinical Oncology, 21, 1524–1529.
Lapointe, R., Letourneau, R., Steward, W., Hawkins, R. E., Batist, G., Vincent, M., et al. (2005). Phase II study of troxacitabine in chemotherapy-naive patients with advanced cancer of the pancreas: Gastrointestinal tumors. Annals of Oncology, 16, 289–293.
Dnt, S. F., Arnold, A., Stewart, D. J., Gertler, S., Ayoub, J., Batist, G., et al. (2005). Phase II study of troxacitabine (BCH-4556) in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung, 183, 265–272.
Walko, C. M., & Lindley, C. (2005). Capecitabine: A review. Clinical Therapeutics, 27, 23–44.
Ishikawa, T., Utoh, M., Sawada, N., Nishida, M., Fukase, Y., Sekiguchi, F., et al. (1998). Tumor selective delivery of 5-fluorouracil by capecitabine, a new oral fluoropyrimidine carbamate, in human cancer xenografts. Biochemical Pharmacology, 55, 1091–1097.
Schmoll, H. J., Buchele, T., Grothey, A., & Dempke, W. (1999). Where do we stand with 5-fluorouracil? Seminars in Oncology, 26, 589–605.
Gati, W. P., Paterson, A. R., Tyrrell, D. L., Cass, C. E., Moravek, J., & Robins, M. J. (1992). Nucleobase transporter-mediated permeation of 2′,3′-dideoxyguanosine in human erythrocytes and human T-lymphoblastoid CCRF-CEM cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 22272–22276.
Cass, C. E., King, K. M., Montano, J. T., & Janowska-Wieczorek, A. (1992). A comparison of the abilities of nitrobenzylthioinosine, dilazep, and dipyridamole to protect human hematopoietic cells from 7-deazaadenosine (tubercidin). Cancer Research, 52, 5879–5886.
Gati, W. P., Larratt, L. M., & Turner, A. R. (2001). Cellular abundance of es nucleoside transporters and differential drug toxicity in myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) bone marrow cell subpopulations. Proceedings of the Western Pharmacology Society, 44, 93–96.
Zhang, J., Sun, X., Smith, K. M., Visser, F., Carpenter, P., Barron, G., et al. (2006). Studies of nucleoside transporters using novel autofluorescent nucleoside probes. Biochemistry, 45, 1087–1098.
Schaner, M. E., Wang, J., Zhang, L., Su, S. F., Gerstin, K. M., & Giacomini, K. M. (1999). Functional characterization of a human purine-selective, Na+-dependent nucleoside transporter (hSPNT1) in a mammalian expression system. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 289, 1487–1491.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Visser, F., King, K.M. et al. The role of nucleoside transporters in cancer chemotherapy with nucleoside drugs. Cancer Metastasis Rev 26, 85–110 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9044-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-007-9044-4