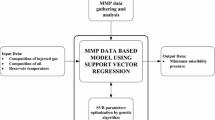
Minimum miscibility pressure (MMP) is a key parameter determining the feasibility of complete miscibility of oil and gas. Using a slim-tube model, we have experimentally established the MMP for gas and six oil samples. We propose an improved mathematical model for determining the MMP, designed using 97 groups of MMP data for hydrocarbons (18 groups for lean-gas flooding and 79 groups for rich-gas flooding). The model obtained is universal and is a function of the reservoir temperature, the average molecular weight of the C 7+ oil fraction, and the mole fraction of volatile components (CH 4 and N 2 ) and intermediate components (CO 2 , H 2 S, C 2 –C 6 ) in the crude oil and in the injected gas. We compare our proposed model with widely used empirical models, showing considerable convergence between the experimental data and the calculations; the percentage average absolute relative error (%AARE) is 7.11%.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. W. Teklu, S. G. Ghedan, R. M. Graves et al., “Minimum miscibility pressure determination: modified multiple mixing cell method,” in: SPE EOR Conference, 16-18 April 2012, Muscat, Oman; SPE 155454-MS
H. Z. Li, J. S. Qin, and D. Y. Yang, “An improved CO2-oil minimum miscibility pressure correlation for live and dead crude oils,” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 51, No. 1, 3516-3523 (2012).
A. M. Amao, S. Siddiqui, H. Menouar, et al., “A new look at the minimum miscibility pressure (MMP) determination from slim tube measurements,” in: SPE Eighteenth Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, 14-18 April 2012, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 153383.
R. K. Srivastava and S. S. Huang, “New interpretation technique for determining minimum miscibility pressure by rising bubble apparatus for enriched-gas drives,” in: SPE India Oil and Gas Conference, 17-19 February 1998, New Dehli, India; SPE 39566-MS.
R. A. Harmon and R. B. Grigg, “Vapor-density measurement for estimating minimum miscibility pressure,” SPE Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 5-8 October 1986, New Orleans; SPE 15403-PA.
W. N. Razak, W. A. Daud, A. H. Faisal et al., “Multi-component mass transfer in multiple contact miscibility test: forward and backward method,” SPE/EAGE Reservoir Characterization and Simulation Conference, 19-21 October 2009, Abu Dhabi, UAE; SPE 125219-MS.
M. Nobakht, S. Moghadam, and Y. A. Gu, “Determination of CO2 minimum miscibility pressure from measured and predicted equilibrium interfacial tensions,” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 47, No. 1, 8918-8925 (2008).
S. S. Kuo, “Prediction of miscibility for the enriched-gas drive process,” in: SPE Sixtieth Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 22-25 September 1985, Las Vegas; SPE 14152.
A. Firoozabadi and K. Aziz, “Analysis and correlation of nitrogen and lean-gas miscibility pressure,” in: SPE California Regional Meeting, 27-29 March 1985, Bakersfield; SPE 13669-PA.
O. Glass, “Generalized minimum miscibility pressure correlation,” SPE Journal, 25, No. 6, 927-934 (1985).
P. Pedrood, “Prediction of minimum miscibility pressure in rich gas injection,” M.Sc. Thesis, Tehran University (1995).
T. Ahmed, “Minimum miscibility pressure from EOS,” in: Canadian International Conference, 4-8 June 2000, Calgary, Alberta; SPE 2000-001.
Y. Wang and M. Franklin, “Calculation of minimum miscibility pressure,” in: SPE/DOE Improved Oil Recovery Symposium, 19-22 April 1998, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 39683-MS.
P. M. Jarrell, C. E. Fox, M. H. Stein et al., “Practical aspects of CO2 flooding,” in: PE Monograph Series, Vol. 22, Society of Petroleum Engineers, Richardson TX (2002).
F. L. Yang, G. B. Zhao, H. Adidharma et al., “Effect of oxygen on minimum miscibility pressure in carbon dioxide flooding,” Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 46, No. 4, 1396-1401 (2007).
H. A. Koch, C. A. Hutchinson, and M. Aime, “Miscible displacements of reservoir oil using flue gas,” in: SPE Thirty-Second Annual Fall Conference , 6-9 October 1957, Dallas; SPE 912-G.
H. J. Welge, E. F. Johnson, and S. P. Ewing et al., “The linear displacement of oil from porous media by enriched gas,” in: SPE Thirty-Fifth Annual Fall Meeting, 2-5 October 1960, Denver; SPE 1525-G.
B. D. Meltzer, J. M. Hurdle, R. W. Cassingham et al., “An efficient gas displacement project: Raleigh field, Mississippi,” in: SPE Annual Fall Conference, 11-14 October 1965, Houston; SPE 945-PA.
J. L. Shelton and L. Yarborough, “Multiple phase behavior in porous media during CO2 or rich-gas flooding,” in: SPE-AIME Fourth Symposium on Improved Oil Recovery, 22-24 March 1977, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 5827.
D. J. Graue and E. T. Zana, “Study of a possible CO2 flood in Rangely field,” in: SPE Fifth Symposium on Improved Methods for Oil Recovery, 16-19 April 1978, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 7060.
C. A. Williams and E. N. Zana, “Use of the Peng-Robinson Equation of State to predict hydrocarbon phase behavior and miscibility for fluid displacement,” in: SPE/DOC First Symposium on Enhanced Oil Recovery, 20-23 April 1980, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 8817-MS.
J. I. Lee and G. A. Reitzel, “High pressure, dry gas miscible flood -Brazeau River Nisku oil pools,” in: Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition, 5-7 October 1981, San Antonio; SPE 10243-PA.
H. M. Sebastian, R. S. Wenger, and T. A. Renner, “Correlation of minimum miscibility pressure for impure CO2 streams,” in: SPE Enhanced Oil Recovery Symposium, 15-18 April 1984, Tulsa, Oklahoma; SPE 12648.
B. E. Eakin and F. J. Mitch, “Measurement and correlation of miscibility pressures of reservoir oils,” in: Sixty-Third Annual Technical Conference and Exhibition of the Society of Petroleum Engineering, 2-5 October 1988, Houston, Texas; SPE 18065.
K. Jessen, M. L. Michelsen, and E. H. Stenby, “Effective algorithm for calculation of minimum miscibility pressure,” in: SPE European Petroleum Conference, 20-22 October 1998, Hague; SPE 50632, pp. 559-567.
B. Liu, J. Zhang, Y. M. Li et al., “Technology for gas injection miscible phase recovery in Pubei Oilfield of Turpan-Hami Basin” [in Chinese], XinJiang Petroleum Geology, 23, No. 5, 424-426 (2002).
Y. Z. Lei, “The technology and application of enhanced oil recovery by CO2 injection for low permeability reservoir” [in Chinese], M.Sc. Thesis, Southwest Petroleum University, Chengdu (2006).
F. Esmaeilzadeh and M. Roshanfekr, “Calculation of minimum miscibility pressure for gas condensate reservoirs,” Fluid Phase Equilibria, 249, No. 1, 75-81 (2006).
N. X. Gong, “The experimental study of hydrocarbon gas drive in Jidong oilfield” [in Chinese], M.Sc. Thesis, China University of Petroleum (2009).
J. F. Du, L. Zhou, P. Guo et al., “The experimental study on minimum miscibility pressure in Shanle oilfield” [in Chinese], Journal of Chongqing University of Science and Technology: Natural Science Edition, 11, No. 1, 16-18 (2009).
This work was done with the financial support of the National Science and Technology Major Project of China (No. 2011ZX05016-005-2) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 50604011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Khimiya i Tekhnologiya Topliv i Masel, No. 3, pp. 19 – 23, May – June, 2015.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, D., He, Y., Luo, P. et al. Improved Method for Calculating Minimum Miscibility Pressure for Gas Flooding. Chem Technol Fuels Oils 51, 257–267 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0600-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10553-015-0600-2