Abstract
Background
Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is a dose-limiting toxicity of several commonly used chemotherapy drugs including taxanes, vinca alkaloids, and platinum compounds. Development of CIPN is highly variable, both in self-reported symptoms and functional consequences, and can be severe enough to alter dose intensity.
Purpose
To describe the natural histories of both patient-reported symptoms of CIPN and functional impairments in breast cancer patients undergoing taxane-based chemotherapy.
Methods
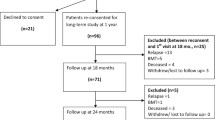
Thirty-three breast cancer patients (32 female/1 male; 47.8 ± 11.2 years; n = 17 stage II/n = 16 stage III) were enrolled. Patients completed self-reports of symptoms and function (e.g., EORTC QLQ-CIPN20) and objective measures of physical function (i.e., balance and gait testing) in an outpatient oncology clinic at five timepoints: (1) baseline—prior to starting chemotherapy, (2–4) before starting subsequent chemotherapy cycles, and (5) 1–3 months after receiving their last taxane infusion.
Results
Significant negative changes in both patient-reported outcomes and objective functional measures were observed. Decreased balance was observed after the first chemotherapy cycle (28% increase in medial–lateral excursion of the center of pressure, p = 0.016) and progressed with cumulative exposure (43% increase, p < 0.001). Patients also demonstrated slower walking speeds (5% decrease, p = 0.003) as they progressed through treatment. These functional deficits were mirrored with increased patient-reported symptom severity for all EORTC QLQ-CIPN20 subscales (all p < 0.05).
Conclusion
This study longitudinally assessed patient-reported outcomes concurrently with balance and gait testing in patients undergoing taxane therapy. Taxane treatment was associated with the development of clinically relevant problems in both CIPN symptoms and patient function.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tofthagen C, Overcash J, Kip K (2012) Falls in persons with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Support Care Cancer 20:583–589
Tinetti ME (2003) Preventing falls in elderly persons. N Engl J Med 348(1):42–49. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp020719
Balducci S, Iacobellis G, Parisi L, Di Biase N, Calandriello E, Leonetti F, Fallucca F (2006) Exercise training can modify the natural history of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Diabetes Complicat 20(4):216–223. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2005.07.005
Bakitas MA (2007) Background noise: the experience of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Nurs Res 56(5):323–331. doi:10.1097/01.NNR.0000289503.22414.79
Seretny M, Currie GL, Sena ES, Ramnarine S, Grant R, MacLeod MR, Colvin LA, Fallon M (2014) Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 155:2461–2470
Ocean AJ, Vahdat LT (2004) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: pathogenesis and emerging therapies. Support Care Cancer 12(9):619–625. doi:10.1007/s00520-004-0657-7
Rubenstein LZ, Josephson KR (2002) The epidemiology of falls and syncope. Clin Geriatr Med 18(2):141–158
Kolb NA, Smith AG, Singleton JR, Beck SL, Stoddard GJ, Brown S, Mooney K (2016) The association of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy symptoms and the risk of falling. JAMA Neurol 73(7):860–866. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0383
Macgilchrist C, Paul L, Ellis B, Howe TE, Kennon B, Godwin J (2010) Lower-limb risk factors for falls in people with diabetes mellitus. Diabet Med 27(2):162–168
Bao T, Basal C, Seluzicki C, Li SQ, Seidman AD, Mao JJ (2016) Long-term chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy among breast cancer survivors: prevalence, risk factors, and fall risk. Breast Cancer Res Treat 159(2):327–333. doi:10.1007/s10549-016-3939-0
Miaskowski C, Mastick J, Paul SM, Topp K, Smoot B, Abrams G, Chen LM, Kober KM, Conley YP, Chesney M, Bolla K, Mausisa G, Mazor M, Wong M, Schumacher M, Levine JD (2017) Chemotherapy-induced neuropathy in cancer survivors. J Pain Symptom Manag. doi:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2016.12.342
Gewandter J, Fan L, Magnuson A, Mustian K, Peppone L, Heckler C, Hopkins J, Tejani M, Morrow G, Mohile S (2013) Falls and functional impairments in cancer survivors with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN): a University of Rochester CCOP study. Support Care Cancer 21(7):2059–2066
Wampler MA, Topp KS, Maiskowski C, Byl NN, Rugo HS, Hamel K (2007) Quantitative and clinical description of postural instability in women with breast cancer treated with taxane chemotherapy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 88:1002–1008
Kneis S, Wehrle A, Freyler K, Lehmann K, Rudolphi B, Hildenbrand B, Bartsch HH, Bertz H, Gollhofer A, Ritzmann R (2016) Balance impairments and neuromuscular changes in breast cancer patients with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Clin Neurophysiol 127(2):1481–1490. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2015.07.022
Streckmann F, Kneis S, Leifert JA, Baumann FT, Kleber M, Ihorst G, Herich L, Grüssinger V, Gollhofer A, Bertz H (2014) Exercise program improves therapy-related side-effects and quality of life in lymphoma patients undergoing therapy. Ann Oncol 25:493–499
Schwenk M, Garland LL, Grewal GS, Holloway D, Muchna A, Mohler J, Najafi B (2015) Wearable sensor-based balance training in older adult cancer patients with chemotherapy-induced neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial. In: ASCO annual meeting proceedings
Winters-Stone KM, Torgrimson B, Horak F, Eisner A, Nail L, Leo MC, Chui S, Luoh SW (2011) Identifying factors associated with falls in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors: a multi-disciplinary approach. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 92(4):646–652. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2010.10.039
Niederer D, Schmidt K, Vogt L, Egen J, Klingler J, Hubscher M, Thiel C, Bernhorster M, Banzer W (2014) Functional capacity and fear of falling in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy. Gait Posture 39(3):865–869. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2013.11.014
Winters-Stone KM, Hilton C, Luoh S-W, Jacobs P, Faithfull S, Horak FB (2016) Comparison of physical function and falls among women with persistent symptoms of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. In: ASCO annual meeting proceedings
Loprinzi CL, Reeves BN, Dakhil SR, Sloan JA, Wolf SL, Burger KN, Kamal A, Le-Lindqwister NA, Soori GS, Jaslowski AJ, Novotny PJ, Lachance DH (2011) Natural history of paclitaxel-associated acute pain syndrome: prospective cohort study NCCTG N08C1. J Clin Oncol 29(11):1472–1478
Monfort SM, Pan X, Patrick R, Singaravelu J, Loprinzi CL, Lustberg MB, Chaudhari AM (2016) Natural history of postural instability in breast cancer patients treated with taxane-based chemotherapy: a pilot study. Gait Posture 48:237–242. doi:10.1016/j.gaitpost.2016.06.011
Maki BE, Holliday PJ, Topper AK (1994) A prospective study of postural balance and risk of falling in an ambulatory and independent elderly population. J Gerontol 49(2):M72–84
Studenski S, Perera S, Patel K, Rosano C, Faulkner K, Inzitari M, Brach J, Chandler J, Cawthon P, Connor EB, Nevitt M, Visser M, Kritchevsky S, Badinelli S, Harris T, Newman AB, Cauley J, Ferrucci L, Guralnik J (2011) Gait speed and survival in older adults. JAMA 305(1):50–58. doi:10.1001/jama.2010.1923
Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA (2006) Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc 54(5):743–749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
MacAulay RK, Allaire TD, Brouillette RM, Foil HC, Bruce-Keller AJ, Han H, Johnson WD, Keller JN (2015) Longitudinal assessment of neuropsychological and temporal/spatial gait characteristics of elderly fallers: taking it all in stride. Front Aging Neurosci 7:34. doi:10.3389/fnagi.2015.00034
Smith EM, Cohen JA, Pett MA, Beck SL (2010) The reliability and validity of a modified total neuropathy score-reduced and neuropathic pain severity items when used to measure chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients receiving taxanes and platinums. Cancer Nurs 33(3):173–183. doi:10.1097/NCC.0b013e3181c989a3
Postma TJ, Aaronson NK, Heimans JJ, Muller MJ, Hildebrand JG, Delattre JY, Hoang-Xuan K, Lanteri-Minet M, Grant R, Huddart R, Moynihan C, Maher J, Lucey R (2005) The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: the QLQ-CIPN20. Eur J Cancer 41(8):1135–1139. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2005.02.012
King MT (1996) The interpretation of scores from the EORTC quality of life questionnaire QLQ-C30. Qual Life Res 5(6):555–567
Aaronson NK, Ahmedzai S, Bergman B, Bullinger M, Cull A, Duez NJ, Filiberti A, Flechtner H, Fleishman SB, de Haes JC et al (1993) The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: a quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J Natl Cancer Inst 85(5):365–376
Caraceni A, Cherny N, Fainsinger R, Kaasa S, Poulain P, Radbruch L, De Conno F (2002) Pain measurement tools and methods in clinical research in palliative care: recommendations of an Expert Working Group of the European Association of Palliative Care. J Pain Symptom Manag 23(3):239–255.
Wildes TM, Dua P, Fowler SA, Miller JP, Carpenter CR, Avidan MS, Stark S (2015) Systematic review of falls in older adults with cancer. J Geriatr Oncol 6(1):70–83. doi:10.1016/j.jgo.2014.10.003
Maki BE (1997) Gait changes in older adults: predictors of falls or indicators of fear? J Am Geriatr Soc 45(3):313–320
Kirkwood RN, de Souza Moreira B, Vallone ML, Mingoti SA, Dias RC, Sampaio RF (2011) Step length appears to be a strong discriminant gait parameter for elderly females highly concerned about falls: a cross-sectional observational study. Physiotherapy 97(2):126–131. doi:10.1016/j.physio.2010.08.007
Verghese J, Holtzer R, Lipton RB, Wang C (2009) Quantitative gait markers and incident fall risk in older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 64(8):896–901. doi:10.1093/gerona/glp033
Richardson JK, Thies SB, DeMott TK, Ashton-Miller JA (2004) A comparison of gait characteristics between older women with and without peripheral neuropathy in standard and challenging environments. J Am Geriatr Soc 52(9):1532–1537. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52418.x
Richardson JK, Thies SB, DeMott TK, Asthon-Miller JA (2005) Gait analysis in a challenging environment differentiates between fallers and nonfallers among older patients with peripheral neuropathy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1539–1544
Capri G, Munzone E, Tarenzi E, Fulfaro F, Gianni L, Caraceni A, Martini C, Scaioli V (1994) Optic nerve disturbances: a new form of paclitaxel neurotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 86(14):1099–1101
Scaioli V, Caraceni A, Martini C, Curzi S, Capri G, Luca G (2006) Electrophysiological evaluation of visual pathways in paclitaxel-treated patients. J Neurooncol 77(1):79–87. doi:10.1007/s11060-005-9008-x
Argyriou AA, Kyritsis A, Matkatsoris T, Kalofonos HP (2014) Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in adults: a comprehensive update of the literature. Cancer Manag Res 6:135–147
Nudelman KN, McDonald BC, Wang Y, Smith DJ, West JD, O’Neill DP, Zanville NR, Champion VL, Schneider BP, Saykin AJ (2016) Cerebral perfusion and gray matter changes associated with chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J Clin Oncol 34(7):677–683. doi:10.1200/JCO.2015.62.1276
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Cancer Institute (Grant No. R03 CA182165-01) and the National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship Program (Grant No. DGE-1343012). The authors would also like to thank Tatiana Sedlak and Samuel Seelbach for their assistance with analyzing gait videos.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants that were included in this study.
Additional information
Ajit M. W. Chaudhari and Maryam B. Lustberg are the senior authors with equal contribution.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monfort, S.M., Pan, X., Patrick, R. et al. Gait, balance, and patient-reported outcomes during taxane-based chemotherapy in early-stage breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 164, 69–77 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4230-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-017-4230-8