Abstract
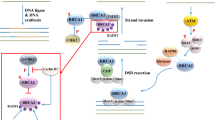
Numerous allelic variants identified in the familial breast cancer and DNA repair genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 are of unknown impact on protein function or clinical relevance, referred to as unclassified variants (UCV). Lymphocytes from pathogenic BRCA1/2 mutation carriers exhibit an increased level of chromosomal damage after irradiation. We established a radiation assay for the discrimination of pathogenic BRCA2 variants versus controls based on the level of chromosomal damage upon irradiation (p < 0.001). As a consequence, lymphocytes from UCV carriers could be separated into two distinct groups with normal or diminished DNA double strand break repair capacity. Our results suggested that all five UCV tested were benign and that one family carried a putative mutation in an as yet undetected DNA-repair gene. Thus, our test may serve as a valuable tool that aids the classification of BRCA2 UCV, but very likely also of BRCA1 UCV or aberrations in other genes involved in the DNA-repair system.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniou AC, Pharoah PD, Narod S, Risch HA, Eyfjord JE, Hopper JL, Olsson H, Johannsson O, Borg A, Pasini B, Radice P, Manoukian S, Eccles DM, Tang N, Olah E, Anton-Culver H, Warner E, Lubinski J, Gronwald J, Gorski B, Tulinius H, Thorlacius S, Eerola H, Nevanlinna H, Syrjakoski K, Kallioniemi OP, Thompson D, Evans C, Peto J, Lalloo F, Evans DG, Easton DF (2005) Breast and ovarian cancer risks to carriers of the BRCA1 5382insC and 185delAG and BRCA2 6174delT mutations: a combined analysis of 22 population based studies. J Med Genet 42(7):602–603
http://www.krebsgesellschaft.de/onkoscout_zentren_familie_brustkrebs,85319.html
Thompson D, Easton DF, Goldgar DE (2003) A full-likelihood method for the evaluation of causality of sequence variants from family data. Am J Hum Genet 73(3):652–655
Abkevich V, Zharkikh A, Deffenbaugh AM, Frank D, Chen Y, Shattuck D, Skolnick MH, Gutin A, Tavtigian SV (2004) Analysis of missense variation in human BRCA1 in the context of interspecific sequence variation. J Med Genet 41(7):492–507
Deffenbaugh AM, Frank TS, Hoffman M, Cannon-Albright L, Neuhausen SL (2002) Characterization of common BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants. Genet Test 6(2):119–121
Goldgar DE, Easton DF, Deffenbaugh AM, Monteiro AN, Tavtigian SV, Couch FJ (2004) Integrated evaluation of DNA sequence variants of unknown clinical significance: application to BRCA1 and BRCA2. Am J Hum Genet 75(4):535–544
Tavtigian SV, Samollow PB, de Silva D, Thomas A (2006) An analysis of unclassified missense substitutions in human BRCA1. Fam Cancer 5(1):77–88
Moynahan ME, Chiu JW, Koller BH, Jasin M (1999) BRCA1 controls homology-directed DNA repair. Mol Cell 4(4):511–518
Powell SN, Kachnic LA (2003) Roles of BRCA1 and BRCA2 in homologous recombination, DNA replication fidelity and the cellular response to ionizing radiation. Oncogene 22(37):5784–5791
Tutt A, Ashworth A (2002) The relationship between the roles of BRCA genes in DNA repair and cancer predisposition. Trends Mol Med 8(12):571–576
Venkitaraman AR (2002) Cancer susceptibility and the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2. Cell 108(2):171–182
Yu V (2000) Caretaker Brca1: keeping the genome in the straight and narrow. Breast Cancer Res 2(2):82–85
Saleh-Gohari N, Helleday T (2004) Conservative homologous recombination preferentially repairs DNA double-strand breaks in the S phase of the cell cycle in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 32(12):3683–3688
Rothkamm K, Kruger I, Thompson LH, Lobrich M (2003) Pathways of DNA double-strand break repair during the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol 23(16):5706–5715
Moore JK, Haber JE (1996) Cell cycle and genetic requirements of two pathways of nonhomologous end-joining repair of double-strand breaks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 16(5):2164–2173
van Gent DC, Hoeijmakers JH, Kanaar R (2001) Chromosomal stability and the DNA double-stranded break connection. Nat Rev Genet 2(3):196–206
Ward JF (1988) DNA damage produced by ionizing radiation in mammalian cells: identities, mechanisms of formation, and reparability. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 35:95–125
Rothfuss A, Schutz P, Bochum S, Volm T, Eberhardt E, Kreienberg R, Vogel W, Speit G (2000) Induced micronucleus frequencies in peripheral lymphocytes as a screening test for carriers of a BRCA1 mutation in breast cancer families. Cancer Res 60(2):390–394
Smart V, Curwen GB, Whitehouse CA, Edwards A, Tawn EJ (2003) Chromosomal radiosensitivity: a study of the chromosomal G(2) assay in human blood lymphocytes indicating significant inter-individual variability. Mutat Res 528(1–2):105–110
Buchholz TA, Wu X, Hussain A, Tucker SL, Mills GB, Haffty B, Bergh S, Story M, Geara FB, Brock WA (2002) Evidence of haplotype insufficiency in human cells containing a germline mutation in BRCA1 or BRCA2. Int J Cancer 97(5):557–561
Ernestos B, Nikolaos P, Koulis G, Eleni R, Konstantinos B, Alexandra G, Michael K (2010) Increased chromosomal radiosensitivity in women carrying BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations assessed with the G2 assay. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 76(4):1199–1205
Kote-Jarai Z, Salmon A, Mengitsu T, Copeland M, Ardern-Jones A, Locke I, Shanley S, Summersgill B, Lu YJ, Shipley J, Eeles R (2006) Increased level of chromosomal damage after irradiation of lymphocytes from BRCA1 mutation carriers. Br J Cancer 94(2):308–310
Baeyens A, Thierens H, Claes K, Poppe B, de Ridder L, Vral A (2004) Chromosomal radiosensitivity in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers. Int J Radiat Biol 80(10):745–756
Baeyens A, Thierens H, Claes K, Poppe B, Messiaen L, De Ridder L, Vral A (2002) Chromosomal radiosensitivity in breast cancer patients with a known or putative genetic predisposition. Br J Cancer 87(12):1379–1385
Barwell J, Pangon L, Georgiou A, Kesterton I, Langman C, Arden-Jones A, Bancroft E, Salmon A, Locke I, Kote-Jarai Z, Morris JR, Solomon E, Berg J, Docherty Z, Camplejohn R, Eeles R, Hodgson SV (2007) Lymphocyte radiosensitivity in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers and implications for breast cancer susceptibility. Int J Cancer 121(7):1631–1636
Meindl A (2002) Comprehensive analysis of 989 patients with breast or ovarian cancer provides BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation profiles and frequencies for the German population. Int J Cancer 97(4):472–480
Scott D, Barber JB, Levine EL, Burrill W, Roberts SA (1998) Radiation-induced micronucleus induction in lymphocytes identifies a high frequency of radiosensitive cases among breast cancer patients: a test for predisposition? Br J Cancer 77(4):614–620
Scott D, Barber JB, Spreadborough AR, Burrill W, Roberts SA (1999) Increased chromosomal radiosensitivity in breast cancer patients: a comparison of two assays. Int J Radiat Biol 75(1):1–10
Kotsopoulos J, Chen Z, Vallis KA, Poll A, Ainsworth P, Narod SA (2007) DNA repair capacity as a possible biomarker of breast cancer risk in female BRCA1 mutation carriers. Br J Cancer 96(1):118–125
Cadwell KK, Curwen GB, Tawn EJ, Winther JF, Boice JD Jr (2011) G2 checkpoint control and G2 chromosomal radiosensitivity in cancer survivors and their families. Mutagenesis 26(2):291–294
Poggioli T, Sterpone S, Palma S, Cozzi R, Testa A (2010) G0 and G2 chromosomal assays in the evaluation of radiosensitivity in a cohort of Italian breast cancer patients. J Radiat Res 51(5):615–619
Easton DF, Deffenbaugh AM, Pruss D, Frye C, Wenstrup RJ, Allen-Brady K, Tavtigian SV, Monteiro AN, Iversen ES, Couch FJ, Goldgar DE (2007) A systematic genetic assessment of 1,433 sequence variants of unknown clinical significance in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 breast cancer-predisposition genes. Am J Hum Genet 81(5):873–883
Kote-Jarai Z, Leongamornlert D, Saunders E, Tymrakiewicz M, Castro E, Mahmud N, Guy M, Edwards S, O’Brien L, Sawyer E, Hall A, Wilkinson R, Dadaev T, Goh C, Easton D, Goldgar D, Eeles R (2011) BRCA2 is a moderate penetrance gene contributing to young-onset prostate cancer: implications for genetic testing in prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer 105(8):1230–1234
Spearman AD, Sweet K, Zhou XP, McLennan J, Couch FJ, Toland AE (2008) Clinically applicable models to characterize BRCA1 and BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance. J Clin Oncol 26(33):5393–5400
Spurdle AB, Lakhani SR, Healey S, Parry S, Da Silva LM, Brinkworth R, Hopper JL, Brown MA, Babikyan D, Chenevix-Trench G, Tavtigian SV, Goldgar DE (2008) Clinical classification of BRCA1 and BRCA2 DNA sequence variants: the value of cytokeratin profiles and evolutionary analysis—a report from the kConFab Investigators. J Clin Oncol 26(10):1657–1663
Karchin R, Agarwal M, Sali A, Couch F, Beattie MS (2008) Classifying variants of undetermined significance in BRCA2 with protein likelihood ratios. Cancer Inform 6:203–216
Akbari MR, Zhang S, Fan I, Royer R, Li S, Risch H, McLaughlin J, Rosen B, Sun P, Narod SA (2011) Clinical impact of unclassified variants of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. J Med Genet 48(11):783–786
Farrugia DJ, Agarwal MK, Pankratz VS, Deffenbaugh AM, Pruss D, Frye C, Wadum L, Johnson K, Mentlick J, Tavtigian SV, Goldgar DE, Couch FJ (2008) Functional assays for classification of BRCA2 variants of uncertain significance. Cancer Res 68(9):3523–3531
Couch FJ, Rasmussen LJ, Hofstra R, Monteiro AN, Greenblatt MS, de Wind N (2008) Assessment of functional effects of unclassified genetic variants. Hum Mutat 29(11):1314–1326
Meindl A, Hellebrand H, Wiek C, Erven V, Wappenschmidt B, Niederacher D, Freund M, Lichtner P, Hartmann L, Schaal H, Ramser J, Honisch E, Kubisch C, Wichmann HE, Kast K, Deissler H, Engel C, Muller-Myhsok B, Neveling K, Kiechle M, Mathew CG, Schindler D, Schmutzler RK, Hanenberg H (2010) Germline mutations in breast and ovarian cancer pedigrees establish RAD51C as a human cancer susceptibility gene. Nat Genet 42(5):410–414
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all probands who participated in this study. This research was supported by a German Cancer Aid grant (RK Schmutzler, grant 107364). We thank Christina Ergang, Institute for Human Genetics, Bonn, Germany, for substantial technical contributions in the establishment of the assay and Karin Boss for constructive revision of the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical standards
Studies involving humans or human material are certified by the Ethics Commission of the University of Cologne, Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Alexandra A. Becker and Monika K. Graeser contributed equally as first authors. Ruthild G. Weber and Rita K. Schmutzler contributed equally as senior authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Becker, A.A., Graeser, M.K., Landwehr, C. et al. A 24-color metaphase-based radiation assay discriminates heterozygous BRCA2 mutation carriers from controls by chromosomal radiosensitivity. Breast Cancer Res Treat 135, 167–175 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2119-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-012-2119-0