Summary
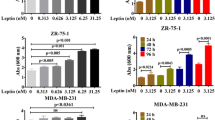
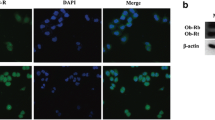
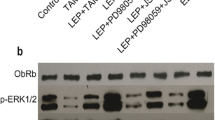
Obesity has been recognized as a risk factor for breast cancer. Adipocyte-derived leptin may play as a paracrine regulator on the growth of breast cancer cells. Expression of both leptin and its OB-Rb receptor was detected in human breast cancer ZR-75-1 cells and further induced by leptin, suggesting that both expression and message mediation of leptin were autoregulated by itself. With cell counting and MTT assay, we had observed leptin stimulated ZR-75-1 growth in dose- and time-dependent manners. To study what steps of cell cycle progression leptin may involve in, we analyzed cell-cycle profile with flow cytometric analysis, mRNA and protein expressions of four cell-cycle regulators with RT-PCR and Western blotting analysis. Under the treatment of leptin, the G1 arrest of cells was reduced accompanied with up-regulation of G1 phase-specific cyclin D1 and proto-oncogene c-Myc, but down-regulation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21WAF1/CIP1 and tumor suppressor p53. Furthermore, JAK2 inhibitor AG490, PI3K/Akt inhibitor Wortmannin, and MEK/ERK1/2 inhibitor PD98059 were efficiently prevented leptin-promoted cell growth. Effect of cooperation between leptin and estrogen on ZR-75-1 growth had been observed. Collectively, the results showed that the proliferative effect of leptin on ZR-75-1 was associated with the up-regulation of cyclin D1 and c-Myc and down-regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and p21WAF1/CIP1 plausibly through a hypothesized JAK2-PI3K/Akt-MEK/ERK pathway. The leptin- and OB-Rb-expressing capability of ZR-75-1 created a possible autocrine control of leptin, in which signal could be effectively amplified by itself, on cell growth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lahmann PH, Hoffmann K, Allen N, van Gils CH, Khaw KT, Tehard B, Berrino F, Tjonneland A, Bigaard J, Olsen A, Overvad K, Clavel-Chapelon F, Nagel G, Boeing H, Trichopoulos D, Economou G, Bellos G, Palli D, Tumino R, Panico S, Sacerdote C, Krogh V, Peeters PH, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Lund E, Ardanaz E, Amiano P, Pera G, Quiros JR, Martinez C, Tormo MJ, Wirfalt E, Berglund G, Hallmans G, Key TJ, Reeves G, Bingham S, Norat T, Biessy C, Kaaks R, Riboli E, Body size and breast cancer risk: findings from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer And Nutrition (EPIC) Int J Cancer 111: 762–771, 2004
Dumitrescu RG, Cotarla I, Understanding breast cancer risk – where do we stand in 2005? J Cell Mol Med 9: 208–221, 2005
Kroenke CH, Chen WY, Rosner B, Holmes MD, Weight, weight gain, and survival after breast cancer diagnosis J Clin Oncol 23: 1370–1378, 2005
Key TJ, Appleby PN, Reeves GK, Roddam A, Dorgan JF, Longcope C, Stanczyk FZ, Stephenson HE Jr, Falk RT, Miller R, Schatzkin A, Allen DS, Fentiman IS, Key TJ, Wang DY, Dowsett M, Thomas HV, Hankinson SE, Toniolo P, Akhmedkhanov A, Koenig K, Shore RE, Zeleniuch-Jacquotte A, Berrino F, Muti P, Micheli A, Krogh V, Sieri S, Pala V, Venturelli E, Secreto G, Barrett-Connor E, Laughlin GA, Kabuto M, Akiba S, Stevens RG, Neriishi K, Land CE, Cauley JA, Kuller LH, Cummings SR, Helzlsouer KJ, Alberg AJ, Bush TL, Comstock GW, Gordon GB, Miller SR, Longcope C, Endogenous Hormones Breast Cancer Collaborative Group: Body mass index, serum sex hormones, and breast cancer risk in postmenopausal women J Natl Cancer Inst95: 1218–1226, 2003
McTiernan A, Rajan KB, Tworoger SS, Irwin M, Bernstein L, Baumgartner R, Gilliland F, Stanczyk FZ, Yasui Y, Ballard-Barbash R, Adiposity and sex hormones in postmenopausal breast cancer survivors J Clin Oncol 21: 1961–1966, 2003
Misso ML, Jang C, Adams J, Tran J, Murata Y, Bell R, Boon WC, Simpson ER, Davis SR, Adipose aromatase gene expression is greater in older women and is unaffected by postmenopausal estrogen therapy Menopause 12: 210–215, 2005
Van Gaal LF, Wauters MA, Mertens IL, Considine RV, De Leeuw IH, Clinical endocrinology of human leptin Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord23:Suppl 1: 29–36, 1999
Tessitore L, Vizio B, Jenkins O, De Stefano I, Ritossa C, Argiles JM, Benedetto C, Mussa A, Leptin expression in colorectal and breast cancer patients Int J Mol Med5: 421–426, 2000
Cleary MP, Phillips FC, Getzin SC, Jacobson TL, Jacobson MK, Christensen TA, Juneja SC, Grande JP, Maihle NJ, Genetically obese MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lep(ob)Lep(ob) female mice do not develop mammary tumors Breast Cancer Res Treat77: 205–215, 2003
Cleary MP, Juneja SC, Phillips FC, Hu X, Grande JP, Maihle NJ, Leptin receptor-deficient MMTV-TGF-alpha/Lepr(db)Lepr(db) female mice do not develop oncogene-induced mammary tumors Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 229: 182–193, 2004
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M, Leopold L, Friedman JM, Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue Nature 372: 425–432, 1994
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, Deng N, Culpepper J, Devos R, Richards GJ, Campfield LA, Clark FT, Deeds J, Muir C, Sanker S, Moriarty A, Moore KJ, Smutko JS, Mays GG, Wool EA, Monroe CA, Tepper RI: Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R Cell 83:1263–1271, 1995
Lee GH, Proenca R, Montez JM, Carroll KM, Darvishzadeh JG, Lee JI, Friedman JM, Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice Nature 379: 632–635, 1996
Fei H, Okano HJ, Li C, Lee GH, Zhao C, Darnell R, Friedman JM, Anatomic localization of alternatively spliced leptin receptors (Ob-R) in mouse brain and other tissues Proc Natl Acad Sci USA94: 7001–7005, 1997
Hegyi K, Fülöp K, Kovács K, Tóth S, Falus A, Leptin-induced signal transduction pathways Cell Biol Int 28: 159–169, 2004
Smith-Kirwin SM, O’Connor DM, De Johnston J, Lancey ED, Hassink SG, Funanage VL, Leptin expression in human mammary epithelial cells and breast milk J Clin Endocrinol Metab83: 1810–1813, 1998
O’Brien SN, Welter BH, Price TM, Presence of leptin in breast cell lines and breast tumors Biochem Biophys Res Commun 259 695–698, 1999
Ishikawa M, Kitayama J, Nagawa H, Enhanced expression of leptin and leptin receptor (OB-R) in human breast cancer Clin Cancer Res10: 4325–4331, 2004
Dieudonne MN, Machinal-Quelin F, Serazin-Leroy V, Leneveu MC, Pecquery R, Giudicelli Y, Leptin mediates a proliferative response in human MCF7 breast cancer cells Biochem Biophys Res Commun293: 622–628, 2002
Garofalo C, Sisci D, Surmacz E, Leptin interferes with the effects of the antiestrogen ICI 182,780 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells Clin Cancer Res10: 6466–6475, 2004
Yin N, Wang D, Zhang H, Yi X, Sun X, Shi B, Wu H, Wu G, Wang X, Shang Y, Molecular mechanisms involved in the growth stimulation of breast cancer cells by leptin Cancer Res64: 5870–5875, 2004
Hu X, Juneja SC, Maihle NJ, Cleary MP, Leptin – a growth factor in normal and malignant breast cells and for normal mammary gland development J Natl Cancer Inst94: 1704–1711, 2002
Laud K, Gourdou I, Pessemesse L, Peyrat JP, Djiane J, Identification of leptin receptors in human breast cancer: functional activity in the T47-D breast cancer cell line Mol Cell Endocrinol188: 219–226, 2002
Vona-Davis L, Skinner H, Jackson B, Riggs D, Somasundar P, McFadden DW, Leptin activates MAPK signaling in human breast and prostate cancer J Surg Res 114: 300–301, 2003
Okumura M, Yamamoto M, Sakuma H, Kojima T, Maruyama T, Jamali M, Cooper DR, Yasuda K, Leptin and high glucose stimulate cell proliferation in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells: reciprocal involvement of PKC-alpha and PPAR expression Biochim Biophys Acta1592: 107–116, 2002
Onuma M, Bub JD, Rummel TL, Iwamoto Y, Prostate cancer cell-adipocyte interaction: leptin mediates androgen-independent prostate cancer cell proliferation through c-Jun NH2-terminal kinaseJ Biol Chem278: 42660–42667, 2003
Somasundar P, Frankenberry KA, Skinner H, Vedula G, McFadden DW, Riggs D, Jackson B, Vangilder R, Hileman SM, Vona-Davis LC, Prostate cancer cell proliferation is influenced by leptin J Surg Res118: 71–81, 2004
Liu Y, Ludes-Meyers J, Zhang Y, Munoz-Medellin D, Kim HT, Lu C, Ge G, Schiff R, Hilsenbeck SG, Osborne CK, Brown PH, Inhibition of AP-1 transcription factor causes blockade of multiple signal transduction pathways and inhibits breast cancer growth Oncogene21: 7680–7689, 2002
Buettner R, Mora LB, Jove R, Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention Clin Cancer Res8: 945–954, 2002
Yu Q, Geng Y, Sicinski P, Specific protection against breast cancers by cyclin D1 ablation Nature411: 1017–1021, 2001
Somasundar P, Yu AK, Vona-Davis L, McFadden DW, Differential effects of leptin on cancer in vitro J Surg Res113: 50–55, 2003
Lagger G, Doetzlhofer A, Schuettengruber B, Haidweger E, Simboeck E, Tischler J, Chiocca S, Suske G, Rotheneder H, Wintersberger E, Seiser C, The tumor suppressor p53 and histone deacetylase 1 are antagonistic regulators of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21/WAF1/CIP1 gene Mol Cell Biol23: 2669–2679, 2003
Catalano S, Marsico S, Giordano C, Mauro L, Rizza P, Panno ML, Andò S, Leptin enhances, via AP-1, expression of aromatase in the MCF-7 cell line J Biol Chem 278: 28668–28676, 2003
O’Neil JS, Burow ME, Green AE, McLachlan JA, Henson MC, Effects of estrogen on leptin gene promoter activation in MCF-7 breast cancer and JEG-3 choriocarcinoma cells: selective regulation via estrogen receptors α and β Mol Cell Endocrinol176: 67–75, 2001
Somasundar P, McFadden DW, Hileman SM, Vona-Davis L: Leptin is a growth factor in cancer J Surg Res116: 337–349, 2004
Marttunen MB, Andersson S, Hietanen P, Karonen SL, Koistinen HA, Koivisto VA, Tiitinen A, Ylikorkala O, Antiestrogenic tamoxifen and toremifene increase serum leptin levels in postmenopausal breast cancer patients Maturitas35: 175–179, 2000
Lambrinoudaki I, Christodoulakos G, Panoulis C, Botsis D, Rizos D, Augoulea A, Creatsas G, Determinants of serum leptin levels in healthy postmenopausal women J Endocrinol Invest26: 1225–1230, 2003
Petridou E, Papadiamantis Y, Markopoulos C, Spanos E, Dessypris N, Trichopoulos D, Leptin and insulin growth factor I in relation to breast cancer (Greece) Cancer Causes Control11: 383–388, 2000
Rose DP, Gilhooly EM, Nixon DW, Adverse effects of obesity on breast cancer prognosis, and the biological actions of leptin (review) Int J Oncol21: 1285–1292, 2002
Menu E, Kooijman R, Van Valckenborgh E, Asosingh K, Bakkus M, Van Camp B, Vanderkerken K, Specific roles for the PI3K and MEK-ERK pathway in IGF-1-stimulated chemotaxis, VEGF secretion and proliferation of multiple myeloma cells: study in the 5T33MM model Br J Cancer90:1076–1083, 2004
Duan C, Li M, Rui L, SH2-B promotes insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1)- and IRS2-mediated activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in response to leptin J Biol Chem279: 43684–43691, 2004
Sahu A Minireview: a hypothalamic role in energy balance with special emphasis on leptin Endocrinology145: 2613–2620, 2004
Fernando RI, Wimalasena J, Estradiol abrogates apoptosis in breast cancer cells through inactivation of BAD: Ras-dependent nongenomic pathways requiring signaling through ERK and Akt Mol Biol Cell 15: 3266–3284, 2004
Catalano S, Mauro L, Marsico S, Giordano C, Rizza P, Rago V, Montanaro D, Maggiolini M, Panno ML, Andò S, Leptin induces, via ERK1/ERK2 signal, functional activation of estrogen receptor alpha in MCF-7 cells J Biol Chem. 279: 19908–19915, 2004
Mawson A, Lai A, Carroll JS, Sergio CM, Mitchell CJ, Sarcevic B, Estrogen and insulin/IGF-1 cooperatively stimulate cell cycle progression in MCF-7 breast cancer cells through differential regulation of c-Myc and cyclin D1 Mol Cell Endocrinol229: 161–173, 2005
Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA, Cyclins and breast cancer J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 9:95–104, 2004
Deming SL, Nass SJ, Dickson RB, Trock BJ, C-myc amplification in breast cancer: a meta-analysis of its occurrence and prognostic relevance Br J Cancer83: 1688–1695, 2000
Liao DJ, Natarajan G, Deming SL, Jamerson MH, Johnson M, Chepko G, Dickson RB, Cell cycle basis for the onset and progression of c-Myc-induced, TGFalpha-enhanced mouse mammary gland carcinogenesis Oncogene 19: 1307–1317, 2000
Oswald F, Lovec H, Moroy T, Lipp M, E2F-dependent regulation of human MYC: trans-activation by cyclins D1 and A overrides tumour suppressor protein functions Oncogene 9: 2029–2036, 1994
Carroll JS, Swarbrick A, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL, Mechanisms of growth arrest by c-myc antisense oligonucleotides in MCF-7 breast cancer cells: implications for the antiproliferative effects of antiestrogens Cancer Res62: 3126–3131, 2002
Mitchell KO, el-Deiry WS, Overexpression of c-Myc inhibits p21WAF1/CIP1 expression and induces S-phase entry in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-sensitive human cancer cells Cell Growth Differ10: 223–230, 1999
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R, Beach D, p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinasesNature366:701–704, 1993
Mukherjee S, Conrad SE, c-Myc suppresses p21WAF1/CIP1 expression during estrogen signaling and antiestrogen resistance in human breast cancer cellsJ Biol Chem 280: 17617–17625, 2005
Seoane J, Le HV, Massague J, Myc suppression of the p21(Cip1) Cdk inhibitor influences the outcome of the p53 response to DNA damageNature 419: 729–734, 2002
Vaque JP, Navascues J, Shiio Y, Laiho M, Ajenjo N, Mauleon I, Matallanas D, Crespo P, Leon J, Myc antagonizes Ras-mediated growth arrest in leukemia cells through the inhibition of the Ras-ERK-p21Cip1 pathway J Biol Chem280: 1112–1122, 2005
Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW, Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy Cell 108: 153–164, 2002
el-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer WE, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B, WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression Cell 75: 817–825, 1993
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Mackay Memorial Hospital and by grants from National Science Council, Republic of China, NSC 91-2313-B-002-387 to I.-C. G., NSC 92-2314-B-195-020 and NSC 93-2314-B-195-026 to C.-L. L., and NSC 91-2320-B-002-160 to K.-J. C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, C., Chang, YC., Liu, CL. et al. Leptin-induced growth of human ZR-75-1 breast cancer cells is associated with up-regulation of cyclin D1 and c-Myc and down-regulation of tumor suppressor p53 and p21WAF1/CIP1 . Breast Cancer Res Treat 98, 121–132 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9139-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-005-9139-y