Abstract
For data preprocessing and artefact removal in an ERP experiment we were confronted with the question how blink artefacts can be detected reliably, even in the absence of usable electrooculogram (EOG) data. We propose an objective and quantitative method for the automatic detection of eyeblink artefacts from raw data using extreme value statistics, with a p-value acting as a threshold parameter. For testing the method, we used 29 channel electroencephalogram recordings of 55 healthy subjects. A total 7,700 s of EEG were analysed. The proposed method was found to detect blink artefacts reliably, showing that extreme value statistics can be employed to detect blink artefacts, even in the absence of EOG recordings.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This is the case for a uniform distribution, for example, but not for an amplifier running into saturation.
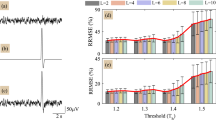
The pROC-software issued a warning about possible unexpected results with different specificity levels, but we see currently no method to evaluate their correctness as the manual offers only a short explanation but no solution to the problem.
References
Anderer P, Roberts S, Schlögl A, Gruber G, Klösch G, Herrmann W, Rappelsberger P, Filz O, Barbanoj M, Dorffner G, Saletu B (1999) Artifact processing in computerized analysis of sleep EEG—a review. Neuropsychobiology 40:150–157
Berg P (1986) The residual after correcting event-related potentials for blink artifacts. Psychophysiology 23(3):354–364
Croft R, Barry R (2000) Removal of ocular artifact from the EEG: a review. Neurophysiol Clin 30(1):5–19
Eaton JW, Bateman D, Hauberg S (2008) GNU octave manual version 3. Network Theory Limited, London
Elul R (1969) Gaussian behavior of the electroencephalogram: changes during performance of mental task. Sci 164(3877):328–331
Gao J, Yang Y, Lin P, Wang P, Zheng C (2010) Automatic removal of eye-movement and blink artifacts from EEG signals. Brain Topogr 23:105–114. doi:10.1007/s10548-009-0131-4
Gasser T, Sroka L, Möcks J (1986) The correction of EOG artifacts by frequency dependent and frequency independent methods. Psychophysiology 23(6):704–712
Ghandeharion H, Erfanian A (2010) A fully automatic ocular artifact suppression from EEG data using higher order statistics: improved performance by wavelet analysis. Med Eng Phys 32:720–729
Girton D, Kamiya J (1973) A simple on-line technique for removing eye movement artifacts from the EEG. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 34(2):212–216
Gratton G, Coles MG, Donchin E (1983) A new method for off-line removal of ocular artifact. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 55(4):468–484
Gumbel E (2004) Statistics of extremes. Dover books on mathematics. Dover Publications, Mineola
Hillyard SA, Galambos R (1970) Eye movement artifact in the CNV. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 28(2):173–182
Hoffmann S, Falkenstein M (2008) The correction of eye blink artefacts in the EEG: a comparison of two prominent methods. PLoS ONE 3(8):e3004
Ille N, Berg P, Scherg M (2002) Artifact correction of the ongoing EEG using spatial filters based on artifact and brain signal topographies. J Clin Neurophysiol 19(2):113–124
Joyce CA, Gorodnitsky IF, Kutas M (2004) Automatic removal of eye movement and blink artifacts from EEG data using blind component separation. Psychophysiology 41(2):313–325
Jung T-P, Humphries C, Lee T-W, Makeig S, Mckeown M, Iragui V, Sejnowski T (1998) Removing electroencephalographic artifacts: comparison between ICA and PCA. In: Neural networks for signal processing VIII, Proceedings of the 1998 IEEE signal processing cociety workshop, pp 63–72
Jung T-P, Makeig S, Humphries C, Lee T-W, McKeown MJ, Iragui V, Sejnowski TJ (2000) Removing electroencephalographic artifacts by blind source separation. Psychophysiology 37(2):163–178
Kawabata N (1976) Test of statistical stability of the electroencephalogram. Biol Cybern 22:235–238. doi:10.1007/BF00365089
Kenemans JL, Molenaar PC, Verbaten MN, Slangen JL (1991) Removal of the ocular artifact from the EEG: a comparison of time and frequency domain methods with simulated and real data. Psychophysiology 28(1):114–121
Kotz S, Nadarajah S (2000) Extreme value distributions. Imperial College Press, London
Lins O, Picton T, Berg P, Scherg M (1993) Ocular artifacts in recording eegs and event-related potentials ii: source dipoles and source components. Brain Topogr 6:65–78
R Development Core Team (2011) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N, Lisacek F, Sanchez J-C, Müller M (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12:77
Schlögl A, Keinrath C, Zimmermann D, Scherer R, Leeb R, Pfurtscheller G (2007) A fully automated correction method of EOG artifacts in EEG recordings. Clin Neurophysiol 118(1):98–104
Skrandies W, Shinoda H (2012) Topographical changes of ERPs related to human semantic learning. Int J Psychophysiol 85(3):337
Sugimoto H, Ishii N, Iwata A, Suzumura N, Tomita T (1978) On the stationarity and normality of the electroencephalographic data during sleep stages. Comput Progr Biomed 8(3–4):224–234
Verleger R (1993) Valid identification of blink artefacts: are they larger than 50 μv in EEG records?. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 87(6):354–363
Vigário RN (1997) Extraction of ocular artefacts from EEG using independent component analysis. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 103(3):395–404
Wallstrom GL, Kass RE, Miller A, Cohn JF, Fox NA (2004) Automatic correction of ocular artifacts in the EEG: a comparison of regression-based and component-based methods. Int J Psychophysiol 53(2):105–119
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Mr. Benjamin Würzer for helping with data recording and visually screening the EEG data for artefacts. All computations for this article were performed with the following free open source software packages: GNU-Octave (Eaton et al. 2008), pROC (Robin et al. 2011), and GNU-R (R Development Core Team 2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klein, A., Skrandies, W. A Reliable Statistical Method to Detect Eyeblink-Artefacts from Electroencephalogram Data Only. Brain Topogr 26, 558–568 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-013-0281-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10548-013-0281-2