Abstract
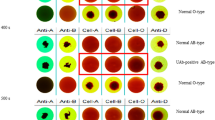
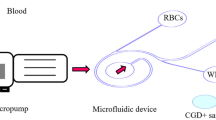
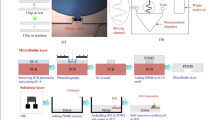
The clinical importance of blood group (BG) antigens is related to their ability to induce immune antibodies that can cause hemolysis. Yet, ABO and D (Rh) are still considered to be the key antigens for healthy blood transfusion and secondary antigens are the next priority. Serological typing is the most widely used typing method. Rapid and accurate blood grouping plays an important role in some clinical conditions, rather than conventional techniques. Hence, developing a simple and economical model for rapid blood grouping would facilitate these tests. In recent decades, paper-based microfluidics such as μPADs has gained much interest in wide application areas such as point-of-care diagnostic. In this study, we evaluated μPADs that are performed for blood grouping and its recent progress. A comprehensive literature search was performed using databases including PUBMED, SCOPUS, Web of Science and Google Scholar. Keywords were blood grouping or typing, paper analytical device, rapid test, etc. After investigation of search results, 16 papers from 2010 to 2020 were included. Further information in detail was classified in Table 1. Generally, two principles for blood typing μPADs are introduced. The lateral chromatographic flow method and the vertical flow-through method that detects BG in a visual-based manner. To detect results with acceptable clarity many factors and challenges like paper, blood sample, buffer, Ab and RBC interaction and also μPADs stability need to be considered, which are discussed. In conclusion, the simplicity, stability, cheapness, portability and biocompatibility of μPADs for blood grouping confirming its utility and also they have the capability to robust, universal blood-grouping platform.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Al-Tamimi et al., Validation of paper-based assay for rapid blood typing. Anal. Chem. 84(3), 1661–1668 (2012)
N. Ansari, et al., A portable microfluidic paper-based analytical device for blood detection and typing assay. Aust. J. Forensic Sci. 1–12 (2020)
P. Arosio et al., On the role of salt type and concentration on the stability behavior of a monoclonal antibody solution. Biophys. Chem. 168–169, 19–27 (2012)
S. Bhattacharya, et al., Paper Microfluidics, (Springer 2019)
J. Casals-Terré et al., Enhanced fully cellulose based forward and reverse blood typing assay. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 108(2), 439–450 (2020)
J. Casals-Terré et al., Novel applications of nonwood cellulose for blood typing assays. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 107(5), 1533–1541 (2019)
L. S. Chitty, M. Kroese, Realising the promise of non-invasive prenatal testing, (British Medical Journal Publishing Group 2015)
M. Diez-Silva et al., Shape and biomechanical characteristics of human red blood cells in health and disease. MRS Bulletin/materials Research Society 35(5), 382 (2010)
L. Guan et al., A preliminary study on the stabilization of blood typing antibodies sorbed into paper. Cellulose 21(1), 717–727 (2014a)
L. Guan et al., Barcode-like paper sensor for smartphone diagnostics: An application of blood typing. Anal. Chem. 86(22), 11362–11367 (2014b)
J. E. Hall, M. E. Hall, Guyton and Hall textbook of medical physiology e-Book, (Elsevier Health Sciences, 2020)
Hangzhou AllTest Biotech Co. from http://www.alltests.com.cn/EN/ProductMain.asp?cclassid=1&classid=1
D. M. Harmening, D. Firestone, The ABO blood group system. Modern Blood Banking & Amp; Transfusion Practices, 6th ed. (Philadelphia: FA Davis Company, 2012), p. 119–149
C.A. Henderson et al., Activity and longevity of antibody in paper-based blood typing diagnostics. Front. Chem. 6, 193 (2018)
M.J. Hertaeg et al., A rapid paper-based blood typing method from droplet wicking. Analyst 146(3), 1048–1056 (2021)
Z. Huang et al., The role of polyaminoamide-epichlorohydrin (PAE) on antibody longevity in bioactive paper. Colloids Surf., B 158, 197–202 (2017)
In vitro flow rapid test system from http://www.mtc-invitro.de/products/invitroflow-rapid-test-system
P. Jarujamrus et al., Mechanisms of red blood cells agglutination in antibody-treated paper. Analyst 137(9), 2205–2210 (2012)
J. Jopling et al., Reference ranges for hematocrit and blood hemoglobin concentration during the neonatal period: data from a multihospital health care system. Pediatrics 123(2), e333–e337 (2009)
R. Junker et al., Point-of-care testing in hospitals and primary care. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 107(33), 561 (2010)
M.S. Khan et al., Paper diagnostic for instantaneous blood typing. Anal. Chem. 82(10), 4158–4164 (2010)
K. Landsteiner, Zur Kenntnis der antifermentativen, lytischen und agglutinierenden Wirkungen des Blutserums und der Lymphe. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. 27, 357–362 (1900)
L. Li et al., Control performance of paper-based blood analysis devices through paper structure design. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 6(23), 21624–21631 (2014a)
L. Li et al., A study of the transport and immobilisation mechanisms of human red blood cells in a paper-based blood typing device using confocal microscopy. Analyst 138(17), 4933–4940 (2013)
M. Li et al., based device for rapid typing of secondary human blood groups. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 406(3), 669–677 (2014b)
M. Li et al., Paper-Based Blood Typing Device That Reports Patient’s Blood Type “in Writing.” Angew. Chem. 124(22), 5593–5597 (2012)
W.Y. Lim et al., Microfluidic paper-based analytical devices for potential use in quantitative and direct detection of disease biomarkers in clinical analysis. J. Chromatogr. B 1060, 424–442 (2017)
A.W. Martinez et al., Patterned paper as a platform for inexpensive, low-volume, portable bioassays. Angew. Chem. 119(8), 1340–1342 (2007)
A. Mujahid, F.L. Dickert, Blood group typing: from classical strategies to the application of synthetic antibodies generated by molecular imprinting. Sensors 16(1), 51 (2016)
L. Neimo, Papermaking Chemistry: Papermaking Science and Technology, book4, Jyväskylä, (Finland: Fapet Oy 1999)
J. Noiphung et al., A novel paper-based assay for the simultaneous determination of Rh typing and forward and reverse ABO blood groups. Biosens. Bioelectron. 67, 485–489 (2015)
C. Parolo, A. Merkoçi, based nanobiosensors for diagnostics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42(2), 450–457 (2013)
S. Parween et al., Cross-linked chitosan biofunctionalized paper-based microfluidic device towards long term stabilization of blood typing antibodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 163, 1233–1239 (2020)
R.W. Peeling et al., Rapid tests for sexually transmitted infections (STIs): the way forward. Sexually Transmitted Infections 82(suppl 5), v1–v6 (2006)
R. Pelton, Bioactive paper provides a low-cost platform for diagnostics. TrAC, Trends Anal. Chem. 28(8), 925–942 (2009)
I. Pereiro et al., Shake It or Shrink It: Mass Transport and Kinetics in Surface Bioassays Using Agitation and Microfluidics. Anal. Chem. 92(15), 10187–10195 (2020)
N. Quraishy, S. Sapatnekar, Advances in blood typing. Advances in Clinical Chemistry, Elsevier. 77, 221–269 (2016)
RBTT (Rapid Blood Type Test) from https://ifworlddesignguide.com/entry/289929-rbttrapid-blood-type-test
T. Songjaroen, W. Laiwattanapaisal, Simultaneous forward and reverse ABO blood group typing using a paper-based device and barcode-like interpretation. Anal. Chim. Acta 921, 67–76 (2016)
T. Songjaroen et al., A simple and low-cost portable paper-based ABO blood typing device for point-of-care testing. J. Immunoassay Immunochem. 39(3), 292–307 (2018)
J.R. Storry et al., International society of blood transfusion working party on red cell immunogenetics and blood group terminology: report of the Dubai, Copenhagen and Toronto meetings. Vox Sang. 114(1), 95–102 (2019)
J. Su et al., Engineering paper as a substrate for blood typing bio-diagnostics. Cellulose 19(5), 1749–1758 (2012)
W.L. Then et al., The detection of blood group phenotypes using paper diagnostics. Vox Sang. 108(2), 186–196 (2015)
J. Wang, et al., Wet-strength resins and surface properties affect paper-based antibody assays. Appita: Technology, Innovation, Manufacturing, Environment 63(1), 32 (2010)
J. Wang et al., Effects of Temperature and Relative Humidity on the Stability of Paper-Immobilized Antibodies. Biomacromol 13(2), 559–564 (2012)
P. Yager et al., Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature 442(7101), 412–418 (2006)
N. Yeow et al., based assay for red blood cell antigen typing by the indirect antiglobulin test. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 408(19), 5231–5238 (2016)
R. Yousuf et al., Study on ABO and RhD blood grouping: Comparison between conventional tile method and a new solid phase method (InTec Blood Grouping Test Kit). Malays. J. Pathol. 40(1), 27–32 (2018)
H. Zhang, et al., A dye-assisted paper-based point-of-care assay for fast and reliable blood grouping. Science Translational Medicine 9(381): eaaf9209 (2017)
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the authorship, research and/or publication of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship, research and/or publication of this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebrahimi Fana, S., Paknejad, M. & Aminian, M. Paper based analytical devices for blood grouping: a comprehensive review. Biomed Microdevices 23, 34 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00569-w
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-021-00569-w