Abstract
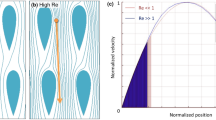
Deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) is a microfluidic technique for size fractionation of particles/cells in continuous flow with a great potential for biological and clinical applications. Growing interest of DLD devices in enabling high-throughput operation for practical applications, such as circulating tumor cell (CTC) separation, necessitates employing higher flow rates, leading to operation at moderate to high Reynolds number (Re) regimes. Recently, it has been shown that symmetric airfoil shaped pillars with neutral angle-of-attack (AoA) can be used for high-throughput design of DLD devices due to their mitigation of vortex effects and preservation of flow symmetry under high Re conditions. While high-Re operation with symmetric airfoil shaped pillars has been established, the effect of AoAs on the DLD performance has not been investigated. In this paper, we have characterized the airfoil DLD device with various AoAs. The transport behavior of microparticles has been observed and analyzed with various AoAs in realistic high-Re. Furthermore, we have modeled the flow fields and anisotropy in a representative airfoil pillar array, for both positive and negative AoA configurations. Unlike the conventional DLD device, lateral displacement has been suppressed with +5° and + 15° AoA configurations regardless of particle sizes. On the other hand, stronger lateral displacement has been seen with −5° and − 15° AoAs. This can be attributed to growing flow anisotropy as Re climbs, and significant expansion or compression of streamlines between airfoils with AoAs. The findings in this study can be utilized for the design and optimization of airfoil DLD microfluidic devices with various AoAs.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. H. Abbott and A. E. Von Doenhoff, Theory of wing sections, including a summary of airfoil data, Corr. , ed. New York,: Dover Publications (1959)
M. Al-Fandi, M. Al-Rousan, M.A.K. Jaradat, L. Al-Ebbini, New Design for the Separation of microorganisms using microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement. Robot. Comput. Integr. Manuf. 27(2), 237–244 (2011)
J.P. Beech, P. Jönsson, J.O. Tegenfeldt, Tipping the Balance of Deterministic Lateral Displacement Devices Using Dielectrophoresis. Lab Chip 9(18), 2698 (2009)
J.P. Beech, S.H. Holm, K. Adolfsson, J.O. Tegenfeldt, Sorting Cells by Size, Shape and Deformability. Lab Chip 12(6), 1048 (2012)
Y. Chen, E.S. Abrams, T.C. Boles, J.N. Pedersen, H. Flyvbjerg, R.H. Austin, J.C. Sturm, Concentrating Genomic Length DNA in a Microfabricated Array. Phys. Rev. Lett. 114(19), 198303 (2015)
C.I. Civin, T. Ward, A.M. Skelley, K. Gandhi, Z. Peilun Lee, C.R. Dosier, J.L. D’Silva, Y. Chen, M. Kim, J. Moynihan, X. Chen, L. Aurich, S. Gulnik, G.C. Brittain, D.J. Recktenwald, R.H. Austin, J.C. Sturm, Automated leukocyte processing by microfluidic deterministic lateral displacement: Automated microfluidic blood leukocyte processing. Cytometry 89(12), 1073–1083 (2016)
R. Devendra, G. Drazer, Gravity driven deterministic lateral displacement for particle separation in microfluidic devices. Anal. Chem. 84(24), 10621–10627 (2012)
Dincau, B., Aghilinejad, A., Kim, J.-H., and Chen, X., Characterizing the High Reynolds Number Regime for Deterministic Lateral Displacement (DLD) Devices. Volume 10: Micro- and Nano-Systems Engineering and Packaging, ASME, Tampa, Florida, USA, p. V010T13A033 (2017)
B.M. Dincau, A. Aghilinejad, T. Hammersley, X. Chen, J.-H. Kim, Deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) in the high Reynolds number regime: High-throughput and dynamic separation characteristics. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 22(6) (2018a)
B.M. Dincau, A. Aghilinejad, X. Chen, S.Y. Moon, J.-H. Kim, Vortex-Free High-Reynolds Deterministic Lateral Displacement (DLD) via Airfoil Pillars. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 22(12), 137 (2018b)
L.R. Huang, Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 304(5673), 987–990 (2004)
M. Jiang, A.D. Mazzeo, G. Drazer, Centrifuge-Based Deterministic Lateral Displacement Separation. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 20(1), 17 (2016)
K. Loutherback, J. D’Silva, L. Liu, A. Wu, R.H. Austin, J.C. Sturm, Deterministic Separation of Cancer Cells from Blood at 10 ML/Min. AIP Adv. 2(4), 042107 (2012)
Y.S. Lubbersen, M.A.I. Schutyser, R.M. Boom, Suspension separation with deterministic ratchets at moderate Reynolds numbers. Chem. Eng. Sci. 73, 314–320 (2012)
H. Okano, T. Konishi, T. Suzuki, T. Suzuki, S. Ariyasu, S. Aoki, R. Abe, M. Hayase, Enrichment of Circulating Tumor Cells in Tumor-Bearing Mouse Blood by a Deterministic Lateral Displacement Microfluidic Device. Biomed. Microdevices 17(3), 59 (2015)
E. Pariset, C. Parent, Y. Fouillet, B. François, N. Verplanck, F. Revol-Cavalier, A. Thuaire, V. Agache, Separation of biological particles in a modular platform of cascaded deterministic lateral displacement modules. Sci. Rep. 8(1), 17762 (2018)
S. Ranjan, K.K. Zeming, R. Jureen, D. Fisher, Y. Zhang, DLD pillar shape Design for Efficient Separation of spherical and non-spherical bioparticles. Lab Chip 14(21), 4250–4262 (2014)
R. Vernekar, T. Krüger, K. Loutherback, K. Morton, W.D. Inglis, Anisotropic permeability in deterministic lateral displacement arrays. Lab Chip 17(19), 3318–3330 (2017)
B.H. Wunsch, J.T. Smith, S.M. Gifford, C. Wang, M. Brink, R.L. Bruce, R.H. Austin, G. Stolovitzky, Y. Astier, Nanoscale lateral displacement arrays for the separation of Exosomes and colloids down to 20 nm. Nat. Nanotech. 11(11), 936–940 (2016)
B.H. Wunsch, S.-C. Kim, S.M. Gifford, Y. Astier, C. Wang, R.L. Bruce, J.V. Patel, E.A. Duch, S. Dawes, G. Stolovitzky, J.T. Smith, Gel-on-a-Chip: Continuous, velocity-dependent DNA separation using Nanoscale lateral displacement. Lab Chip 19(9), 1567–1578 (2019)
M. Xavier, S.H. Holm, J.P. Beech, D. Spencer, J.O. Tegenfeldt, R.O.C. Oreffo, H. Morgan, Label-free enrichment of primary human skeletal progenitor cells using deterministic lateral displacement. Lab Chip 19(3), 513–523 (2019)
K.K. Zeming, T. Salafi, C.-H. Chen, Y. Zhang, Asymmetrical deterministic lateral displacement gaps for dual functions of enhanced separation and throughput of red blood cells. Sci. Rep. 6(1) (2016a)
K.K. Zeming, N.V. Thakor, Y. Zhang, C.-H. Chen, Real-time modulated nanoparticle separation with an ultra-large dynamic range. Lab Chip 16(1), 75–85 (2016b)
Z. Zhang, E. Henry, G. Gompper, D.A. Fedosov, Behavior of Rigid and Deformable Particles in Deterministic Lateral Displacement Devices with Different Post Shapes. J. Chem. Phys. 143(24), 243145 (2015)
Acknowledgements
JK acknowledges partial financial support from the National Science Foundation (NSF CBET- 1707056). XC acknowledges partial financial support from the National Science Foundation (NSF ECCS- 1917299).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2227 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahasan, K., Landry, C.M., Chen, X. et al. Effect of angle-of-attacks on deterministic lateral displacement (DLD) with symmetric airfoil pillars. Biomed Microdevices 22, 42 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00496-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-020-00496-2