Abstract
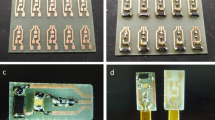
This paper reports and analyzes the feasibility study of a parylene-on-oil encapsulation packaging method of pressure sensors targeted for long-term implantation. Commercial barometric digital-output pressure sensors are enclosed in silicone oil and then encapsulated in situ with parylene-C or –D (PA-C, PA-D) chemical vapor deposition. Experimentally, sensors encapsulated with 30,000 cSt silicone oil and 27 μm PA-D show good performance for 6 weeks in 77 °C saline with >99 % of original sensitivity, corresponding to an extrapolated lifetime of around 21 months in 37 °C saline. This work shows that, with proper designs, such a packaging method can preserve the original pressure sensor sensitivity without offset, validated throughout accelerated lifetime tests. In experiments, wires on the prototypes are used for external electronics but it is found that they contributed to early failures, which would be absent in real wireless versions, indicating a potential for even longer lifetimes. Finally, a verified model is presented to predict the pressure sensor sensitivity of parylene-on-oil packaging with and without the presence of a bubble in the oil.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Binh-Khiem, K. Matsumoto, I. Shimoyama, Tensile film stress of parylene deposited on liquid, Langmuir. Am. Chem. Soc. 26(24), 18771–18775 (2010). doi:10.1021/la102790w
N. Binh-Khiem, K. Matsumoto, I. Shimoyama, Porous parylene and effects of liquid on parylene films deposited on liquid. IEEE MEMS, 111–114 (2011). doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.2011.5734374
J. H. C. Chang, Wireless parylene-based retinal implant, Ph.D. Thesis, California Inst. of Tech. (2013)
J. H. C. Chang, Y. Liu, D. Kang, Y.-C. Tai, Reliable packaging for parylene-based flexible retinal implant. Digest Tech. Papers Transducers, 2612–2615 (2013). doi:10.1109/Transducers.2013.6627341
S. Choi, J. Hutchinson, A. Evans, Delamination of multilayer thermal barrier coatings. Mech. Mater. 31(7), 431–447 (1999)
I. Clausen, T. Glott, Development of clinically relevant implantable pressure sensors: perspectives and challenges. Sensors 14(9), 17686–17702 (2014). doi:10.3390/s140917686
P. Cong, W. H. Ko, D. J. Young, Wireless batteryless implantable blood pressure monitoring microsystem for small laboratory animals. IEEE Sensors J. 10(2), 243–254 (2010). doi:10.1109/JSEN.2009.2030982
W. F. Gorham, A new, general synthetic method for the preparation of linear poly-p-xylylenes, journal of polymer science part A-1: polymer chemistry, 4 3027–3039 (1966). doi:10.1002/pol.1966.150041209
A. Homsy, E. Laux, L. Jeandupeux, J. Charmet, R. Bitterli, C. Botta, Y. Rebetez, O. Banakh, H. Keppner, Solid on liquid deposition, a review of technological solutions. Microelectronic Eng. 141, 267–279 (2015). doi:10.1016/j.mee.2015.03.068
L. Hsu, Development of a low-cost hemin-based dissolved oxygen sensor with anti-biofouling coating for water monitoring. IEEE Sensors J. 14(10), 3400–3407 (2014). doi:10.1109/JSEN.2014.2332513
G. Jiang and D. D. Zhou, in Implantable neural prostheses 2, ed. By D.D. Zhou and E. Greenbaum, Techniques and Engineering Approaches. (Springer Science & Business Media, LLC, 2010). p. 27–61 doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-98120-8_2
T. Kan, H. Aoki, N. Binh-Khiem, K. Matsumoto, I. Shimoyama, Ratiometric optical temperature sensor using two fluorescent dyes dissolved in an ionic liquid encapsulated by parylene film. Sensors 13(4), 4138–4145 (2013). doi:10.3390/s130404138
H. Keppner, and M. Benkhaïra, Method for producing a plastic membrane device and the thus obtained device. WO/2006/063955 (2004)
A. Koutsonas, P. Walter, G. Roessler, N. Plange, Implantation of a novel telemetric intraocular pressure sensor with glaucoma (ARGOS study): 1-year results. Invest. Opthamol. Vis. Sci. 56(2), 1063–1069 (2015). doi:10.1167/iovs.14-14925
K. B. Liland, K. Eidnes, K. Bjorneklett, S. Hvisdten, Measurement of solubility and water content of insulating oils for HV XLPE cable terminations. IEEE Electrical Insulation (2008). doi:10.1109/ELINSL.2008.4570264
B. Lutz, Z. Guan, L. Wang, F. Zhang, Z. Lü, Water absorption and water vapor permeation characteristics of HTV silicone rubber material. Electrical Insulation (ISEI) 478-482 (2012). doi:10.1109/ELINSL.2012.6251514
S. J. A. Majerus, P. C. Fletter, M. S. Damaser, S. L. Garverick, Low-power wireless micromanometer system for acute and chronic bladder-pressure monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomedical Eng. 58(3), 763–767 (2011). doi:10.1109/ TBME.2010.2085002
B. Nguyen, E. Iwase, K. Matsumoto, I. Shomoyama, Electrically driven varifocal micro lens fabricated by depositing parylene directly on liquid. IEEE MEMS, 305–308 (2007). doi:10.1109/MEMSYS.2007.4433059
K. S. Pister, S. B. Dong, Elastic bending of layered plates. Proc ASCE J Eng Mech Div 84(1–10) (1959)
V. Quaglini, S. Mantero, T. Villa, Mechanical properties of breast periprosthetic capsule and the correlation to capsule contracture. J. of App. Biomat. & Biomech. 3(3), 184–191 (2005)
S. Sankaranaravanan, S. Cular, V. Bhethanabotla, and B. Joseph, Subramanian flow induced by acoustic streaming on surface-acoustic-wave devices and its application in biofouling removal: a computational study and comparisons to experiment. 77(6), 06683 (2008) doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.77.066308
W. K. Schombur, Introduction to microsystem design (Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2011)
SCS Parylene Properties, (Specialty Coating Systems, 2007), http://www.physics.rutgers.edu/~podzorov/parylene%20properties.pdf. Accessed 9 Sept 2015
A. Shapero, Y. Liu, Y.-C. Tai, Parylene-on-oil packaging for implantable pressure sensors. IEEE MEMS, 403–406 (2016). doi:10.1109/MEMSYS .2016.7421646
Shin-Etsu Silicone, Silicone Fluid, KF-96, (performance test results, 2004), http://www.silicone.jp/e/. Accessed 1 Aug 2015
E. Ventsel, T. Krauthammer, Thin plates and shells, theory, analysis, and applications (Marcel Dekker, Inc, New York, 2001), pp. 231–232
P. Wang, S. J. A. Majerus, R. Karam, B. Hanzlicek, D. L. Lin, H. Zhu, J. M. Anderson, M. S. Damaser, C. A. Zorman, W. H. Ko, Long-term evaluation of a non-hermetic micropackage technology for MEMS-based, implantable pressure sensors. Digest Tech. Papers Transducers, 484–487 (2015). doi:10.1109/Transducers.2015.7180966
W. Wessel, Fluid pressure sensor, particularly diesel engine injection pump pressure sensor. US4430899 A (1984)
C. Xu, X. Hu, J. Wang, Y. M. Zhang, X. J. Liu, B. B. Xie, C. Yao, Y. Li, X. S. Li, Library of antifouling surfaces derived from natural amino acids by click reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7(31), 17337–17345 (2015). doi:10.1021/acsami.5b04520
L. Yu, B. Kim, E. Meng, Chronically implanted pressure sensors: challenges and state of the field. Sensors 14(11), 20620–20644 (2014). doi:10.3390/s141120620
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Mr. Trevor Roper for his help on all the equipment at the Caltech MEMS Lab.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shapero, A.M., Liu, Y. & Tai, YC. Parylene-on-oil packaging for long-term implantable pressure sensors. Biomed Microdevices 18, 66 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0089-4
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-016-0089-4