Abstract
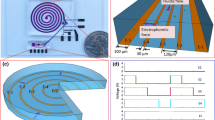
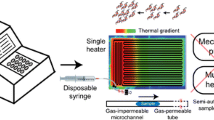
Here we report the demonstration of an integrated microfluidic chip that performs helicase dependent amplification (HDA) on samples containing live bacteria. Combined chip-based sample preparation and isothermal amplification are attractive for world health applications, since the need for instrumentation to control flow rate and temperature changes are reduced or eliminated. Bacteria lysis, nucleic acid extraction, and DNA amplification with a fluorescent reporter are incorporated into a disposable polymer cartridge format. Smart passive fluidic control using a flap valve and a hydrophobic vent (with a nanoporous PTFE membrane) with a simple on-chip mixer eliminates multiple user operations. The device is able to detect as few as ten colony forming units (CFU) of E. coli in growth medium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Andresen, M. von Nickisch-Rosenegk, F.F. Bier, Helicase dependent onchip-amplification and its use in multiplex pathogen detection. Clin. Chim. Acta 403(1–2), 244–248 (2009)
D.A. Bartholomeusz, R.W. Boutte, J.D. Andrade, Xurography: rapid prototyping of microstructures using a cutting plotter. J Microelectromech S 14(6), 1364–1374 (2005)
A. Bhattacharyya, C.M. Klapperich, Thermoplastic microfluidic device for on-chip purification of nucleic acids for disposable diagnostics. Anal. Chem. 78(3), 788–792 (2006)
A. Bhattacharyya, C.M. Klapperich, Microfluidics-based extraction of viral rna from infected mammalian cells for disposable molecular diagnostics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 129(2), 693–698 (2008)
L. Chen, A. Manz, P.J.R. Day, Total nucleic acid analysis integrated on microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 7(11), 1413–1423 (2007)
W.H. Chow, C. McCloskey, Y. Tong, L. Hu, Q. You, C.P. Kelly, H. Kong, Y.W. Tang, W. Tang, Application of isothermal helicase-dependent amplification with a disposable detection device in a simple sensitive stool test for toxigenic clostridium difficile. J. Mol. Diagnostics 10(5), 452–458 (2008)
I.K. Dimov, J.L. Garcia-Cordero, J. O’Grady, C.R. Poulsen, C. Viguier, L. Kent, P. Daly, B. Lincoln, M. Maher, R. O’Kennedy, T.J. Smith, A.J. Ricco, L.P. Lee, Integrated microfluidic tmrna purification and real-time nasba device for molecular diagnostics. Lab Chip 8(12), 2071–2078 (2008)
J. Do, J.Y. Zhang, C.M. Klapperich, The 13th International Conference on Micro Total Analysis Systems, Jeju, Korea, (2009)
C.J. Easley, J.M. Karlinsey, J.M. Bienvenue, L.A. Legendre, M.G. Roper, S.H. Feldman, M.A. Hughes, E.L. Hewlett, T.J. Merkel, J.P. Ferrance, J.P. Landers, A fully integrated microfluidic genetic analysis system with sample-in-answer-out capability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 103(51), 19272–19277 (2006)
P. Gill, A. Ghaemi, Nucleic acid isothermal amplification technologies: a review. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 27(3), 224–243 (2008)
S. Gillers, C.D. Atkinson, A.C. Bartoo, M. Mahalanabis, M.O. Boylan, J.H. Schwartz, C. Klapperich, S.K. Singh, Microscale sample preparation for pcr of c. Difficile infected stool. J. Microbiol. Methods 78(2), 203–207 (2009)
J. Goldmeyer, H. Kong, W. Tang, Development of a novel one-tube isothermal reverse transcription thermophilic helicase-dependent amplification platform for rapid rna detection. J. Mol. Diagnostics 9(5), 639–644 (2007)
J. Goldmeyer, H. Li, M. McCormac, S. Cook, C. Stratton, B. Lemieux, H. Kong, W. Tang, Y.W. Tang, Identification of staphylococcus aureus and determination of methicillin resistance directly from positive blood cultures by isothermal amplification and a disposable detection device. J. Clin. Microbiol. 46(4), 1534–1536 (2008)
M.D. Kulinski, M. Mahalanabis, S. Gillers, J.Y. Zhang, S. Singh, C.M. Klapperich, Sample preparation module for bacterial lysis and isolation of DNA from human urine. Biomed. Microdevices 11(3), 671–678 (2009)
K.-Y. Lien, C.-J. Liu, P.-L. Kuo, G.-B. Lee, Microfluidic system for detection of î±-thalassemia-1 deletion using saliva samples. Anal. Chem. 81(11), 4502–4509 (2009)
C.-J. Liu, K.-Y. Lien, C.-Y. Weng, J.-W. Shin, T.-Y. Chang, G.-B. Lee, Magnetic-bead-based microfluidic system for ribonucleic acid extraction and reverse transcription processes. Biomed. Microdevices 11(2), 339–350 (2009)
M. Mahalanabis, H. ALMuayad, M.D. Kulinski, D. Altman, C.M. Klapperich, Cell lysis and DNA extraction of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria from whole blood in a disposable microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 9, 2811–2817 (2009). doi:10.1039/b905065p
N. Ramalingam, T.C. San, T.J. Kai, M.Y.M. Mak, H.-Q. Gong, Microfluidic devices harboring unsealed reactors for rel-time isothermal helicase-dependent amplification. Microfluid. Nanofluid. (2009). doi:10.1007/s10404-008-0378-1
A.F. Sauer-Budge, P. Mirer, A. Chatterjee, C.M. Klapperich, D. Chargin, A. Sharon, Low cost and manufacturable complete microtas for detecting bacteria. Lab Chip 9(19), 2803–2810 (2009)
Y. Tong, W. Tang, H.J. Kim, X. Pan, T. Ranalli, H. Kong, Development of isothermal taqman assays for detection of biothreat organisms. Biotechniques 45(5), 543–557 (2008)
M. Vincent, Y. Xu, H. Kong, Helicase-dependent isothermal DNA amplification. EMBO Rep. 5(8), 795–800 (2004)
L. Yobas, L. Feng Cheow, K.-C. Tang, S.-E. Yong, E. Kye-Zheng Ong, L. Wong, W. Cheng-Yong Teo, H. Ji, S. Rafeah, C. Yu, A self-contained fully-enclosed microfluidic cartridge for lab on a chip. Biomed. Microdevices 11(6), 1279–1288 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Madhumita Mahalanabis and Jaephil Do contributed equally to this work.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10544-011-9518-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mahalanabis, M., Do, J., ALMuayad, H. et al. An integrated disposable device for DNA extraction and helicase dependent amplification. Biomed Microdevices 12, 353–359 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9391-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10544-009-9391-8