Abstract
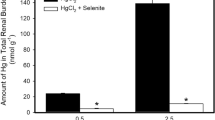
Methylmercury is a toxic pollutant and is generated by microbial methylation of elemental or inorganic mercury in the environment. Previous study found decreased hepatic MDA levels and urinary mercury levels in methylmercury poisoned rats after sodium selenite treatment. This study further found increased mercury levels in serum samples from methylmercury poisoned rats after selenium treatment. By using size exclusion chromatography coupled to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, three Hg- binding protein fractions and two Se-binding protein fractions were identified with the molecular weight of approximately 21, 40, and 75 kDa and of 40 and 75 kDa, respectively. Elevated mercury level in the 75 kDa protein fraction was found binding with both Hg and Se, which may explain the decreased urinary Hg excretion in MeHg poisoned rats after Se treatment. MALDI-TOF-MS analysis of the serum found that the 75 kDa protein fractions were albumin binding with both Hg and Se and the 21 kDa fraction was Hg- binding metallothionein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourdineaud JP, Marumoto M, Yasutake A, Fujimura M (2012) Dietary mercury exposure resulted in behavioral differences in mice contaminated with fish-associated methylmercury compared to methylmercury chloride added to diet. Biomed Res Int 2012:213–219
Chen C, Qu L, Zhao J, Liu S, Deng G, Li B, Zhang P, Chai Z (2006a) Accumulation of mercury, selenium and their binding proteins in porcine kidney and liver from mercury-exposed areas with the investigation of their redox responses. Sci Total Environ 366:627–637
Chen CY, Yu HW, Zhao JJ, Li B, Qu LY, Liu SP, Zhang PQ, Chai ZF (2006b) The roles of serum selenium and selenoproteins on mercury toxicity in environmental and occupational exposure. Environ Health Perspect 114:297–301
Cheng J, Yang Y, Ma J, Wang W, Liu X, Sakamoto M, Qu Y, Shi W (2009) Assessing noxious effects of dietary exposure to methylmercury, PCBs and Se coexisting in environmentally contaminated rice in male mice. Environ Int 35:619–625
Gailer J, George G, Ij Madden S, Prince R, Yu E, Denton M, Younis H, Aposhian H (2000) Structural basis of the antagonism between inorganic mercury and selenium in mammals. Chem Res Toxicol 13:1135–1142
Ganther HE, Goudie C, Wagner P, Sunde ML, Kopecky MJ, Oh SH, Hoekstra WG (1972) Selenium-relation to decreased toxicity of methylmercury added too diets containing tuna. Science 175:1122–1124
Garcia-Sevillano MA, Jara-Biedma R, Gonzalez-Fernandez M, Garcia-Barrera T, Gomez-Ariza JL (2013) Metal interactions in mice under environmental stress. Biometals 26:651–666
García-Sevillano MA, García-Barrera T, Gómez-Ariza JL (2014) Application of metallomic and metabolomic approaches in exposure experiments on laboratory mice for environmental metal toxicity assessment. Metallomics 6:237–248
García-Sevillano MA, Rodríguez-Moro G, García-Barrera T, Navarro F, Gómez-Ariza JL (2015) Biological interactions between mercury and selenium in distribution and detoxification processes in mice under controlled exposure. Effects on selenoprotein. Chem Bio Interact 229:82–90
George GN, MacDonald TC, Korbas M, Singh SP, Myers GJ, Watson GE, O’Donoghue JL, Pickering IJ (2011) The chemical forms of mercury and selenium in whale skeletal muscle. Metallomics 3:1232–1237
Grotto D, Valentini J, Serpeloni JM, Ponte Monteiro PA, Latorraca EF, de Oliveira RS, Greggi Antunes LM, Garcia SC, Barbosa F Jr (2011) Evaluation of toxic effects of a diet containing fish contaminated with methylmercury in rats mimicking the exposure in the Amazon riverside population. Environ Res 111:1074–1082
Hu HY, Lin H, Zheng W, Tomanicek SJ, Johs A, Feng XB, Elias DA, Liang LY, Gu BH (2013) Oxidation and methylation of dissolved elemental mercury by anaerobic bacteria. Nat Geosci 6:751–754
Jiang DT, Heald SM, Sham TK, Stillman MJ (2002) Structures of the cadmium, mercury, and zinc thiolate clusters in metallothionein: XAFS Study of Zn7-MT, Cd7-MT, Hg7-MT, and Hg18-MT formed from rabbit liver metallothionein 2. J Am Chem Soc 116:11004–11013
Jing H, Yu-Feng LI, Shen Y, Zhao JT, Bai LI, Zhang W, Ni LI, Xiong QC (2014) Effects of sodium selenite on methyl mercury poisoned rats. J Mountain Agric Bio 32:55–60
Karagas MR, Choi AL, Oken E, Horvat M, Schoeny R, Kamai E, Cowell W, Grandjean P, Korrick S (2012) Evidence on the human health effects of low-level methylmercury exposure. Environ Health Perspect 120:799–806
Lau S, Sarkar B (1979) Inorganic mercury(II)-binding components in normal human blood serum. J Toxicol Environ Health 5:907–916
Li Y-F, Dong Z, Chen C, Li B, Gao Y, Qu L, Wang T, Fu X, Zhao Y, Chai Z (2012) Organic selenium supplementation increases mercury excretion and decreases oxidative damage in long-term mercury-exposed residents from Wanshan, China. Environ Sci Technol 46:11313–11318
Li X, Yin D, Yin J, Chen Q, Wang R (2014) Dietary selenium protect against redox-mediated immune suppression induced by methylmercury exposure. Food Chem Toxicol 72:169–177
Li Y, Zhao J, Li Y-F, Xu X, Zhang B, Liu Y, Cui L, Li B, Gao Y, Chai Z (2015a) Comparative metalloproteomic approaches for the investigation proteins involved in the toxicity of inorganic and organic forms of mercury in rice roots (Oryza sativa L.). Metallomics. doi:10.1039/C5MT00264H
Li Y-F, Zhao J, Li Y, Li H, Zhang J, Li B, Gao Y, Chen C, Luo M, Huang R (2015b) The concentration of selenium matters: a field study on mercury accumulation in rice by selenite treatment in qingzhen, Guizhou, China. Plant Soil 391:195–205
Liu Y-R, Yu R-Q, Zheng Y-M, He J-Z (2014) Analysis of the microbial community structure by monitoring an Hg methylation gene (hgcA) in Paddy Soils along an Hg gradient. Appl Environ Microbiol 80:2874–2879
Mailman M, Bodaly RA, Paterson MJ, Thompson S, Flett RJ (2014) Low-level experimental selenite additions decrease mercury in aquatic food chains and fish muscle but increase selenium in fish gonads. Arch Environ Contamina Toxicol 66:32–40
Marettova E, Maretta M, Legat J, Nad P (2003) The effect of selenium on phenyl mercury toxicity and mercury retention in chicken. Acta Veterinaria-Beograd 53:211–217
Moreno F, Garcia-Barrera T, Gomez-Jacinto V, Luis Gomez-Ariza J, Garbayo-Nores I, Vilchez-Lobato C (2014) Antagonistic interaction of selenomethionine enantiomers on methylmercury toxicity in the microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Metallomics 6:347–355
Ralston NVC, Raymond LJ (2010) Dietary selenium’s protective effects against methylmercury toxicity. Toxicol 278:112–123
Reyes LH, Marchante-Gayón JM, Alonso JIG, Sanz-Medel A (2003) Quantitative speciation of selenium in human serum by affinity chromatography coupled to post-column isotope dilution analysis ICP-MS. J Anal At Spectrom 18:1210–1216
Sakulsak N (2012) Metallothionein: an overview on its metal homeostatic regulation in mammals. Int J Morph 30:1007–1012
Seppanen K, Kantola M, Laatikainen R, Nyyssonen K, Valkonen VP, Kaarlopp V, Salonen JT (2000) Effect of supplementation with organic selenium on mercury status as measured by mercury in pubic hair. J Trace Elem Med Bio 14:84–87
Shcharbin D, Janicka M, Wasiak M, Palecz B, Przybyszewska M, Zaborski M, Bryszewska M (2007) Serum albumins have five sites for binding of cationic dendrimers. Biochim Et Bioph Acta-Proteins Proteomics 1774:946–951
Siscar R, Koenig S, Torreblanca A, Sole M (2014) The role of metallothionein and selenium in metal detoxification in the liver of deep-sea fish from the NW Mediterranean Sea. Sci Total Environ 466:898–905
Suzuki KT, Sasakura C, Yoneda S (1998) Binding sites for the (Hg-Se) complex on selenoprotein P. Biochim Biophys Acta 1429:102–112
Tang W, Cheng J, Zhao W, Wang W (2015) Mercury levels and estimated total daily intakes for children and adults from an electronic waste recycling area in Taizhou, China: key role of rice and fish consumption. J Environ Sci-China 34:107–132
Wang C, Wu QH, Wang Z, Zhao J (2006) Study of the interaction of carbamazepine with bovine serum albumin by fluorescence quenching method. Anal Sci 22:435–438. doi:10.2116/analsci.22.435
Yang PJ, Jonathan P, Jerome C, Hu DL (2014) Duration of urination does not change with body size. P Nat Academy Sci USA 111:11932–11937
Yasutake A, Nakamura M (2011) Induction by mercury compounds of metallothioneins in mouse tissues: inorganic mercury accumulation is not a dominant factor for metallothionein induction in the liver. J Toxicol Sci 36:365–372
Yoneda S, Suzuki KT (1997a) Detoxification of mercury by selenium by binding of equimolar Hg-Se complex to a specific plasma protein. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 143:274–280
Yoneda S, Suzuki KT (1997b) Equimolar Hg–Se complex binds to selenoprotein P. Biochem Bioph Res Commun 231:7–11
Yun Z, Li L, Liu L, He B, Zhao X, Jiang G (2013) Characterization of mercury-containing protein in human plasma. Metallomics 5:821–827
Zalups RK (2000) Molecular interactions with mercury in the kidney. Pharmacol Rev 52:113–143
Zalups RK, Barfuss DW (1993) Intrarenal distribution of inorganic mercury and albumin after coadministration. J Toxicol Environ Health 40:77–103
Zhao J, Gao Y, Li Y-F, Hu Y, Peng X, Dong Y, Li B, Chen C, Chai Z (2013) Selenium inhibits the phytotoxicity of mercury in garlic (Allium sativum). Environ Res 125:75–81
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (11205168, 11375213, 41173024, 11475196 and U1432241). L Shang gratefully acknowledges the support of the CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2011280). Y-F Li gratefully acknowledges the support of K. C. Wong Education Foundation, Hong Kong and the CAS Youth Innovation Promotion Association, Chinese Academy of Sciences (2011017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yunyun Li and Yuqin Fan have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Fan, Y., Zhao, J. et al. Elevated mercury bound to serum proteins in methylmercury poisoned rats after selenium treatment. Biometals 29, 893–903 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9961-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-016-9961-1