Abstract
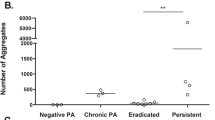
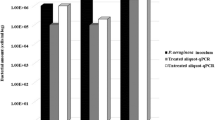
The lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis become chronically infected with the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa, which heralds progressive lung damage and a decline in health. Iron is a crucial micronutrient for bacteria and its acquisition is a key factor in infection. P. aeruginosa can acquire this element by secreting pyoverdine and pyochelin, iron-chelating compounds (siderophores) that scavenge iron and deliver it to the bacteria. Siderophore-mediated iron uptake is generally considered a key factor in the ability of P. aeruginosa to cause infection. We have investigated the amounts of pyoverdine in 148 sputum samples from 36 cystic fibrosis patients (30 infected with P. aeruginosa and 6 as negative controls). Pyoverdine was present in 93 samples in concentrations between 0.30 and 51 μM (median 4.6 μM) and there was a strong association between the amount of pyoverdine and the number of P. aeruginosa present. However, pyoverdine was not present, or below the limits of detection (~0.3 μM), in 21 sputum samples that contained P. aeruginosa. Pyochelin was also absent, or below the limits of detection (~1 μM), in samples from P. aeruginosa-infected patients with little or no detectable pyoverdine. Our data show that pyoverdine is an important iron-scavenging molecule for P. aeruginosa in many cystic fibrosis patients, but other P. aeruginosa iron-uptake systems must be active in some patients to satisfy the bacterial need for iron.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CF:
-
Cystic fibrosis
References
Braud A, Hannauer M, Mislin GL, Schalk IJ (2009) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyochelin-iron uptake pathway and its metal specificity. J Bacteriol 191:3517–3525
Brown MRW, Anwar H, Lambert PA (1984) Evidence that mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the cystic fibrosis lung grows under iron-restricted conditions. FEMS Microbiol Lett 21:113–117
Buckling A, Harrison F, Vos M, Brockhurst MA, Gardner A, West SA, Griffin A (2007) Siderophore-mediated cooperation and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:135–141
Budzikiewicz H (2004) Siderophores of the Pseudomonadaceae sensu stricto (fluorescent and non-fluorescent Pseudomonas spp.). Fortschr Chem Org Naturst 87:81–237
Burns JL, Gibson RL, McNamara S, Yim D, Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, Hiatt P, McCoy K, Castile R, Smith AL, Ramsey BW (2001) Longitudinal assessment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in young children with cystic fibrosis. J Infect Dis 183:444–452
Cornelis P, Matthijs S (2002) Diversity of siderophore-mediated iron uptake systems in fluorescent pseudomonads: not only pyoverdines. Environ Microbiol 4:787–798
Cox CD, Graham R (1979) Isolation of an iron-binding compound from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 137:357–364
Davies JC, Alton EW, Bush A (2007) Cystic fibrosis. BMJ 335:1255–1259
De Vos D, De Chial M, Cochez C, Jansen S, Tummler B, Meyer JM, Cornelis P (2001) Study of pyoverdine type and production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from cystic fibrosis patients: prevalence of type II pyoverdine isolates and accumulation of pyoverdine-negative mutations. Arch Microbiol 175:384–388
del Olmo A, Caramelo C, SanJose C (2003) Fluorescent complex of pyoverdin with aluminum. J Inorg Biochem 97:384–387
Emerson J, Rosenfeld M, McNamara S, Ramsey B, Gibson RL (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other predictors of mortality and morbidity in young children with cystic fibrosis. Pediatr Pulmonol 34:91–100
Haas B, Kraut J, Marks J, Zanker SC, Castignetti D (1991) Siderophore presence in sputa of cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun 59:3997–4000
Harris JK, De Groote MA, Sagel SD, Zemanick ET, Kapsner R, Penvari C, Kaess H, Deterding RR, Accurso FJ, Pace NR (2007) Molecular identification of bacteria in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from children with cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:20529–20533
Harrison F (2007) Microbial ecology of the cystic fibrosis lung. Microbiology 153:917–923
Harrison F, Browning LE, Vos M, Buckling A (2006) Cooperation and virulence in acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections. BMC Biol 4:21
Hoegy F, Celia H, Mislin GL, Vincent M, Gallay J, Schalk IJ (2005) Binding of iron-free siderophore, a common feature of siderophore outer membrane transporters of Escherichia coli and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 280:20222–20230
Hunt TA, Peng WT, Loubens I, Storey DG (2002) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa alternative sigma factor PvdS controls exotoxin A expression and is expressed in lung infections associated with cystic fibrosis. Microbiology 148:3183–3193
King EO, Ward MK, Raney DE (1954) Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescein. J of Lab Medicine 44:301–307
Konstan MW, Morgan WJ, Butler SM, Pasta DJ, Craib ML, Silva SJ, Stokes DC, Wohl ME, Wagener JS, Regelmann WE, Johnson CA (2007) Risk factors for rate of decline in forced expiratory volume in one second in children and adolescents with cystic fibrosis. J Pediatr 151:134–139
Lamont IL, Konings AF, Reid DW (2009) Iron acquisition by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the lungs of patients with cystic fibrosis. Biometals 22:53–60
Liang C-Y, Zeger SL (1986) Longitudinal data analysis using generalized linear models. Biometrika 73:13–22
Meyer J-M, Abdallah MA (1978) The fluorescent pigment of Pseudomonas fluorescens: biosynthesis, purification and physicochemical properties. J Gen Microbiol 107:319–328
Meyer JM, Neely A, Stintzi A, Georges C, Holder IA (1996) Pyoverdin is essential for virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 64:518–523
Meyer J-M, Stintzi A, Vos DD, Cornelis P, Tappe R, Taraz K, Budzikiewicz H (1997) Use of siderophores to type pseudomonads: the three Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdine systems. Microbiology 143:35–43
Moreau-Marquis S, Bomberger JM, Anderson GG, Swiatecka-Urban A, Ye S, O’Toole GA, Stanton BA (2008) The ΔF508-CFTR mutation results in increased biofilms formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa by increasing iron bioavailability. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295:L25–L37
Mureseanu M, Renard G, Galarneau A, Lerner DA (2003) A demonstration model for a selective and recyclable uptake of metals from water: Fe(III) ions complexation and release by a supported natural fluorescent chelator. Talanta 60:515–522
Ochsner A, Johnson Z, Vasil ML (2000) Genetics and regulation of two distinct haem-uptake systems, phu and has, in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 146:185–198
Poole K, McKay GA (2003) Iron acquisition and its control in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: many roads lead to Rome. Front Biosci 8:d661–d686
Ratledge C, Dover LG (2000) Iron metabolism in pathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:881–941
Reid DW, Carroll V, O’May C, Champion A, Kirov SM (2007) Increased airway iron as a potential factor in the persistence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection in cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 30:286–292
Reid DW, Anderson GJ, Lamont IL (2008) Cystic fibrosis: ironing out the problem of infection? Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295:L23–L24
Reid DW, Anderson GJ, Lamont IL (2009) The role of lung iron in determining the bacterial and host struggle in cystic fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 295(5):795–802
Rogers GB, Hoffman LR, Whiteley M, Daniels TW, Carroll MP, Bruce KD (2010) Revealing the dynamics of polymicrobial infections: implications for antibiotic therapy. Trends Microbiol 18:357–364
Schalk IJ, Abdallah MA, Pattus F (2002) Recycling of pyoverdin on the FpvA receptor after ferric pyoverdin uptake and dissociation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Biochemistry 41:1663–1671
Smith EE, Buckley DG, Wu Z, Saenphimmachak C, Hoffman LR, D’Argenio DA, Miller SI, Ramsey BW, Speert DP, Moskowitz SM, Burns JL, Kaul R, Olson MV (2006) Genetic adaptation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa to the airways of cystic fibrosis patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(22):8487–8492
Son MS, Matthews WJ Jr, Kang Y, Nguyen DT, Hoang TT (2007) In vivo evidence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa nutrient acquisition and pathogenesis in the lungs of cystic fibrosis patients. Infect Immun 75:5313–5324
Sriyosachati S, Cox CD (1986) Siderophore-mediated iron acquisition from transferrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 52:885–891
StataCorp (2009) Stata statistical software: release 11. StataCorp LP, College Station
Stites SW, Walters B, O’Brien-Ladner AR, Bailey K, Wesselius LJ (1998) Increased iron and ferritin content of sputum from patients with cystic fibrosis or chronic bronchitis. Chest 114:814–819
Stites SW, Plautz MW, Bailey K, O’Brien-Ladner AR, Wesselius LJ (1999) Increased concentrations of iron and isoferritins in the lower respiratory tract of patients with stable cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 160:796–801
Stover CK, Pham XQ, Erwin AL, Mizoguchi SD, Warrener P, Hickey MJ, Brinkman FSL, Hufnagle WO, Kowalik DJ, Lagrou M, Garber RL, Goltry L, Tolentino E, Westbrock-Wadman S, Yuan Y, Brody LL, Coulter SN, Folger KR, Kas A, Larbig K, Lim R, Smith K, Spencer D, Wong GK-S, Wu Z, Paulsen IT, Reizer J, Saier MH, Hancock REW, Lory S, Olson MV (2000) Complete genome sequence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA01, an opportunistic pathogen. Nature 406:959–964
Takase H, Nitanai H, Hoshino K, Otani T (2000) Impact of siderophore production on Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections in immunocompromised mice. Infect Immun 68:1834–1839
Upritchard HG, Cordwell SJ, Lamont IL (2008) Immunoproteomics to examine cystic fibrosis host interactions with extracellular Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteins. Infect Immun 76:4624–4632
Visca P (2004). Iron regulation and siderophore signalling in virulence by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, vol. 2. In: Ramos JL (ed) Pseudomonas. Kluwer Academic Press/Plenum, New York, pp 69–123
Wehmhoner D, Haussler S, Tummler B, Jansch L, Bredenbruch F, Wehland J, Steinmetz I (2003) Inter- and intraclonal diversity of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa proteome manifests within the secretome. J Bacteriol 185:5807–5814
Weinberg ED (2009) Iron availability and infection. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:600–605
Xiao R, Kisaalita WS (1997) Iron acquisition from transferrin and lactoferrin by Pseudomonas aeruginosa pyoverdin. Microbiology 143(Pt 7):2509–2515
Xiao R, Kisaalita WS (1998) Fluorescent pseudomonad pyoverdines bind and oxidize ferrous ion. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1472–1476
Yoder MF, Kisaalita WS (2006) Fluorescence of pyoverdin in response to iron and other common well water metals. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng 41:369–380
Zamri A, Abdallah MA (2000a) Corrigendum to “An improved stereocontrolled synthesis of pyochelin, siderophore of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia”: (Tetrahedron 56 (2000) 249). Tetrahedron 56:9397
Zamri A, Abdallah MA (2000b) An improved stereocontrolled synthesis of pyochelin, siderophore of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Burkholderia cepacia. Tetrahedron 56:249–256
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Research Grant 352611 from The Australian National Health Research Council. We gratefully acknowledge the generous gift of pyochelin from Gaetan Mislin and Isabelle Schalk.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, L.W., Reid, D.W., Sharples, K.J. et al. Pseudomonas siderophores in the sputum of patients with cystic fibrosis. Biometals 24, 1059–1067 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9464-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-011-9464-z