Abstract
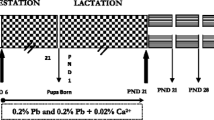
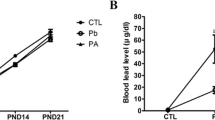
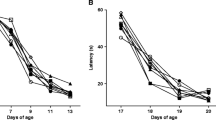
Since alterations in monoamines and monoamine oxidase (MAO) have been postulated to play a role in toxic effects of lead (Pb) on the central nervous system, we have examined the protective effects of calcium (Ca2+) and zinc (Zn2+) supplementation on Pb-induced perturbations in the levels of monoamines and the activity of MAO. Swiss albino mice were lactationally exposed to low (0.2%) and high (1%) levels of Pb-acetate via drinking water of the mother. Pb-exposure commenced on postnatal day (PND) 1, continued up to PND 21 and stopped at weaning. Ca2+ or Zn2+ (0.02% in 0.2% Pb–water or 0.1% in 1% Pb–water) was supplemented separately to the mother up to PND 21. The levels of monoamines (epinephrine, norepinephrine, dopamine and serotonin) and the activity of MAO in the brain regions such as hippocampus, cortex, cerebellum and medulla of young (1 month old) and adult (3 month old) mice were determined in the synaptosomal fractions. The synaptosomal monoamines though increased with low level (0.2%) Pb-exposure, significantly decreased with high level (1%) Pb-exposure in all the brain regions in both the age groups. In general, the young mice seem to be more vulnerable to Pb-neurotoxicity. Ca2+ or Zn2+ supplementation significantly reversed the Pb-induced perturbations both in the levels of monoamines and in the activity of MAO. However, the recovery in monoamine levels and MAO activity was more pronounced with Ca2+ supplementation as compared to Zn2+. These results provide evidence that dietary Ca2+ and/or Zn2+ provide protection against Pb-induced neurotoxic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DP Alfano TL Petit JC LeBoutillier (1983) ArticleTitleDevelopment and plasticity of the hippocampal-cholinergic system in normal and early lead exposed rats Brain Res 312 117–124 Occurrence Handle6686078 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c%2FotFCrtg%3D%3D
L Altmann K Sveinson H Wiegand (1991) ArticleTitleLong term potentiation in rat hippocampal slice is impaired following acute lead perfusion Neurosci Lett 128 109–112 Occurrence Handle1922937 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3940(91)90771-K Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXltVyisL0%3D
GB Ansell MF Beeson (1968) ArticleTitleA rapid and sensitive procedure for the combined assay of noradrenalin, dopamine and serotonin in a single brain sample Anal Biochem 23 196–206 Occurrence Handle5657791 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0003-2697(68)90351-5 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF1cXhtFWrsbc%3D
MT Antonio I Corpas ML Leret (1999) ArticleTitleNeurochemical changes in new born rat’s brain after gestational cadmium and lead exposure Toxicol Lett 104 1–9 Occurrence Handle10048743 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0378-4274(98)00125-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXnsFajsbY%3D
MT Antonio N Lopez ML Leret (2002) ArticleTitleLead and cadmium poisoning during development alters cerebellar and striatal function in rats Toxicology 176 59–66 Occurrence Handle12062930 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0300-483X(02)00137-3 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XksValsrw%3D
MT Antonio ML Leret (2000) ArticleTitleStudy of the neurochemical alterations produced in discrete brain areas by perinatal low level lead exposure Life Sci 67 635–642 Occurrence Handle12659169 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00655-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXkslKmsr8%3D
ATSDR. 1999 Toxicological profile for lead. Atlanta, GA: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry.
D Bagchi PJ Vuchetich M Bagchi et al. (1997) ArticleTitleInduction of oxidative stress by chronic administration of sodium dichromate (choromium VI) and cadmium chloride (cadmium II) to rats Free Radic Biol Med 22 IssueID3 471–478 Occurrence Handle8981039 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0891-5849(96)00352-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXitFKisQ%3D%3D
SN Baksi MJ Hughes (1982) ArticleTitleRegional alterations of brain catecholamines by lead ingestion in adult rats. Influence of dietary calcium Arch Toxicol 50 IssueID1 11–18 Occurrence Handle7115079 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00569232 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL38Xks1Ogtbw%3D
JC Barton ME Conrad L Harrison S Nuby (1978) ArticleTitleEffects of calcium of the absorption and retention of lead J Lab Clin Med 91 366–376 Occurrence Handle24077 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXhtFKjt7k%3D
MJ Boykin CS Chetty B Rajanna (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of lead on kinetics of 3H-Dopamine uptake by rat brain synaptosomes Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 22 IssueID1 88–93 Occurrence Handle1914999 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0147-6513(91)90050-Y Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXlt12mtb0%3D
JP Bressler GW Goldstein (1991) ArticleTitleMechanisms of lead neurotoxicity Biochem Pharmacol 41 479–484 Occurrence Handle1671748 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0006-2952(91)90617-E Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK3MXhtlOnur0%3D
HH Chen T Ma AS Hume (1998) ArticleTitleDevelopmental lead exposure alters the distribution of protein kinase activity in rat hippocampus Biomed Environ Sci 11 IssueID1 61–64 Occurrence Handle9559103 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1c3hvFymtQ%3D%3D
I Cohen VW Kloot (1985) ArticleTitleCalcium and transmitter release Int Rev Neurobiol 27 299–336 Occurrence Handle2867980 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL287htVyqtw%3D%3D
DA Cory-Slechta (1995) ArticleTitleRelationships between lead-induced learning impairments and changes in dopaminergic, cholinergic and glutaminergic neurotransmitter system functions Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 35 391–415 Occurrence Handle7598500 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXlt1Gru7w%3D
CW Cotman DA Matthews (1971) ArticleTitleSynaptic plasma membranes from rat brain synaptosomes: isolation and partial characterization Biochem Biophys Acta 249 380–394 Occurrence Handle4257325 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE38Xjt1Cnug%3D%3D
CB Devi GH Reddy RPJ Prasanthi CS Chetty GR Reddy (2005) ArticleTitleDevelopmental lead exposure alters mitochondrial monoamine oxidase and synaptosomal catecholamine levels in rat brain Int J Dev Neurosci 23 IssueID4 375–381 Occurrence Handle15927761 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD2MXltVegu7c%3D
TC Dubas PD Hrdina (1978) ArticleTitleBehavioural and neurochemical consequences of neonatal exposure to lead in rats J Environ Pathol Toxicol 2 IssueID2 473–484 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXpvVWkug%3D%3D
TC Dubas A Stevenson RL Singhal PD Hrdina (1978) ArticleTitleRegional alterations of brain biogenic amines in young rats following chronic lead exposure Toxicology 9 185–190 Occurrence Handle653738 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0300-483X(78)90044-6 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXkslWks74%3D
S Govoni M Memo L Lucchi PF Spano M Trabucchi (1980) ArticleTitleBrain neurotransmitter systems and chronic lead intoxication Pharmacol Res Commun 12 447–460 Occurrence Handle6108572 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3cXlt1Kls7Y%3D
S Govoni M Memo PF Spano (1979) ArticleTitleChronic lead treatment differentially affects dopamine synthesis in various brain areas Toxicology 12 343–349 Occurrence Handle494315 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0300-483X(79)90081-7 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1MXls12gtLk%3D
AL Green TM Haughton (1961) ArticleTitleA colorimetric method for the estimation of monoamine oxidase Biochem J 78 172–175 Occurrence Handle13708157 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaF3MXjvVCjtA%3D%3D
E Habermann K Crowell P Janicki (1983) ArticleTitleLead and other metals can substitute for calcium in calmodulin Arch Toxicol 54 IssueID1 61–70 Occurrence Handle6314931 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00277816 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXlsFenur0%3D
P Hammond RL Bornschein H Zenick (1984) ArticleTitleToxicology considerations in the assessment of lead exposure Neurotoxicology 5 33–66
L Jablonska M Walski U Rafalowska (1994) ArticleTitleLead as an inductor of some morphological and functional changes in synaptosomes from rat brain Cell Mol Neurobiol 14 IssueID6 701–709 Occurrence Handle7641230 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXmt1Ojs7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF02088678
HP Kari PP Davidson HH Herbert MH Kochbar (1978) ArticleTitleEffects of Ketoamine on brain monoamine levels in rats Res Comm Chem Path Pharamacol 20 475–488 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXlsVSnsb0%3D
SM Lasley ME Gilbert (1999) ArticleTitleLead inhibits the rat N-Methyl D-Aspartate receptor channel by binding to a site distinct from zinc allosteric site Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 159 IssueID3 224–233 Occurrence Handle10486309 Occurrence Handle10.1006/taap.1999.8743 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXlvVajs70%3D
EN Levina MP Chekunova NA Minkina (1973) ArticleTitleEffect of lead acetate used in small doses on the level of biogenetic amines. Leningr. Nauchno - Issled. Inst. Gig. Jr. Prafzabol. Uningrad, USSR Farmakologiya i Toksikologiya (Moscow) 36 IssueID5 640–644
KR Mahaffey R Goyer JK Haseman (1973) ArticleTitleDose-response to lead ingestion in rats fed low dietary calcium J Lab Clin Med 82 IssueID1 92–100 Occurrence Handle4352267 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3sXkvVyjs7k%3D
MJ McIntosh PA Meredith MA Petty JL Reid (1988) ArticleTitleInfluence of lead exposure on catecholamine metabolism in discrete rat brain nuclei Comp Biochem Physiol C Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 89 IssueID2 211–213 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3ntV2itQ%3D%3D
JJ Mejia F Diaz-Barriga J Calderon C Rios ME Jimenez-Capdeville (1997) ArticleTitleEffects of lead, arsenic combined exposure on central monoaminergic systems Neurotoxicol Terratol 19 489–497 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXns12ksbk%3D
PA Meredith MJ McIntosh MA Petty JL Reid (1988) ArticleTitleEffects of lead exposure on rat brain catecholaminergic neurochemistry Comp Biochem Physiol C Comp Pharmacol Toxicol Endocrinol 89 IssueID2 215–219 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL1c3ntV2iug%3D%3D
HL Needleman C Gunnoe A Levinton et al. (1979) ArticleTitleDeficits in psychological and classroom performance of children with elevated dentine lead levels New Engl J Med 300 689–695 Occurrence Handle763299 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE1M7hsVeltQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1056/NEJM197903293001301
N Pages R Deloncle (1997) Inorganic lead Neurotransmitters and Neuropeptides M Yasui MJ Strong K Ota MA, Verity (Eds) Mineral and Metal Neurotoxicology CRC Press New York 262–274
O Pascal C Liliane F Gilles (1989) ArticleTitleThe effects of inorganic lead on the spontaneous and K- evoked release of 3H-5HT from rat cortical synaptosome interaction with calcium Pharmacol Toxicol 64 IssueID5 459–463
MA Peraza FA Fierro DS Barber E Casarez LT Rael (1998) ArticleTitleEffects of micronutrients on metal toxicity Eniron Health Persp 106 IssueID1 203–216 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXitlajtLY%3D
GR Reddy MR Basha CB Devi et al. (2003) ArticleTitleLead induced effects on acetylcholinesterase activity in cerebellum and hippocampus of developing rat Int J Dev Neurosci 21 347–352 Occurrence Handle12927583 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXmsVGksL8%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0736-5748(03)00071-6
GR Reddy A Suresh KS Murthy CS Chetty (2002) ArticleTitleLead neurotoxicity: Heme oxygenase and nitric oxide synthase activities in developing rat brain Neurotox Res 4 33–39 Occurrence Handle12826491 Occurrence Handle10.1080/10298420290007600 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38Xmsl2jtbk%3D
MW Sauerhoff IA Michaelson (1973) ArticleTitleHyperactivity and brain catecholamines in lead exposed developing rats Science 182 1022–1024 Occurrence Handle4795926 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2cXkt1Wrurg%3D
Schuld MJ. 2005. Lead toxicity: Its effects on fetal and infant development http://web.indstate.edu/thcme/anderson/MJS. html
P Sidhu B Nehru (2003) ArticleTitleRelationship between lead induced biochemical and behavioral changes with trace element concentrations in rat brain Biol Trace Elem Res 92 245–256 Occurrence Handle12794276 Occurrence Handle10.1385/BTER:92:3:245 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXltVShsL0%3D
EK. Silbergeld (1985) NoChapterTitle K Blum L Manzo (Eds) Neurotoxicology of Lead Marcel Dekker New York 299–322
EK Silbergeld AM Goldberg (1975) ArticleTitlePharmacological and neurochemical investigations of lead induced hyperactivity Neuropharmacology 14 431–444 Occurrence Handle1171389 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0028-3908(75)90026-X Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE2MXltV2gtbg%3D
KM Six RW Goyer (1970) ArticleTitleExperimental enhancement of lead toxicity by low dietary calcium J Lab Clin Med 76 933–942 Occurrence Handle5485382 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE3MXltFOgsw%3D%3D
G Stoltenburg-Didinger (1994) ArticleTitleNeuropathology of the hippocampus and its susceptibility to neurotoxic insult Neurotoxicology 15 445–450 Occurrence Handle7854577 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2MXitFCru78%3D
L Struzynska G Sulkowski A Lenkiewicz U Rafalowska (2002) ArticleTitleLead stimulates the glutathione system in selective regions of rat brain Folia Neuropathol 40 IssueID4 203–209 Occurrence Handle12572777 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktFKit7k%3D
WT Sturges RM Harrison (1985) ArticleTitleAn assessment of the contribution from paint flakes to the lead content of some street and household dusts Sci Total Environ 44 IssueID3 225–234 Occurrence Handle4048930 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0048-9697(85)90096-8 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2MXlvVart7s%3D
JL Tomsig JB Suszkiw (1993) ArticleTitleIntracellular mechanism of Pb2+-induced norepinephrine release from bovine chromaffin cells Am J Physiol 265 C1630–C1636 Occurrence Handle8279523 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXhsFKitb0%3D
HR Widmer EE Butikofer M Schlumpf W Lichtensteigner (1991) ArticleTitlePre and postnatal lead exposure affects the serotonergic system in the immature rat brain Experientia 47 IssueID5 463–466 Occurrence Handle1710574 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01959945 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK3M3lslahtA%3D%3D
RF Willes E Lok F Truelove A Sunderan (1977) ArticleTitleA retention and tissue distribution of 210P(NO3)2 administered orally to infant and adult monkeys J Toxicol Env Hlth 3 395–406 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE1cXksFygtw%3D%3D
MA Wilson MV Johnston GW Goldstein ME Blue (2000) ArticleTitleNeonatal lead exposure impairs development of rodent barrel field cortex Proc Natl Acada Sci USA 97 5540–5545 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsVWms7Y%3D
LC Wince CH Donovan AJ Assaro (1976) ArticleTitleBehavioral and biochemical analysis of the lead-exposed hyperactive rat Pharmacologist 18 198
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaya Prasanthi, R.P., Hariprasad Reddy, G., Bhuvaneswari Devi, C. et al. Zinc and Calcium Reduce Lead Induced Perturbations in the Aminergic System of Developing Brain. Biometals 18, 615–626 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-005-2993-6
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-005-2993-6