Abstract
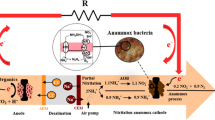
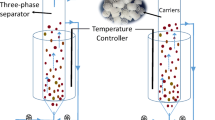
The inoculum biomass was collected from a pilot-scale (3 m3 process tank) nitritation-anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) (deammonification moving bed biofilm (DeaMBBR)) reactor demonstrating the highest total nitrogen removal rate (TNRR) of 0.33 kg N m−3 day−1. This biomass was used for inoculating the anodic chamber of a microbial fuel cell (MFC) to investigate the capacity of DeaMBBR biomass to act as an exo-electrogenic consortia. Performance of MFCs inoculated with ANAMMOX-specific consortia collected from DeaMBBR (MFC-ANA) and another MFC-CON inoculated with a septic tank mixed anaerobic consortium as a control was investigated for electrochemical performance and wastewater treatment efficiency. These MFCs were operated for the total duration of 419 days during which regular feed was given and performance was monitored for first 30 cycles and last 30 cycles, with each cycle of 3 day duration. The MFC-ANA continuously generated bio-energy with higher volumetric power density (9.5 W m−3 and 6.0 W m−3) in comparison to MFC-CON (4.9 and 2.9 W m−3) during the first 30 and last 30 cycles of operational period, respectively. MFC-ANA also achieved 84 ± 2% and 80 ± 2% of COD removal efficiency and 89 ± 4% and 73 ± 2% of total nitrogen removal efficiency during first 30 and last 30 cycles of operational period, respectively. The improvement of nitrogen removal and power production in case of MFC-ANA over MFC-CON could be attributed to the ANAMMOX-denitrifiers populations and Trichococcus (14.92%) as denitrifying exo-electrogenic microbes (4.46%), respectively.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA-AWWA-WPCF (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th edn. American Public HealthAssociation American Water Works Association and WaterPollution Control Federation.
Bhowmick GD, Noori MT, Das I, Neethu B, Ghangrekar MM, Mitra A (2018) Bismuth doped TiO2 as an excellent photocathode catalyst to enhance the performance of microbial fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43(15):7501–7510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.02.188
Bhowmick GD, Kibena-Põldsepp E, Matisen L, Merisalu M, Kook M, Käärik M, Leis J, Sammelselg V, Ghangrekar MM, Tammeveski K (2019a) Multi-walled carbon nanotube and carbide-derived carbon supported metal phthalocyanines as cathode catalysts for microbial fuel cell application. Sustain Energy Fuels 3:3525–3537. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SE00574A
Bhowmick GD, Das S, Ghangrekar MM, Mitra A, Banerjee R (2019b) Improved wastewater treatment by combined system of microbial fuel cell with activated carbon/TiO2 cathode catalyst and membrane bioreactor. J Inst Eng Ser A 100:675–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-019-00406-7
Bhowmick GD, Das S, Verma HK, Neethu B, Ghangrekar MM (2019c) Improved performance of microbial fuel cell by using conductive ink printed cathode containing Co3O4 or Fe3O4. Electrochim Acta 310:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.04.127
Chamchoi N, Nitisoravut S, Schmidt JE (2008) Inactivation of ANAMMOX communities under concurrent operation of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (ANAMMOX) and denitrification. Biores Technol 99:3331–3336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2007
Chatterjee P, Ghangrekar MM, Rao S (2016) Development of anammox process for removal of nitrogen from wastewater in a novel self-sustainable biofilm reactor. Biores Technol 218:723–730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.07.002
Chen CJ, Zhang M, Yu XL, Mei J, Jiang Y, Wang YQ, Zhang T, Tian C (2018) Effect of C/N ratios on nitrogen removal and microbial communities in the anaerobic baffled reactor (ABR) with an anammox-coupling-denitrification process. Wat Sci Technol 70:2338–2348. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.516
Ciesielski S, Czerwionka K, Sobotka D, Dulski T, Makinia J (2018) The metagenomic approach to characterization of the microbial community shift during the long-term cultivation of anammox-enriched granular sludge. J Appl Gen 59:109–117
Clauwaert P, Rabaey K, Aelterman P, De Schamphelaire L, Pham TH, Boeckx P, Boon N, Verstraete W (2007) Biological denitrification in microbial fuel cells. Environ Sci Technol 41:3354–3360. https://doi.org/10.1021/es062580r
Di Domenico EG, Petroni G, Mancini D, Geri A, Palma LD, Ascenzioni F (2015) Development of electroactive and anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing (Anammox) biofilms from digestate in microbial fuel cells. Biomed Res Int 351014:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/351014
Feng Y, Wang X, Logan BE, Lee H (2008) Brewery wastewater treatment using air-cathode microbial fuel cells. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:873–880. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1360-2
Ferousi C, Lindhoud S, Baymann F, Kartal B, Jetten MSM, Reimann J (2017) Iron assimilation and utilization in anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Curr Opin Chem Biol 37:129–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.03.009
Ghadge AN, Jadhav DA, Pradhan H, Ghangrekar MM (2015) Enhancing waste activated sludge digestion and power production using hypochlorite as catholyte in clayware microbial fuel cell. Bioresour Technol 182:225–231
Gregoire KP, Glaven SM, Hervey J, Lin B, Tender LM (2014) Enrichment of a High-Current Density Denitrifying Microbial Biocathode. J Electrochem Soc 161:3049–3057
Guven D, Dapena A, Kartal B, Schmid MC, Maas B, van de Pas-Schoonen K, Sozen S, Mendez R, Op den Camp HJM, Jetten MSM, Strous M, Schmidt I (2005) Propionate oxidation by and methanol inhibition of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:1066–1071. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.71.2.1066-1071.2005
Jadhav DA, Ghangrekar MM (2015) Effective ammonium removal by anaerobic oxidation in microbial fuel cells. Environ Technol 36:767–775. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.960481
Jadhav GS, Ghangrekar MM (2009) Performance of microbial fuel cell subjected to variation in pH, temperature, external load and substrate concentration. Bioresour Technol 100:717–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2008.07.041
Lee Y, Martin L, Grasel P, Tawfiq K, Chen G (2013) Power generation and nitrogen removal of landfill leachate using microbial fuel cell technology. Environ Technol 34:2727–2736. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.788040
Li C, Ren H, Xu M, Cao J (2015) Study on anaerobic ammonium oxidation process coupled with denitrification microbial fuel cells (MFCs) and its microbial community analysis. Bioresour Technol 175:545–552. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.10.156
Light SH, Su L, Rivera-Lugo R, Cornejo JA, Louie A, Iavarone AT, Ajo-Franklin CM, Portnoy DA (2018) A flavin-based extracellular electron transfer mechanism in diverse Gram-positive bacteria. Nature 562:140–144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0498-z
Liu C, Yamamoto T, Nishiyama T, Fujii T, Furukawa K (2009) Effect of salt concentration in anammox treatment using non-woven biomass carrier. Jour Biosci Bioeng 107:519–523. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiosc.2009.01.020
Lotti T, Kleerebezem R, Hu Z, Kartal B, de Kreuk MK, van Erp Taalman C, Kruit Kip J, Hendrickx TLG, van Loosdrecht MCM (2015) Pilot-scale evaluation of anammox based mainstream nitrogen removal from municipal wastewater. Environ Technol 36(9):1167–1177. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2014.982722
Logan BE, Hamelers B, Rozendal R, Schröder U, Keller J, Freguia S, Aelterman P, Verstraete W, Rabaey K (2006) Microbial fuel cells: methodology and technology. Environ Sci Technol 40:5181–5192. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0605016
Logan BE, Regan JM (2006) Microbial fuel cells—challenges and applications. Environ Sci Technol 40:5172–5180. https://doi.org/10.1021/es0627592
Mandel A, Zekker I, Jaagura M, Tenno T (2019) Enhancement of anoxic phosphorus uptake of denitrifying phosphorus removal process by biomass adaption. Int J Env Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-021
McDonald JE, Larsen N, Pennington A, Connolly J, Wallis C, Rooks DJ, Hall N, McCarthy AJ, Allison HE (2016) Characterising the canine oral microbiome by direct sequencing of reverse-transcribed rRNA molecules. PLoS ONE 11:e0157046
Noori MT, Bhowmick GD, Tiwari BR, Ghangrekar MM, Mukhrejee CK (2018) Application of low-cost Cu–Sn bimetal alloy as oxygen reduction reaction catalyst for improving performance of the microbial fuel cell. MRS Adv Mater Res Soc 3:663–668. https://doi.org/10.1557/adv.2018
Noori MT, Ghangrekar MM, Mukherjee CK (2016) V2O5 microflower decorated cathode for enhancing power generation in air-cathode microbial fuel cell treating fish market wastewater. Int J Hydrogen Energy 41:3638–3645. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.12.163
Park T-J, Ding W, Cheng S, Brar MS, Ma APY, Tun HM, Leung FC (2014) Microbial community in microbial fuel cell (MFC) medium and effluent enriched with purple photosynthetic bacterium (Rhodopseudomonas sp.). AMB Express 4:1–8
Rikmann E, Zekker I, Tenno T, Saluste A, Tenno T (2018) Inoculum-free start-up of biofilm- and sludge-based deammonification systems in pilot scale. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:133–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-017-1374-3
Shaw, D.R., Ali, M., Katuri, K. P., Gralnick, J.A., Reimann, J., Mesman, R., van Niftrik, L., Jetten, M.S.M., Saikaly, P.E., 2019. Extracellular electron transfer-dependent anaerobic oxidation of ammonium by anammox bacteria. https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/855817v1. https://doi.org/10.1101/855817
Sheng S, Liu B, Hou XY, Liang Z, Sun XB, Du LF, Wang DP (2018) Effects of different carbon sources and C/N ratios on the simultaneous anammox and denitrification process. Int Biodeter Biodegradation 127:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibiod.2017.11.002
Strous M, Van Gerven E, Zheng P, Kuenen JG, Jetten MSM (1997) Ammonium removal from concentrated waste streams with the anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) process in different reactor configurations. Water Res 31:1955–1962. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(97)00055-9
Takai K, Horikoshi K (2000) Rapid detection and quantification of members of the archaeal community by quantitative PCR using fluorogenic probes. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:5066–5072. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.66.11.5066-5072.2000
Tharali AD, Sain N, Osborne WJ (2016) Microbial fuel cells in bioelectricity production. Front Life Sci 9:252–266
Zekker I, Rikmann E, Tenno T, Lemmiksoo V, Menert A, Loorits L, Vabamäe P, Tominga SM, Tenno T (2012) Anammox Bacteria enrichment and phylogenic analysis in moving bed biofilm reactors. Environ Eng Sci 29:946–950
Zekker I, Kivirüüt A, Rikmann E, Mandel A, Jaagura M, Tenno T, Artemchuk O, Rubin S, Tenno T (2019) Enhanced efficiency of nitritating-anammox SBR achieved at low decrease rates of oxidation-reduction potential. Env Eng Sci. https://doi.org/10.1089/ees.2018.0225
Zekker I, Raudkivi M, Artemchuk O, Rikmann E, Priks H, Jaagura M, Tenno T (2020) Mainstream-sidestream wastewater switching promotes anammox nitrogen removal rate in organic-rich, low-temperature streams. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2020.1721566
Zhang C, Liang P, Yang X, Jiang Y, Bian Y, Chen C (2016) Binder-free graphene and manganese oxide coated carbon felt anode for high-performance microbial fuel cell. Biosens Bioelectron 81:32–53
Zhao H, Zhao J, Li F, Li X (2016) Performance of denitrifying microbial fuel cell with biocathode over nitrite. Front Microbiol 7:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.00344
Kosari SF, Rezania B, Lo KV, Mavinic DS (2014) Operational strategy for nitrogen removal from centrate in a two-stage partial nitrification–Anammox process. Environ Technol 35:1110–1120. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2013.861872
van Loosdrecht MC, Salem S (2006) Biological treatment of sludge digester liquids. Water Sci Technol 53:11–20
Veit K, Ehlers C, Schmitz RA (2005) Effects of nitrogen and carbon sources on transcription of soluble methyltransferases in Methanosarcina mazei Strain Go¨1. J Bacteriol 187:6147–6154. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.17.6147-6154.2005
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the EU-India research co-funding mechanism INNO-INDIGO, by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India (BT/IN/INNO-INDIGO/28/MMG/2015-16) for IIT Kharagpur, India. This research was financially supported by IUT20-16, BT/IN/INNO-INDIGO/28/MMG/2015-16) and Saraswati 2.0 for University of Tartu, Estonia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
10532_2020_9907_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file1 (PDF 9 kb)—Figure S1. Autotrophic and heterotrophic N-removing culture variation in initial inoculum and DeaMBBRbiofilm samples.
10532_2020_9907_MOESM2_ESM.pdf
Supplementary file2 (PDF 28 kb)—Figure S2. Distribution of total strains in initial inoculum, DeaMBBR biomass, and anodic biofilm of MFCANA.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zekker, I., Bhowmick, G.D., Priks, H. et al. ANAMMOX-denitrification biomass in microbial fuel cell to enhance the electricity generation and nitrogen removal efficiency. Biodegradation 31, 249–264 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-020-09907-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-020-09907-w