Abstract
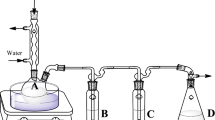
The effect of the terpenes α-pinene, eucalyptol, and limonene, individually and as mixtures, on atrazine (ATZ) biodegradation and on biological activity in a biobed biomixture was evaluated. Additionally, terpenes emitted from the biomixture were captured using solid-phase microextraction. Terpenes added individually at relatively low concentrations (50 μg kg−1) significantly enhanced ATZ degradation and biological activity during the first incubation days. No significant effect on ATZ degradation was found from adding the terpene mixture, and, interestingly, an inhibitory effect on phenoloxidase activity was found during the first 20 days of incubation when mixed terpenes were present at 100 μg kg−1. Capturing terpenes demonstrated that during the first hour of incubation a significant fraction of the terpenes was volatilized. These results are the first to demonstrate the feasibility of using terpenes to enhance the degradation of a pesticide. However, successive applications of terpenes or the addition of materials that slowly release terpenes could sustain the ATZ degradation enhancement.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamczyk S, Adamczyk B, Kitunen V, Smolander A (2011) Influence of diterpenes (colophony and abietic acid) and a triterpene (beta-sitosterol) on net N mineralization, net nitrification, soil respiration, and microbial biomass in birch soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47(6):715–720
Amaral JA, Knowles R (1998) Inhibition of methane consumption in forest soils by monoterpenes. J Chem Ecol 24(4):723–734
Barriuso E, Houot S (1996) Rapid mineralization of the s-triazine ring of atrazine in soils in relation to soil management. Soil Biol Biochem 28:1341–1348
Bento FM, Camargo FAO, Okeke BC, Frankenberger WT (2005) Comparative bioremediation of soils contaminated with diesel oil by natural attenuation, biostimulation and bioaugmentation. Bioresour Technol 96(9):1049–1055
Castillo MdP, Torstensson L (2007) Effect of biobed composition, moisture, and temperature on the degradation of pesticides. J Agric Food Chem 55(14):5725–5733
Castillo MdP, Stenström J, Ander P (1994) Determination of manganese peroxidase activity with 3-methyl-2- benzothiazolinone hydrazone and 3-(dimethylamino) benzoic acid. Anal Biochem 218(2):399–404
Castillo MdP, Torstensson L, Stenström J (2008) Biobeds for environmental protection from pesticide use-a review. J Agric Food Chem 56(15):6206–6219
Coppola L, Castillo MdP, Monaci E, Vischetti C (2007) Adaptation of the biobed composition for chlorpyrifos degradation to southern Europe conditions. J Agric Food Chem 55(2):396–401
Dudášová H, Lukáčová L, Murínová S, Dercová K (2012) Effects of plant terpenes on biodegradation of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs). Int Biodet Biodeg 69:23–27
Gan JY, Koskinen WC (1998) Pesticide fate and behavior in soil at evaluated concentrations. In: Kearney PC, Roberts TR (eds) Pesticide remediation in soil and water. Wiley, Chichester, pp 59–84
Hernandez BS, Koh SC, Chial M, Focht DD (1997) Terpene-utilizing isolates and their relevance to enhanced biotransformation of polychlorinated biphenyls in soil. Biodegradation 8(3):153–158
Insam H, Seewald MSA (2010) Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in soils. Biol Fertil Soils 46(3):199–213
Leff JW, Fierer N (2008) Volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions from soil and litter samples. Soil Biol Biochem 40(7):1629–1636
McLoughlin E, Rhodes AH, Owen SM, Semple KT (2009) Biogenic volatile organic compounds as a potential stimulator for organic contaminant degradation by soil organisms. Environ Pollut 157(1):86–94
Monard C, Martin-Laurent F, Devers-Lamrani M, Lima O, Vandenkoornhuyse P, Binet F (2010) Atz gene expressions during atrazine degradation in the soil drilosphere. Mol Ecol 19(4):749–759
Omotayo AE, Ilori MO, Amund OO, Ghosh D, Roy K, Radosevich MA (2011) Establishment and characterization of atrazine degrading cultures from Nigerian agricultural soil using traditional and Bio-Sep bead enrichment techniques. Appl Soil Ecol 48(1):63–70
Owen SM, Clark S, Pompe M, Semple KT (2007) Biogenic volatile organic compounds as potential carbon sources for microbial communities in soil from the rhizosphere of Populus tremula. FEMS Microbiol Lett 268(1):34–39
Pesyna GM, Venkataraghavan R, Dayringer HE, McLafferty FW (1976) Probability based matching system using a large collection of reference mass spectra. Anal Chem 48(9):1362–1368
Rhodes AH, Owen SM, Semple KT (2007) Biodegradation of 2,4-dichlorophenol in the presence of volatile organic compounds in soils under different vegetation types. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269(2):323–330
Schalchli H, Hormazabal E, Becerra J, Birkett M, Alvear M, Vidal J, Quiroz A (2011) Antifungal activity of volatile metabolites emitted by mycelial cultures of saprophytic fungi. Chem Ecol 27(6):503–513
Schnürer J, Rosswall T (1982) Fluorescein diacetate hydrolysis as a measure of total microbial activity in soil and litter. Appl Environ Microbiol 6:256–1261
Schulz R (2004) Field study on exposure, effects, and risk mitigation of aquatic nonpoint-source insecticide pollution: a review. J Environ Qual 33(2):419–448
Sene L, Converti A, Ribeiro-Secchi GA, Garcia-Simão RdC (2010) New aspect on atrazine biodegradation. Braz Arch Biol Technol 53(2):487–496
Suttinun O, Lederman BP, Luepromchai E (2004) Application of terpene-induced cell for enhancing biodegradation of TCE contaminated soil. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 26(1):131–142
Torstensson L, Castillo MdP (1997) Use of biobeds in Sweden to minimize environmental spillages from agricultural spraying equipment. Pestic Outlook 8:24–27
Tortella GR, Rubilar O, Castillo MdP, Cea M, Mella-Herrera R, Diez MC (2012) Chlorpyrifos degradation in a biomixture of biobed at different maturity stages. Chemosphere 88(2):224–228
Tyagi M, da Fonseca MMR, de Carvalho CCCR (2011) Bioaugmentation and biostimulation strategies to improve the effectiveness of bioremediation processes. Biodegradation 22(2):231–241
Vischetti C, Monaci E, Cardinali A, Casucci C, Perucci P (2008) The effect of initial concentration, co-application and repeated applications on pesticide degradation in a biobed mixture. Chemosphere 72(11):1739–1743
Acknowledgments
This study was financed by Dirección de Investigación de la Universidad de La Frontera PIA-Project DI10-7004 and partially financed by Fondecyt Project 11100236 and Fondecyt 3110085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tortella, G.R., Rubilar, O., Stenström, J. et al. Using volatile organic compounds to enhance atrazine biodegradation in a biobed system. Biodegradation 24, 711–720 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9619-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-013-9619-4