Abstract
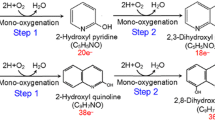
A Pseudomonas sp. strain, which can utilize quinoline as its sole carbon, nitrogen and energy source, was isolated from activated sludge in a coking wastewater treatment plant. Quinoline can be degraded via the 8-hydroxycoumarin pathway. We quantified the first two organic intermediates of the biodegradation, 2-hydroxyquinoline and 2,8-dihydroxyquinoline. We tracked the transformation of the nitrogen in quinoline in two media containing different C/N ratios. At least 40.4% of the nitrogen was finally transformed into ammonium when quinoline was the sole C and N source. But addition of an external carbon source like glucose promoted the transformation of N from NH3 into NO3 −, NO2 −, and then to N2. The product analysis and gene characteristics indicated that the isolate accomplished heterotrophic nitrification and aerobic denitrification simultaneously. The study also demonstrated that quinoline and its metabolic products can be eliminated if the C/N ratio is properly controlled in the treatment of quinoline-containing wastewater.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
State Environmental Protection Administration of China (1989) Monitoring and analysis method of water and wastewater. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (In Chinese)
Aislabie J, Bej AK, Hurst H, Rothenburger S, Atlas RM (1990) Microbial degradation of quinoline and methylquinolines. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(2):345–351
Arai H, Mizutani M, Igarashi Y (2003) Transcriptional regulation of the nos genes for nitrous oxide reductase in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology-SGM 149:29–36
Bläse M, Bruntner C, Tshisuaka B, Fetzner S, Lingens F (1996) Cloning, expression, and sequence analysis of the three genes encoding quinoline 2-oxidoreductase, a molybdenum-containing hydroxylase from Pseudomonas putida 86. J Biol Chem 271(38):23068–23079
Bothe H, Jost G, Schloter M, Ward BB, Witzel KP (2000) Molecular analysis of ammonia oxidation and denitrification in natural environments. FEMS Microbiol Rev 24(5):673–690
Brockman FJ, Denovan BA, Hicks RJ, Fredrickson JK (1989) Isolation and characterization of quinoline-degrading bacteria from subsurface sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 55(4):1029–1032
Carl B, Fetzner S (2005) Transcriptional activation of quinoline degradation operons of Pseudomonas putida 86 by the AraC/XylS-type regulator OxoS and cross-regulation of the PqorM promoter by XylS. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(12):8618–8626
Carl B, Arnold A, Hauer B, Fetzner S (2004) Sequence and transcriptional analysis of a gene cluster of Pseudomonas putida 86 involved in quinoline degradation. Gene 331:177–188
Chen FZ, Cui MC, Fu JM, Sheng GY, Sun GP, Xu MY (2003) Biodegradation of quinoline by freely suspended and immobilized cells of Comamonas sp. strain Q10. J Gen Appl Microbiol 49(2):123–128
Crossman LC, Moir JWB, Enticknap JJ, Richardson DJ, Spiro S (1997) Heterologous expression of heterotrophic nitrification genes. Microbiology-UK 143:3775–3783
Cui MC, Chen FZ, Fu JM, Sheng GY, Sun GP (2004) Microbial metabolism of quinoline by Comamonas sp. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20(6):539–543
Cutruzzola F, Brown K, Wilson EK, Bellelli A, Arese M, Tegoni M, Cambillau C, Brunori M (2001) The nitrite reductase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: essential role of two active-site histidines in the catalytic and structural properties. P Natl Acad Sci USA 98(5):2232–2237
Fetzner S (1998) Bacterial degradation of pyridine, indole, quinoline, and their derivatives under different redox conditions. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 49(3):237–250
Grant DJ, Al-Najjar TR (1976) Degradation of quinoline by a soil bacterium. Microbios 15(61–62):177–189
Hallin S, Lindgren PE (1999) PCR detection of genes encoding nitrite reductase in denitrifying bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 65(4):1652–1657
Jetten MSM, deBruijn P, Kuenen JG (1997) Hydroxylamine metabolism in Pseudomonas PB16: involvement of a novel hydroxylamine oxidoreductase. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 71(1–2):69–74
Kaiser JP, Feng YC, Bollag JM (1996) Microbial metabolism of pyridine, quinoline, acridine, and their derivatives under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Microbiol Rev 60(3):483–498
Kilbane JJ, Ranganathan R, Cleveland L, Kayser KJ, Ribiero C, Linhares MM (2000) Selective removal of nitrogen from quinoline and petroleum by Pseudomonas ayucida IGTN9m. Appl Environ Microbiol 66(2):688–693
Licht D, Johansen SS, Arvin E, Ahring BK (1997) Transformation of indole, quinoline by Desulfobacterium indolicum (DSM 3383). Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47(2):167–172
Nemergut DR, Schmidt SK (2002) Disruption of narH, narJ, and moaE inhibits heterotrophic nitrification in Pseudomonas strain M19. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(12):6462–6465
O’Loughlin EJ, Kehrmeyer SR, Sims GK (1996) Isolation, characterization, and substrate utilization of a quinoline-degrading bacterium. Int Biodeter Biodegr 38(2):107–118
Rich JJ, Heichen RS, Bottomley PJ, Cromack K, Myrold DD (2003) Community composition and functioning of denitrifying bacteria from adjacent meadow and forest soils. Appl Environ Microbiol 69(10):5974–5982
Robertson LA, Cornelisse R, Devos P, Hadioetomo R, Kuenen JG (1989) Aerobic denitrification in various heterotrophic nitrifiers. A Van Leeuw J Microb 56(4):289–299
Rösch C, Mergel A, Bothe H (2002) Biodiversity of denitrifying and dinitrogen-fixing bacteria in an acid forest soil. Appl Environ Microbiol 68(8):3818–3829
Rosche B, Tshisuaka B, Hauer B, Lingens F, Fetzner S (1997) 2-oxo-1, 2-dihydroquinoline 8-monooxygenase: Phylogenetic relationship to other multicomponent nonheme iron oxygenases. J Bacteriol 179(11):3549–3554
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Scala DJ, Kerkhof LJ (1998) Nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) gene-specific PCR primers for detection of denitrifiers and three nosZ genes from marine sediments. FEMS Microbiol Lett 162(1):61–68
Shukla OP (1986) Microbial transformation of quinoline by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 51(6):1332–1442
Shukla OP (1989) Microbiological degradation of quinoline by Pseudomonas stutzeri: the coumarin pathway of quinoline catabolism. Microbios 59(238):47–63
Sugaya K, Nakayama O, Hinata N, Kamekura K, Ito A, Yamagiwa K, Ohkawa A (2001) Biodegradation of quinoline in crude oil. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76(6):603–611
Sun QH, Bai YH, Zhao C, Xiao YN, Wen DH, Tang XY (2009) Aerobic biodegradation characteristics and metabolic products of quinoline by a Pseudomonas strain. Bioresour Technol 100(21):5030–5036
Tian S, Qian C, Yang XS (2006) Biodegradation of biomass gasification wastewater by two species of Pseudomonas using immobilized cell reactor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 128(2):141–147
USEPA (2003) EPA test methods. http://www.epa.gov/
Wallenstein MD, Myrold DD, Firestone M, Voytek M (2006) Environmental controls on denitrifying communities and denitrification rates: Insights from molecular methods. Ecol Appl 16(6):2143–2152
Wang JL, Quan XC, Han LP, Qian Y, Hegemann W (2002) Microbial degradation of quinoline by immobilized cells of Burkholderia pickettii. Water Res 36(9):2288–2296
Wang JL, Wu WZ, Zhao X (2004) Microbial degradation of quinoline: Kinetics study with Burkholderia pickttii. Biomed Environ Sci 17(1):21–26
Wehrfritz JM, Reilly A, Spiro S, Richardson DJ (1993) Purification of hydroxylamine oxidase from Thiosphaera pantotropha. Identification of electron acceptors that couple heterotrophic nitrification to aerobic denitrification. FEBS Lett 335(2):246–250
Wehrfritz JM, Carter JP, Spiro S, Richardson DJ (1996) Hydroxylamine oxidation in heterotrophic nitrate-reducing soil bacteria and purification of a hydroxylamine-cytochrome c oxidoreductase from a Pseudomonas species. Arch Microbiol 166(6):421–424
Zhang XY, Yan KL, Ren DJ, Wang HX (2007) Studies on quinoline biodegradation by a white rot fungus (Pleurotus ostreatus BP) in liquid and solid state substrates. Fresen Environ Bull 16(6):632–638
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by an exploration project grant from the National High-tech Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, Grant No. 2006AA06Z336) and a general Project grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 50878001). We would like to express our appreciation to Prof Yi Li and Mr Mian Xia in the Beijing Weiming Kaituo Agro-biotechnology Ltd., for assistance with the molecular biology. We also thank Prof. Iain Bruce in Zhejiang University School of Medicine for critical checking and revising the paper’s English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The accession numbers of the isolates 16S rRNA gene, nirS, and nosZ on GenBank are EU266621, FJ393272 and FJ393273.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bai, Y., Sun, Q., Zhao, C. et al. Quinoline biodegradation and its nitrogen transformation pathway by a Pseudomonas sp. strain. Biodegradation 21, 335–344 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9304-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-009-9304-9