Abstract
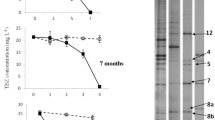
Bisphenol A (2,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl) propane, BPA), which is used as a synthetic resin material or a plasticizer, is a pollutant that␣possesses endocrine-disrupting activity. Bioremediation of BPA is used to decrease its polluting effects, and here we report a novel bacterial strain AO1, which is able to degrade BPA. This strain was isolated using enrichment cultivation from a soil sample from a vegetable-growing field; the sample was one of 500 soil samples collected across Japan. Strain AO1 degraded 100 mg/l BPA to an undetectable level within 6 h in MYPG medium (containing malt extract, yeast extract, peptone, and glucose) and within 48 h in minimum medium containing 1% glucose at 30°C. Strain AO1 can utilize BPA as a sole source of carbon and as an energy source under aerobic conditions. The estrogenic activity of BPA in MYPG medium was ultimately reduced by strain AO1, although the activity initially increased. Taxonomical analysis showed that strain␣AO1 is closely related to Sphingomonas chlorophenolicum and S. herbicidovorans, neither of which have a capacity for BPA degradation. DNA–DNA hybridization showed that strain AO1 is a novel species of the Sphingomonas genus, and we designated AO1 as S. bisphenolicum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Colborn T (1995) Environmental estrogens: Health implications for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 103:135–136
Dorn PB, Chou CS, Gentempo JJ (1987) Degradation of bisphenol A in natural waters. Chemosphere 16:1501–1507
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid-deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Fukuda T, Uchida H, Takashima Y, Uwajima T, Kawabata T, Suzuki M (2001) Degradation of bisphenol A by purified laccase from Trametes villosa. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:704–706
Hasegawa T (1985) Classification and Identification of Microorganisms (2nd edn.). Japan Scientific Society Press, Tokyo (in Japanese)
Hirano T, Honda Y, Watanabe T, Kuwahara M (2000) Degradation of bisphenol A by the lignin-degrading enzyme, manganese peroxidase, produced by the white-rot bacidiomycete, Pleurotus ostreatus. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 64:1958–1962
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PHA, Staley JT, Williams ST (1994) Bergey’s Manual of Detaminative Bacteriology. (9th edn.), Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Howdeshell KL, Hotchkiss AK, Thayer KA Vandenbergh JG, Vom Saal FS (1999) Environmental toxins: Exposure to bisphenol A advances puberty. Nature 401:763–764
Hucker GJ, Conn HJ (1923) Methods of Gram staining. Technical Bulletin 129, Ithaca. New York State Agricultural Experiment Station
Hugh R, Leifson E (1953) The taxonomic significance of fermentative versus oxidative metabolism of carbohydrates by various gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol 66:24–26
Iizuka H, Komagata K (1963) An attempt at grouping of the genus Pseudomonas. J Gen Appl Microbiol 9:73–82
Ike M, Chen MY, Jin CS, Fujita M (2002) Acute toxicity, mutagenicity, and estrogenicity of biodegradation products of bisphenol-A. Environ Toxicol 17:457–461
Ike M, Jin CS, Fujita M (1995) Isolation and characterization of novel bisphenol A-degrading bacterium Pseudomonas paucimobilis strain FJ-4. Japanese J Water Biol 31:203–212
Ike M, Jin CS, Fujita M (2000) Biodegradation of bisphenol A in the aquatic environment. Wat Sci Technol 42:31–38
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rate of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Lobos JH, Leib TK, Su TM (1992) Biodegradation of bisphenol A and other bisphenols by a Gram-negative aerobic bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 58:1823–1831
Nohynek LJ, Suhonen EL, Nurmiaho-Lassila EL, Hantula J, Salkinoja-Salonen M (1995) Description of four pentachlorophenol-degrading bacterial strains of Sphingomonas chlorophenolica sp. nov. Syst Appl Microbiol 18:527–538
Ohtani Y, Shimada Y, Shiraishi F, Kozawa K (2003) Variation of estrogenic activities during the bio-degradation of bisphenol A. J Environ Chem 13:1027–1031 (in Japanese)
Quinn PJ, Carter ME, Markey B, Carter GR (1994) Bacillus species. In Clinical veterinary microbiology. Mosby-Year Book, St Louis, 178–183
Ronen Z, Abeliovich A (2000) Anaerobic-aerobic process for microbial degradation of tetrabromobisphenol A. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:2372–2377
Saito H, Miura K (1963) Preparation of transforming deoxyribonucleic acid by phenol treatment. Biochim Biophy Acta 72:619–629
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) A neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Satomi M, Kimura B, Mizoi M, Sato T, Fujii T (1997) Tetragenococcus muriaticus sp. nov., a new moderately halophilic lactic acid bacterium isolated from fermented squid liver sauce. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:832–836
Sasaki M, Maki J, Oshiman K, Matsumura Y, Tsuchido T (2005) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by cells lysate from Sphingomonas sp. strain AO1. Biodegradation 16:449–459
Spivak J, Leib TK, Lobos JH (1994) Novel pathway for bacterial metabolism of bisphenol A. J Biol Chem 269:7323–7329
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Staples CA, Dom PB, Klecka GM, O’Block ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36:2149–2173
Tsutsumi Y, Haneda T, Nishida T (2001) Removal of estrogenic activities of bisphenol A and nonylphenol by oxidative enzymes from lignin-degrading basidiomycetes. Chemosphere 42:271–276
Takeuchi M, Hamana K, Hiraishi A (2001) Proposal of the genus Sphingomonas sensu stricto and three new genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, on the basis of phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic analysis. Int J Syst Bacteriol 51:1405–1417
Uchino M, Kosako Y, Uchimura T, Komagata K (2000) Emendation of Pseudomonas straminea Iizuka & Komagata 1963. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1513–1519
vom Saal F, Cooke PS, Buchanan DL, Palanza P, Thayer KA, Nagel SC, Parmigiani S, Welshons WV (1998) A physiologically based approach to the study of bisphenol A and other estrogenic chemicals on the size of reproductive organs, daily sperm production, and behavior. Toxicol Ind Health 14:239–260
Weisburg WG, Barns SM, Pelletier DA, Lane DJ (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Yabuuchi E, Yano I, Oyaizu H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T, Yamamoto H (1990) Proposals of Sphingomonas paucimobilis gen. nov. and comb. nov., Sphingomonas parapaucimobilis sp. nov., Sphingomonas yanoikuyae sp. nov., Sphingomonas adhaesiva sp. nov., Sphingomonas capsulata comb. nov., and two genospecies of␣the genus Sphingomonas. Microbiol Immunol 34:99–119
Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Fujiwara N, Naka T, Matsunaga I, Ogura H, Kobayashi K (2002) Emendation of the genus Sphingomonas Yabuuchi et al. 1990 and junior objective synonymy of the species of three genera, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium and Sphingopyxis, in conjunction with Blastomonas ursincola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:1485–1496
Yamamoto T, Yasuhara A, Shiraishi H, Nakasugi O (2001) Bisphenol A in hazardous waste landfill leachates. Chemosphere 42:415–418
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Akiko Oishi for her technical assistance. The authors thank Dr. Osamu Shida, R&D Department, Higeta Shoyu Co. Ltd., Chiba, Japan for physiological and biochemical characterization of strain AO1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oshiman, Ki., Tsutsumi, Y., Nishida, T. et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel bacterium, Sphingomonas bisphenolicum strain AO1, that degrades bisphenol A. Biodegradation 18, 247–255 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-006-9059-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10532-006-9059-5