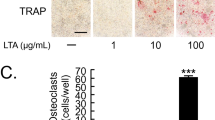
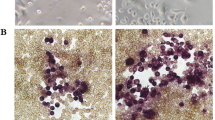
Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effects of heat-killed Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 and P25RC clinical strain (derived from an obturated root canal with apical periodontitis) on osteoclast differentiation within an osteoblast/osteoclast co-culture system.
Results
Heat-killed E. faecalis significantly increased the proportion of multinucleated osteoclastic cells (MNCs) within the co-culture system. The IL-6 level was significantly increased upon exposure to heat-killed E. faecalis. Gene expression levels of NFATc1 and cathepsin K were significantly up-regulated compared to the untreated control. EphrinB2 and EphB4 expressions at both the mRNA and protein levels were also significantly upregulated compared to the untreated control.
Conclusions
Heat-killed E. faecalis can induce osteoclast differentiation within the osteoblast/osteoclast co-culture system in vitro, possibly through ephrinB2-EphB4 bidirectional signaling.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker PJ, Dixon M, Evans RT, Dufour L, Johnson E, Roopenian DC (1999) CD4(+) T cells and the proinflammatory cytokines gamma interferon and interleukin-6 contribute to alveolar bone loss in mice. Infect Immun 67:2804–2809
Boyce BF (2013) Advances in the regulation of osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res 92:860–867
Edwards CM, Mundy GR (2008) Eph receptors and ephrin signaling pathways: a role in bone homeostasis. Int J Med Sci 5:263–272
Feng X, McDonald JM (2011) Disorders of bone remodeling. Annu Rev Pathol 6:121–145
Fujisaki K, Tanabe N, Suzuki N, Kawato T, Takeichi O, Tsuzukibashi O, Makimura M, Ito K, Maeno M (2007) Receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand induces the expression of carbonic anhydrase II, cathepsin K, and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in osteoclast precursor RAW264.7 cells. Life Sci 80:1311–1318
Gomes BP, Pinheiro ET, Gade-Neto CR, Sousa EL, Ferraz CC, Zaia AA, Teixeira FB, Souza-Filho FJ (2004) Microbiological examination of infected dental root canals. Oral Microbiol Immunol 19:71–76
Graves DT, Oates T, Garlet GP (2011) Review of osteoimmunology and the host response in endodontic and periodontal lesions. J Oral Microbiol 3:5304. doi:10.3402/jom.v3i0.5304
Hienz SA, Paliwal S, Ivanovski S (2015) Mechanisms of bone resorption in periodontitis. J Immunol Res 2015:615486
Kurihara N, Bertolini D, Suda T, Akiyama Y, Roodman GD (1990) IL-6 stimulates osteoclast-like multinucleated cell-formation in long-term human marrow cultures by inducing IL-1 release. J Immunol 144:4226–4230
Pfeilschifter J, Chenu C, Bird A, Mundy GR, Roodman GD (1989) Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor stimulate the formation of human osteoclastlike cells-invitro. J Bone Miner Res 4:113–118
Rocas IN, Siqueira JF, Santos KRN (2004) Association of Enterococcus faecalis with different forms of periradicular diseases. J Endod 30:315–320
Takayanagi H (2007) Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 7:292–304
Wang S, Deng Z, Seneviratne CJ, Cheung GS, Jin L, Zhao B, Zhang C (2015a) Enterococcus faecalis promotes osteoclastogenesis and semaphorin 4D expression. Innate Immun 21:726–735
Wang S, Deng Z, Ye X, Geng X, Zhang C (2015b) Enterococcus faecalis attenuates osteogenesis through activation of p38 and ERK1/2 pathways in MC3T3-E1 cells. Int Endod J. doi:10.1111/iej.12578
Yamashita T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N (2012) New roles of osteoblasts involved in osteoclast differentiation. World J Orthop 3:175–181
Zhan X, Zhang C, Dissanayaka WL, Cheung GS, Jin L, Yang Y, Yan F, Tong EH (2013) Storage media enhance osteoclastogenic potential of human periodontal ligament cells via RANKL-independent signaling. Dent Traumatol 29:59–65
Zhao C, Irie N, Takada Y, Shimoda K, Miyamoto T, Nishiwaki T, Suda T, Matsuo K (2006) Bidirectional ephrinB2-EphB4 signaling controls bone homeostasis. Cell Metab 4:111–121
Zhu XF, Wang QQ, Zhang CF, Cheung GSP, Shen Y (2010) Prevalence, phenotype, and genotype of Enterococcus faecalis isolated from saliva and root canals in patients with persistent apical periodontitis. J Endod 36:1950–1955
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by RFCID/HHSRF HMRF Grant No. 12110772 and Shenzhen Key Laboratory of ENT (No. ZDSYS 201506050935272).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Zuhui Deng and Shuai Wang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, Z., Wang, S., Heng, B.C. et al. Enterococcus faecalis promotes osteoclast differentiation within an osteoblast/osteoclast co-culture system. Biotechnol Lett 38, 1443–1448 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2142-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2142-z