Abstract
Objectives
To establish an efficient expression system for a fusion protein GST-pgLTP (Lipid Transfer Protein) and to test its antifungal activity.
Results
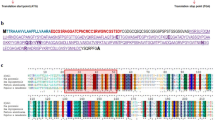
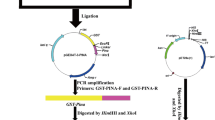
The nucleotide sequence of LTP gene was obtained from Panax ginseng using RT-PCR. The ORF of the cDNA is 363 bp, codING for a protein OF 120 amino acids with a calculated MW of 12.09 kDa. The pgLTP gene with a His6-tag at the C-terminus was cloned into the pGEX-6p1 vector to generate a GST-fusion pgLTP protein construct that was expressed in Escherichia coli Rosetta. Following purification by Ni–NTA, the fusion protein exhibited antifungal activity against five fungi found in ginseng.
Conclusion
The fusion protein GST-pgLTP has activity against a broad spectrum of phytopathogenic fungi, and can potentially be adapted for production to combat fungal diseases that affect P. ginseng.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blein JP, Coutos-Thevenot P, Marion D, Ponchet M (2002) From elicitins to lipid-transfer proteins: a new insight in cell signalling involved in plant defence mechanisms. Trends Plant Sci 7:293–296
Boutrot F, Chantret N, Gautier MF (2008) Genome-wide analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis non-specific lipid transfer protein (nsLtp) gene families and identification of wheat nsLtp genes by EST data mining. BMC Genomics 9:86
Diz MS et al (2011) Characterisation, immunolocalisation and antifungal activity of a lipid transfer protein from chili pepper (Capsicum annuum) seeds with novel alpha-amylase inhibitory properties. Physiol Plant 142:233–246
Elmorjani K, Lurquin V, Lelion A, Rogniaux H, Marion D (2004) A bacterial expression system revisited for the recombinant production of cystine-rich plant lipid transfer proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 316:1202–1209
Harper S, Speicher DW (2011) Purification of proteins fused to glutathione S-transferase. Methods Mol Biol 681:259–280
Kader JC (1996) Lipid-transfer proteins in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:627–654
Kirubakaran SI, Begum SM, Ulaganathan K, Sakthivel N (2008) Characterization of a new antifungal lipid transfer protein from wheat. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:918–927
Lascombe MB et al (2008) The structure of “defective in induced resistance” protein of Arabidopsis thaliana, DIR1, reveals a new type of lipid transfer protein. Protein Sci 17:1522–1530
Liu J, Wang Q, Sun M, Zhu L, Yang M, Zhao Y (2014) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in Panax ginseng at different stages of growth and in different organs. PLoS One 9:e112177
Nawrot R, Barylski J, Nowicki G, Broniarczyk J, Buchwald W, Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A (2014) Plant antimicrobial peptides. Folia Microbiol (Praha) 59:181–196
Park DW, Kim SS, Nam MK, Kim GY, Kim J, Rhim H (2011) Improved recovery of active GST-fusion proteins from insoluble aggregates: solubilization and purification conditions using PKM2 and HtrA2 as model proteins. BMB Rep 44:279–284
Segura A, Moreno M, Garcia-Olmedo F (1993) Purification and antipathogenic activity of lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) from the leaves of Arabidopsis and spinach. FEBS Lett 332:243–246
Sels J, Mathys J, De Coninck BM, Cammue BP, De Bolle MF (2008) Plant pathogenesis-related (PR) proteins: a focus on PR peptides. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:941–950
Thevissen K, Terras FR, Broekaert WF (1999) Permeabilization of fungal membranes by plant defensins inhibits fungal growth. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5451–5458
Wong JH et al (2010) Proteins with antifungal properties and other medicinal applications from plants and mushrooms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1221–1235
Zottich U et al (2011) Purification, biochemical characterization and antifungal activity of a new lipid transfer protein (LTP) from Coffea canephora seeds with alpha-amylase inhibitor properties. Biochim Biophys Acta 1810:375–383
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from the National Nature Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81373937, 81503212, and 81503324).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence of P. ginseng LTP identified has been submitted to GenBank and the accession number is KU589275.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cai, K., Wang, J., Wang, M. et al. Molecular cloning, recombinant expression, and antifungal functional characterization of the lipid transfer protein from Panax ginseng . Biotechnol Lett 38, 1229–1235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2100-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-016-2100-9