Abstract
Objective
To determine whether IKK-NF-κB is activated either directly by compressive mechanical stress or by proinflammatory cytokines produced by MC3T3-E1 cells under compressive stress loading.
Results
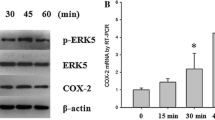
MC3T3-E1 cells subjected to cyclic uniaxial compressive stress showed increased expression of proinflammatory cytokines and activation of the IKK-NF-κB signaling pathway with nuclear translocation of p65. Following treatment with antibodies to neutralize the action of the proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and IL-6, the activation of IKK-NF-κB signaling was notably inhibited in MC3T3-E1 cells subjected to force loading.
Conclusion
IKK-NF-κB signaling in MC3T3-E1 cells may be activated by proinflammatory cytokines that are produced as a consequence of mechanical stress loading and not by direct compressive mechanical stress.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes PJ, Karin M (1997) Nuclear factor-kappaB: a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. New Engl J Med 336:1066–1071
Boyce BF (2013) Advances in osteoclast biology reveal potential new drug targets and new roles for osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 28:711–722
Brunner M, Jurdic P, Tuckerman JP, Block MR, Bouvard D (2013) New insights into adhesion signaling in bone formation. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 305:1–68
Carmeliet G, Vico L, Bouillon R (2001) Space flight: a challenge for normal bone homeostasis. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 11:131–144
Ehrlich PJ, Lanyon LE (2002) Mechanical strain and bone cell function: a review. Osteoporos Int 13:688–700
Franzoso G, Carlson L, Xing L, Poljak L, Shores EW, Brown KD, Leonardi A, Tran T, Boyce BF, Siebenlist U (1997) Requirement for NF-kappaB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes Dev 11:3482–3496
Kook SH, Son YO, Choe Y, Kim JH, Jeon YM, Heo JS, Kim JG, Lee JC (2009) Mechanical force augments the anti-osteoclastogenic potential of human gingival fibroblasts in vitro. J Periodontal Res 44:402–410
Liu J, Liu T, Zheng Y, Zhao Z, Liu Y, Cheng H, Luo S, Chen Y (2006) Early responses of osteoblast-like cells to different mechanical signals through various signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 348:1167–1173
Liu J, Zou L, Zheng Y, Zhao Z, Li Y, Yang P, Luo S (2007) NF-kappaB responds to mechanical strains in osteoblast-like cells, and lighter strains create an NF-kappaB response more readily. Cell Biol Int 31:1220–1224
Meikle MC (2006) The tissue, cellular, and molecular regulation of orthodontic tooth movement: 100 years after Carl Sandstedt. Eur J Orthod 28:221–240
Muthukuru M, Darveau RP (2014) TLR signaling that induces weak inflammatory response and SHIP1 enhances osteogenic functions. Bone Res 2:1–13
Wuertz K, Vo N, Kletsas D, Boos N (2012) Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: the roles of NF-kappaB and MAP kinases. Eur Cell Mater 23:103–119
Yamamoto K, Yamamoto T, Ichioka H, Akamatsu Y, Oseko F, Mazda O, Imanishi J, Kanamura N, Kita M (2011) Effects of mechanical stress on cytokine production in mandible-derived osteoblasts. Oral Dis 17:712–719
Zhang Y, Lei CQ, Hu YH, Xia T, Li M, Zhong B, Shu HB (2014) Krüppel-like factor 6 is a co-activator of NF-κB that mediates p65-dependent transcription of selected downstream genes. J Biol Chem 289:12876–12885
Zhou S, Zhang J, Zheng H, Zhou Y, Chen F, Lin J (2013) Inhibition of mechanical stress-induced NF-κB promotes bone formation. Oral Dis 19:59–64
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 11472183 and 81300876) and accomplished in the State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China College of Stomatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
Supporting Information
Supplementary Table 1—Gene-specific primers for qPCR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Y., Zheng, Q., Lu, W. et al. Compressive mechanical stress may activate IKK-NF-κB through proinflammatory cytokines in MC3T3-E1 cells. Biotechnol Lett 37, 1729–1735 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1849-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-015-1849-6