Abstract
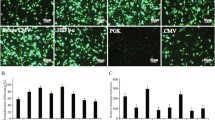
The expression enhancement by cytomegalovirus promoter and different intron A (IA) variants were evaluated in CHO-K1, HepG2, HEK-293 and COS-7 cells by assessing the levels of luciferase activity. This data along with mRNA levels measurement indicated that the construct harboring an IA variant with a 200-nucleotide deletion (Δ200) had the greatest impact on increasing luciferase expression among all constructs evaluated. Based on these results, we redesigned pCMV–IA variants and cloned them into plasmids expressing a humanized antibody. These plasmids were then used to transfect CHO-K1 cells. Production of the antibody was not augmented with the Δ200 promoter variant. The 600-nucleotide deletion (Δ600) and whole IA promoter variants expressed similar levels of the recombinant protein. These data indicate that the IA-based enhanced expression of transgenes depends on a small region within the intron.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade EV, Albuquerque FC, Moraes LMP, Brigido MM, Santos-Silva MA (2000) Single-chain Fv with Fc fragment of the human igG1 tag: construction, Pichia pastoris expression and antigen binding characterization. J Biochem 128:891–895
Awasti S, Isler JA, Alwine JC (2004) Analysis of splice variants of the immediate-early 1 region of human cytomegalovirus. J Virol 78:8191–8200
Bubner B, Gase K, Baldwin IT (2004) Two-fold differences are the detection limit for determining transgene copy numbers in plants by real-time PCR. BMC Biotechnol 4:1–11
Campos-da-Paz M, Costa CS, Quilici LS, Simões IC, Kyaw CM, Maranhão AQ, Brigido MM (2008) Production of recombinant human Factor VIII in different cell lines and the effect of human XBP-1 co-expression. Mol Biotechnol 39:155–158
Chapman BS, Thayer RM, Vincent KA, Haigwood NL (1991) Effect of intron A from human cytomegalovirus (Towne) immediate-early gene of heterologous expression in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res 19:3979–3986
Gomez N, Subramanian J, Ouyang J, Nguyen MDH, Hutchinson M, Sharma VK, Lin AA, Yuk IH (2012) Culture temperature modulates aggregation of recombinant antibody in CHO cells. Biotechnol Bioeng 109(1):125–136
Gudikote JP, Imam JS, Garcia RF, Wilkinson MF (2005) RNA splicing promotes translation and RNA surveillance. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 12:801–809
Jaillon O, Bouhouche K, Gout JF, Aury JM et al (2008) Translational control of intron splicing in eukaryotes. Nature 451:359–362
Kwek KY, Murphy S, Funger A, Thomas B, O’Gorman W, Kimura H, Proudfoot NJ, Akoulitchev A (2002) U1 snRNA associates with TFIIH and regulates transcriptional initiation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 9:800–805
Le Hir H, Nott A, Moore MJ (2003) How introns influence and enhance eukaryotic gene expression. Trends Biochem Sci 28:215–220
Mariati Ho SCL, Yap MGS, Yang Y (2010b) Evaluating post-transcriptional regulatory elements for enhancing transient gene expression levels in CHO K1 and HEK293 cells. Protein Exp Purif. 69:9–15
Mariati Ng YK, Chao S-H, Yap MGS, Yang Y (2010a) Evaluating regulatory elements of human major immediate early gene for enhancing transgene expression levels in CHO K1 and HEK 293 cells. J Biotechnol 147:160–163
Silva HM, Vieira PMMM, Costa PLN, Pimentel BMS, Moro AM, Kalil J, Maranhão AQ, Coelho V, Brigido MM (2009) Novel humanized anti CD-3 antibodies induce a predominantly immunoregulatory profile in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Immunol Lett 125:129–136
Thomas P, Smart GT (2005) HEK293 cell line: a vehicle for the expression of recombinant proteins. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 51:187–200
Xia W, Bringmann P, McClary J, Jones PP, Manzana W et al (2006) High levels of protein expression using different mammalian CMV promoters in several cell lines. Protein Exp Purif. 45:115–124
Xu ZL, Mizuguchi H, Watabe AI, Uchida E, Mayumi T, Hayakawa T (2001) Optimization of transcriptional regulatory elements for constructing plasmid vectors. Gene 272:149–156
Acknowledgments
We thank Izabel CristinaRodrigues Silva for assistance with the statistical analysis. This work was supported by Conselho Nacional do Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) and Financiadora de Estudos e Projetos (FINEP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Quilici, L.S., Silva-Pereira, I., Andrade, A.C. et al. A minimal cytomegalovirus intron A variant can improve transgene expression in different mammalian cell lines. Biotechnol Lett 35, 21–27 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1043-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-1043-z