Abstract
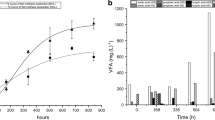
A 700 ml membrane-aerated, stirred glass reactor equipped with four vertical baffles was constructed. Biodesulfurization of model oil (n-dodecane containing dibenzothiophene—DBT) and hydrodesulfurized diesel was carried out using Pseudomonas delafieldii strain R-8. Microbubble aeration gave an activity of 1.3 mg DBT removed g−1 h−1 and 277 μg sulfur g−1 h−1 for model oil and hydrodesulfurized diesel, respectively. These values were 1.9- and 1.6-times higher than using a traditional bubble aeration process. This is a promising method for the biodesulfurization of petroleum feedstocks.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ago K, Nagasawa K, Takita J, Itano R, Morii N, Matsuda K, Takahashi K (2005) Development of an aerobic cultivation system by using a microbubble aeration technology. J Chem Eng Jpn 38:757–762
Del Olmo CH, Santos VE, Alcon A, Garcia-Ochoa F (2005) Production of a Rhodococcus erythropolis IGTS8 biocatalyst for DBT biodesulfurization: influence of operational conditions. Biochem Eng J 22:227–237
Duetz WA, Van Beilen JB, Witholt B (2001) Using proteins in their natural environment: potential and limitations of microbial whole-cell hydroxylations in applied biocatalysis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 12:419–425
Luo MF, Xing JM, Gou ZX, Li S, Liu HZ, Chen JY (2003) Desulfurization of dibenzothiophene by lyophilized cells of Pseudomonas delafieldii R-8 in the presence of dodecane. Biochem Eng J 13:1–6
Monticello DJ (2000) Biodesulfurization and the upgrading of petroleum distillates. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:540–546
Nehring D, Czermak P, Vorlop J, Lubben H (2004) Experimental study of a ceramic microsparging aeration system in a pilot-scale animal cell culture. Biotechnol Prog 20:1710–1717
Shan GB, Xing JM, Guo C, Liu HZ, Chen JY (2005) Biodesulfurization using Pseudomonas delafieldii in magnetic polyvinyl alcohol beads. Lett Appl Microbiol 40:30–36
Van Beilen JB, Duetz WA, Schmid A, Witholt B (2003) Practical issues in the application of oxygenases. Trends Biotechnol 21:170–177
Xiong XC, Xing JM, Li X, Bai XJ, Li WL, Li YG, Liu HZ (2007) Enhancement of biodesulfurization in two-liquid systems by heterogeneous expression of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2394–2397
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20976186).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, X., Liu, H., Zhu, F. et al. Enhancement of biodesulfurization by Pseudomonas delafieldii in a ceramic microsparging aeration system. Biotechnol Lett 34, 1029–1032 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0872-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-012-0872-0