Abstract
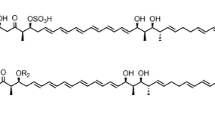
Dihydrochalcomycin from Streptomyces sp. KCTC 0041BP is a 16-membered macrolide antibiotic containing two deoxysugars (d-chalcose and d-mycinose) that are O-glycosylated at the C-5 and C-20 positions, respectively. The desosamine sugar cassette was constructed from pikromycin-deoxysugar biosynthetic genes and transformed into Streptomyces sp. GerSM1, which was engineered for deletion of the genes related to TDP-d-chalcose biosynthesis (gerB, gerN and gerMI). Novel 16-membered macrolides (5-O-desosaminyl derivatives of dihydrochalcomycin) were detected by ESI-MS, LC/MS, and MS/MS thereby demonstrating combinatorial biosynthesis of the deoxysugar in 16-membered macrolide antibiotics.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltz RH (2006) Molecular engineering approaches to peptide, polyketide and other antibiotics. Nat Biotechnol 24:1533–1540
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K et al (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Borisova SA, Zhao L, Melancon CE III et al (2004) Characterization of the glycosyltransferase activity of DesVII: analysis of and implications for the biosynthesis of macrolide antibiotics. J Am Chem Soc 126:6534–6535
Burgie ES, Holden HM (2007) Molecular architecture of DesI: a key enzyme in the biosynthesis of desosamine. Biochemistry 46:8999–9006
Burgie ES, Holden HM (2008) Three-dimensional structure of DesVI from Streptomyces venezuelae: a sugar N, N-dimethyltransferase required for dTDP-desosamine biosynthesis. Biochemistry 47:3982–3988
Burgie ES, Thoden JB, Holden HM (2007) Molecular architecture of DesV from Streptomyces venezuelae: a PLP-dependent transaminase involved in the biosynthesis of the unusual sugar desosamine. Protein Sci 16:887–896
Denis F, Brzezinski R (1991) An improved aminoglycoside resistance gene cassette for use in Gram-negative bacteria and Streptomyces. FEMS Microbiol Lett 65:261–264
Goo YM, Lee YY, Kim BT (1997) A new 16-membered chalcomycin type macrolide antibiotic, 250-144C. J Antibiot 50:85–88
Jaishy BP, Lim SK, Yoo ID et al (2006) Cloning and characterization of gene cluster for the production of polyketide macrolide dihydrochalcomycin in Streptomyces sp. KCTC 0041BP. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:764–770
Khosla C, Keasling JD (2003) Metabolic engineering for drug discovery and development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2:1019–1025
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ et al (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Centre Foundation, Norwich
Kim SD, Ryoo IJ, Kim CJ et al (1996) GERI-155 a new macrolide antibiotic related to chalcomycin. J Antibiot 49:955–957
Kinoshita K, Takenaka S, Suzuki H et al (1992) Mycinamicins, new macrolide antibiotics. XIII. Isolation and structures of novel fermentation products from Micromonospora griseorubida (FERM BP-705). J Antibiot 45:1–9
Lee HC, Sohng JK, Kim HJ et al (2004a) Cloning and expression of the glucose-1-phosphate thymidylyltransferase gene (gerD) from Streptomyces sp. GERI-155. Mol Cells 17:274–280
Lee HC, Sohng JK, Kim HJ et al (2004b) Cloning, expression, and biochemical characterization of dTDP-glucose 4, 6-dehydratase gene (gerE) from Streptomyces sp. GERI-155. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:576–583
Lombo F, Gibson M, Greenwell L et al (2004) Engineering biosynthetic pathways for deoxysugars: branched-chain sugar pathways and derivatives from the antitumor tetracenomycin. Chem Biol 11:1709–1718
Macneil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL et al (1992) Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene 111:61–68
Marki M, Renkonen R (2004) Biosynthesis of 6-deoxyhexose glycans in bacterial. Glycobiology 14:1–15
Mochizuki S, Hiratsu K, Suwa M et al (2003) The large linear plasmid pSLA2-L of Streptomyces rochei has an unusually condensed gene organization for secondary metabolism. Mol Microbiol 48:1501–1510
Ochsner UA, Fiechter A, Reiser J (1994) Isolation, characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlAB genes encoding a rhamnosyltransferase involved in rhamnolipid bio-surfactant synthesis. J Biol Chem 269:19787–19795
Pageni BB, Oh T-J, Thuy TTT et al (2008) Characterization of a chalcosyltransferase (gerGTII) in dihydrochalcomycin biosynthesis. Mol Cells 26:278–284
Quiros LM, Salas JA (1995) Biosynthesis of the macrolide oleandomycin by Streptomyces antibioticus. J Biol Chem 270:18234–18239
Quiros LM, Carbajo JR, Salas JA (2000) Inversion of the anomeric configuration of the transferred sugar during inactivation of the macrolide antibiotic oleandomycin catalyzed by a macrolide glycosyltransferase. FEBS Lett 476:186–189
Salah-Bey K, Doumith M, Michel JM et al (1998) Targeted gene inactivation for the elucidation of deoxysugar biosynthesis in the erythromycin producer Saccharopolyspora erythraea. Mol Gen Genet 257:542–553
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA
Solenberg PJ, Matsushima P, Stack DR et al (1997) Production of hybrid glycopeptide antibiotics in vitro and in Streptomyces toyocaensis. Chem Biol 4:195–202
Ward SL, Hu Z, Schirmer A et al (2004) Chalcomycin biosynthesis gene cluster from Streptomyces bikinensis: Novel feature of unusual ketolide produce through expression of chm polyketide synthase in Streptomyces fradiae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:4703–4712
Woo PWK, Rubin JR (1996) Chalcomycin: single-crystal X-ray crystallographic analysis; biosynthetic and stereochemical correlations with polyoxo macrolide antibiotics. Tetrahedron 52:3857–3872
Xue Y, Sherman DH (2001) Biosynthesis and combinatorial biosynthesis of pikromycin-related macrolides in Streptomyces venezuelae. Metab Eng 3:15–26
Xue Y, Zhao L, Liu HW et al (1998) A gene cluster for macrolide antibiotic biosynthesis in Streptomyces venezuelae: architecture of metabolic diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:12111–12116
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the 21C Frontier Microbial Genomics and Application Center Program, the Ministry of Science and Technology (Grant MG02-0301-004-2-3-1), Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pageni, B.B., Oh, TJ. & Sohng, J.K. Novel desosaminyl derivatives of dihydrochalcomycin from a genetically engineered strain of Streptomyces sp.. Biotechnol Lett 31, 1759–1768 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0074-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-009-0074-6