Abstract
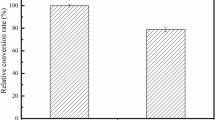
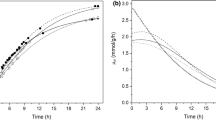
Escherichia coli cells expressing l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana (TNAI) were immobilized in calcium alginate beads. The resulting cell reactor (2.4 U, t 1/2 = 43 days at 70°C) in a continuous recycling mode at 70°C produced 49 and 38 g d-tagatose/l from 180 and 90 g d-galactose/l, respectively, within 12 h.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi S, Sugawara H (1963) Separation of ketose and aldose by chromatography on an ion-exchange column. Arch Biochem Biophys 100:468–471
Beadle JR, Saunders JP, Wajda TJ (1992) Process for manufacturing tagatose. U.S. Patent 5,078,796
Busto MD (1998) An experiment illustrating the effect of immobilization on enzyme properties. Biochem Educ 26:304–308
Cheetham PSJ, Wootton AN (1992) Bioconversion of d-galactose into d-tagatose. Enzyme Microb Technol 15:105–108
Dische Z, Borefreund E (1951) A new spectrophotometric method for the detection and determination of keto sugars and trioses. J Biol Chem 192:583–587
Ibrahim OO, Spradlin JE (2000) Process for manufacturing d-tagatose. U.S. Patent 6,057,135
Jørgensen F, Hansen OC, Stougaard P (2004) Enzymatic conversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose:heterologous expression and characterization of a thermostable l-arabinose isomerase from Thermoanaerobacter mathranii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64:816–822
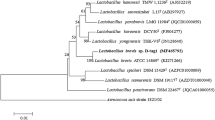
Kim BC, Lee YH, Lee HS, Lee DW, Choe EA, Pyun YR (2002) Cloning, expression and characterization of l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana: bioconversion of d-galactose to d-tagatose using the enzyme. FEMS Microbiol Lett 212:121–126
Lee DW, Jang HJ, Choe EA, Kim BC, Lee SJ, Kim SB, Hong YH, Pyun YR (2004) Characterization of a thermostable l-arabinose isomerase (d-galactose) isomerase from the hyperthermophilic eubacterium Thermotoga maritima. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:1397–1404
Lee DW, Choe EA, Kim SB, Eom SH, Hong YH, Lee SJ, Lee HS, Lee DY, Pyun YR (2005a) Distinct metal dependence for catalytic and structural functions in the l-arabinose isomerases from the mesophilic Bacillus halodurans and the thermophilic Geobacillus stearothermophilius. Arch Biochem Biophys 434:333–343
Lee DW, Hong YH, Choe EA, Lee SJ, Kim SB, Lee HS, Oh JW, Shin HH, Pyun YR (2005b) A thermodynamic study of mesophilic, thermophilic, and hyperthermophilic l-arabinose isomerases: the effects of divalent metal ions on protein stability at elevated temperatures. FEBS Lett 579:1261–1266
Lernia ID, Schiraldi C, Generoso M, Rosa MD (2002) Trehalose production at high temperature exploiting an immobilized cell reactor. Extremophiles 6:341–347
Levin GV (2002) Tagatose, the new GRAS sweetener and health product. J Med Food 5:23–36
Nabors LO (2002) Sweet choices:sugar replacements for foods and beverages. Food Technol 56:28–45
Ortega N, Busto MD, Perez-Mateos M (1998) Stabilization of β-glucosidase entrapped in alginate and polyacrylamide gels towards thermal and proteolytic deactivation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 73:7–12
Ryu SA, Kim CS, Kim HJ, Baek DH, Oh DK (2003) Continuous d-tagatose production by immobilized thermostable l-arabinose isomerase in a packed-bed bioreactor. Biotechnol Prog 19:1643–1647
Shaw CJ, Huang A, Zhang X (2003) Quantitation and test of enantiomeric purity of the l-ketohexoses by liquid chromatography with dual refractive index and laser-based chiroptical detection. J Chromatogr A 987:439–443
Tewari YB, Goldberg RN (1985) An investigation of the equilibria between aqueous ribose, ribulose, and arabinose. Biophys Chem 22:197–204
Tewari YB, Steckler DK, Goldberg RN (1985) Thermodynamics of the conversion of aqueous xylose to xylulose. Biophys Chem 22:181–185
Zehner LR (1988) d-Tagatose as a low-calorie carbohydrate sweetener and bulking agent. U.S. Patent 4,786,722
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grant 2001-2-0109 from the Korea Science and Engineering Foundation and grant AIC-08-02 from the Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Energy, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, YH., Lee, DW., Lee, SJ. et al. Production of d-tagatose at high temperatures using immobilized Escherichia coli cells expressing l-arabinose isomerase from Thermotoga neapolitana . Biotechnol Lett 29, 569–574 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9277-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9277-2