Abstract
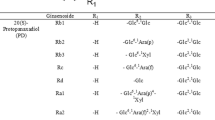
Ginsenosides Rb1 and Re, respectively belonging to the major protopanaxadiol and protopanaxatriol ginsenosides, were transformed using cell-free extracts from food microorganisms. Rb1 was transformed into compound K via Rd and F2 by Bifidobacterium sp. Int57, Bif. sp. SJ32, Aspergillus niger and A.␣usamii. Lactobacillus delbrueckii, and Leuconostoc paramesenteroides transformed Rb1 into Rh2 via Rd and F2. Bifidobacterium sp. SH5 transformed Rb1 into F2 via Rd. Re was transformed into Rh1 via Rg2 by Bif. sp. Int57 and Bif. sp. SJ32. A. niger transformed Re into Rh1 via Rg1. A. usamii transformed Re into Rg2. Transformation of Rb1 proceeded at a higher rate and needed less amount of enzymes than that of Re. Taken together, these processes would allow a specific bioconversion process possible to obtain specific ginsenosides using an appropriate combination of ginsenoside substrates and specific microbial enzymes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D Aling Y Min G Hongzhu Z Junhua G Dean (2003) ArticleTitleMicrobial transformation of ginsenoside Rb1 by Rhizopus stolonifer and Curvularia lunata Biotechnol. Lett. 25 339–344 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1022320824000 Occurrence Handle12882549
EA Bae SY Park DH Kim (2000) ArticleTitleConstitutive beta-glucosidases hydrolyzing ginsenoside Rb1 and Rb2 from human intestinal bacteria Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23 1481–1485 Occurrence Handle11145182
EA Bae MJ Han MK Choo SY Park DH Kim (2002) ArticleTitleMetabolism of 20(S)- and 20(R)-ginsenoside Rg3 by human intestinal bacteria and its relation to in vitro biological activities Biol. Pharm. Bull. 25 58–63 Occurrence Handle10.1248/bpb.25.58 Occurrence Handle11824558
Chang HM (1986) Pharmacology and Application of Chinese Material Medica. Vol 1. Singapore. World Scientific
EK Choi GE Ji (2005) ArticleTitleFood microorganisms that effectively hydrolyze O-glycoside but not C-glycoside isoflavones in Puerariae radix J. Food Sci. 70 C25–C28
BH Han MH Park YN Han LK Woo U Sankawa S Yahara O Tanaka (1982) ArticleTitleDegradation of ginseng saponins under mild acidic conditions Planta Med. 44 146–149
HS Kim EH Lee SR Ko KJ Choi JH Park DS Im (2004) ArticleTitleEffects of ginsenosides Rg3 and Rh2 on the proliferation of prostate cancer cells Arch. Pharm. Res. 27 429–435 Occurrence Handle15180309
SR Ko KJ Choi K Uchida Y Suzuki (2003) ArticleTitleEnzymatic preparation of ginsenosides Rg2, Rh1, and F1 from protopanaxatriol-type ginseng saponin mixture Planta Med. 69 285–286 Occurrence Handle10.1055/s-2003-38476 Occurrence Handle12677539
K Kudo E Tachikawa T Kashimoto E Takahashi (1998) ArticleTitleProperties of ginseng saponin inhibition of catecholamine secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells Eur. J. Pharmacol. 341 139–144 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0014-2999(97)01350-2 Occurrence Handle9543231
SJ Lee WG Ko JH Kim JH Sung CK Moon BH Lee (2000) ArticleTitleInduction of apoptosis by a novel intestinal metabolite of ginseng saponin via cytochrome c-mediated activation of caspase-3 protease Biochem. Pharmacol. 60 677–685 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0006-2952(00)00362-2 Occurrence Handle10927026
M Mochizuki CY Yoo K Mtsuzawa K Sato I Saiki S Tono-oda K Samukiwa I Azuma (1995) ArticleTitleInhibitory effect of tumor metastasis in mice by saponins, ginsenoside Rb2, 20(R)- and 20(S)-ginsenoside Rg3, of Red ginseng Biol. Pharm. Bull. 18 1197–1202 Occurrence Handle8845804
EK Park MK Choo MJ Han DH Kim (2004) ArticleTitleGinsenoside Rh1 possesses antiallergic and anti-inflammatory activities Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 133 113–120 Occurrence Handle10.1159/000076383 Occurrence Handle14739579
SY Park GE Ji YT Ko HK Jung Z Ustunol JJ Pestka (1999) ArticleTitlePotentiation of hydrogen peroxide, nitric oxide, and cytokine production in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells exposed to human and commercial isolates of Bifidobacterium Int. J. Food Microbiol. 46 231–241 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-1605(98)00197-4 Occurrence Handle10100903
YC Park CH Lee HS Kang KW Kim HT Chung HD Kim (1996) ArticleTitleGinsenoside-Rh1 and Rh2 inhibit the induction of nitric oxide synthesis in murine peritoneal macrophages Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 40 751–757 Occurrence Handle8950033
E Tachikawa K Kudo H Hasegawa T Kashimoto K Sasaki M Miyazaki H Taira JM Lindstrom (2003) ArticleTitleIn vitro inhibition of adrenal catecholamine secretion by steroidal metabolites of ginseng saponins Biochem. Pharmacol. 68 441–452
MA Tawab U Bahr M Karas M Wurglics M Schubert-Zsilavecz (2003) ArticleTitleDegradation of ginsenosides in humans after oral administration Drug Metab. Dispos. 31 1065–1071 Occurrence Handle10.1124/dmd.31.8.1065 Occurrence Handle12867496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chi, H., Ji, GE. Transformation of Ginsenosides Rb1 and Re from Panax ginseng by Food Microorganisms. Biotechnol Lett 27, 765–771 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-5632-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-005-5632-y