Abstract
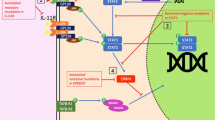
The nuclear factor of activated T lymphocytes (NFATc1) plays a critical role during valvular and septal development. Genetic variants may influence the biological function of the protein and thus play a role in susceptibility to valvuloseptal defects. Tandem repeat polymorphisms and a common nonsynonymous polymorphism (Cys751Gly) of NFATc1 were genotyped in a hospital-based case–control study of 241 patients with valvuloseptal cardiac defects and 557 controls. The risk of valvuloseptal defect associated with the variant homozygote (LL) was significantly greater than that of the wild-type homozygote. Based on stratification analyses by congenital heart disease types, individuals with the LL genotype were postulated to have a higher risk of perimembranous ventricular septal defect (adjusted OR = 1.68, 95% CI = 1.02–2.78). These findings suggest the usefulness of the NFATc1 tandem repeat polymorphism as a biomarker of perimembranous ventricular septal defect susceptibility.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allwork SP, Anderson RH (1979) Developmental anatomy of the membranous part of the ventricular septum in the human heart. Brit Heart J 41:275–280
Armesilla AL, Lorenzo E, Gomez del Arco P, Martinez-Martinez S, Alfranca A, Redondo JM (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor activates nuclear factor of activated T cells in human endothelial cells: a role for tissue factor gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 19:2032–2043
Armstrong EJ, Bischoff J (2004) Heart valve development: endothelial cell signaling and differentiation. Circ Res 95:459–470
Barnett JV, Desgrosellier JS (2003) Early events in valvulogenesis: a signaling perspective. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today 69:58–72
Burn J, Brennan P, Little J, Holloway S, Coffey R, Somerville J, Dennis NR, Allan L, Arnold R, Deanfield JE, Godman M, Houston A, Keeton B, Oakley C, Scott O, Silove E, Wilkinson J, Pembrey M, Hunter AS (1998) Recurrence risks in offspring of adults with major heart defects: results from first cohort of British collaborative study. Lancet 351:311–316
Chakraborty S, Combs MD, Yutzey KE (2010) Transcriptional regulation of heart valve progenitor cells. Pediatr Cardiol 31:414–421
Chang CP, Neilson JR, Bayle JH, Gestwicki JE, Kuo A, Stankunas K, Graef IA, Crabtree GR (2004) A field of myocardial-endocardial NFAT signaling underlies heart valve morphogenesis. Cell 118:649–663
Cleaver O, Melton DA (2003) Endothelial signaling during development. Nat Med 9:661–668
Combs MD, Yutzey KE (2009) VEGF and RANKL regulation of NFATc1 in heart valve development. Circ Res 105:565–574
de la Pompa JL, Timmerman LA, Takimoto H, Yoshida H, Elia AJ, Samper E, Potter J, Wakeham A, Marengere L, Langille BL, Crabtree GR, Mak TW (1998) Role of the NF-ATc transcription factor in morphogenesis of cardiac valves and septum. Nature 392:182–186
Ferencz C, Rubin JD, McCarter RJ, Brenner JI, Neill CA, Perry LW, Hepner SI, Downing JW (1985) Congenital heart disease: prevalence at livebirth. The Baltimore-Washington Infant Study. Am J Epidemiol 121:31–36
Fu YC, Bass J, Amin Z, Radtke W, Cheatham JP, Hellenbrand WE, Balzer D, Cao QL, Hijazi ZM (2006) Transcatheter closure of perimembranous ventricular septal defects using the new Amplatzer membranous VSD occluder: results of the U.S. phase I trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 47:319–325
Hoffman JI (1995a) Incidence of congenital heart disease: I. Postnatal incidence. Pediatr Cardiol 16:103–113
Hoffman JI (1995b) Incidence of congenital heart disease: II. Prenatal incidence. Pediatr Cardiol 16:155–165
Johnson EN, Lee YM, Sander TL, Rabkin E, Schoen FJ, Kaushal S, Bischoff J (2003) NFATc1 mediates vascular endothelial growth factor-induced proliferation of human pulmonary valve endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 278:1686–1692
Lange AW, Molkentin JD, Yutzey KE (2004) DSCR1 gene expression is dependent on NFATc1 during cardiac valve formation and colocalizes with anomalous organ development in trisomy 16 mice. Dev Biol 266:346–360
Marino B, Digilio MC (2000) Congenital heart disease and genetic syndromes: specific correlation between cardiac phenotype and genotype. Cardiovasc Pathol 9:303–315
Nemer G, Nemer M (2002) Cooperative interaction between GATA5 and NF-ATc regulates endothelial-endocardial differentiation of cardiogenic cells. Development 129:4045–4055
Nora JJ (1993) Causes of congenital heart diseases: old and new modes, mechanisms, and models. Am Heart J 125:1409–1419
Peng SL, Gerth AJ, Ranger AM, Glimcher LH (2001) NFATc1 and NFATc2 together control both T and B cell activation and differentiation. Immunity 14:13–20
Pierpont ME, Markwald RR, Lin AE (2000) Genetic aspects of atrioventricular septal defects. Am J Med Genet 97:289–296
Ranger AM, Grusby MJ, Hodge MR, Gravallese EM, de la Brousse FC, Hoey T, Mickanin C, Baldwin HS, Glimcher LH (1998) The transcription factor NF-ATc is essential for cardiac valve formation. Nature 392:186–190
Runyan RB, Markwald RR (1983) Invasion of mesenchyme into three-dimensional collagen gels: a regional and temporal analysis of interaction in embryonic heart tissue. Dev Biol 95:108–114
Srivastava D (2001) Genetic assembly of the heart: implications for congenital heart disease. Annu Rev Physiol 63:451–469
Vannay A, Vasarhelyi B, Kornyei M, Treszl A, Kozma G, Gyorffy B, Tulassay T, Sulyok E (2006) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms of VEGF gene are associated with risk of congenital valvuloseptal heart defects. Am Heart J 151:878–881
Wu H, Kao SC, Barrientos T, Baldwin SH, Olson EN, Crabtree GR, Zhou B, Chang CP (2007) Down syndrome critical region-1 is a transcriptional target of nuclear factor of activated T cells-c1 within the endocardium during heart development. J Biol Chem 282:30673–30679
Yehya A, Souki R, Bitar F, Nemer G (2006) Differential duplication of an intronic region in the NFATC1 gene in patients with congenital heart disease. Genome 49:1092–1098
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30900630), a Jiangsu Province Import Foreign Talent Program grant (S2008320072), a Jiangsu Province Health Department Program grant (H200821, H201046), and the Jiangsu Province Natural Science Foundation (BK2009207).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Haiyong Gu and Jie Gong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, H., Gong, J., Qiu, W. et al. Association of a Tandem Repeat Polymorphism in NFATc1 with Increased Risk of Perimembranous Ventricular Septal Defect in a Chinese Population. Biochem Genet 49, 592–600 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9434-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9434-8