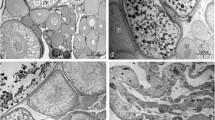
The vasa (vas)-related gene encodes an RNA helicase protein member of the DEAD-box family and plays key roles in germ-cell formation in higher metazoans. Using degenerate PCR and RACE, we cloned the vasa gene of the rice field eel (Monopterus albus), which is homologous to the Drosophila vasa gene. We named it ma-vas (Monopterus albus vas). Ma-vas encodes a protein of 618 amino acids, which contains all of the known characteristics of vasa homologs. RT-PCR analysis revealed that ma-vas was exclusively expressed in the gonads of the female, intersex, and male. During gonadal natural sex reversal, ma-vas is expressed in oocytes at all stages of oogenesis, in degenerating oocytes of ovotestis, and in spermatogonia and spermatocytes at early stages. The vasa positive signal was also observed in the peripheral layer of late ovary. It was not found, however, in that layer of the testis. Alkaline phosphatase (AKP) staining on the ovary and testis also indicated that some cells had differentiational potential in the peripheral layer of the ovary, suggesting that spermatogonia might arise from cells with AKP and vasa-positive staining in the peripheral layer of the female gonad.





Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Castrillon, D. H., Quade, B. J., Wang, T. Y., Quigley, C., and Crum, C. P. (2000). The human VASA gene is specifically expressed in the germ cell lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 97:9585–9590.
Chan, S. T. H. (1975). On the gonadal and adenohypophsial functions of natural sex reversal. In Reinboth, R. (ed.), Intersexuality in the Animal Kingdom, Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 201–222.
Chan, S. T. H. (1977). Spontaneous sex reversal in fishes. In Money, J., and Musaph, H. (eds.), Handbook of Sexology, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 91–105.
Chomczynski, P., and Sacchi, N. (1987). Single step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate phenol chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162:156–159.
Dayhoff, M. O., and Eck, R. V. (1968). Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, National Biomedical Research Foundation, Silver Spring, MD, vol. 3, p. 33.
Dayhoff, M. O., Schwartz, R. M., and Orcutt, B. C. (1979). Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure, National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington, DC, vol. 5, p. 345.
Fan, J., Cai, H., Lin, Y., and Zhang, X. (1999). The serum protein contents and electrophoretic analysis at different developing stages of Monopterus albus. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 18:216–218.
Fujimura, N., and Takamura, K. (2000). Characterization of an ascidian DEAD-box gene, Ci-DEAD1: Specific expression in the germ cells and its mRNA localization in the posterior-most blastomeres in early embryos. Dev. Genes Evol. 210:64–72.
Fujiwara, Y., Komiya, T., Kawabata, H., Sato, M., Fujimoto, H., Furusawa, M., and Noce, T. (1994). Isolation of a DEAD-family protein gene that encodes a murine homolog of Drosophila vasa and its specific expression in germ cell lineage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:12258–12262.
Gould, D. A., Moscoso, G. J., Young, M. P. A., and Barton, D. P. J. (2000). Human first trimester fetal ovaries express oncofetal antigens and steroid receptors. J. Soc. Gynecol. Invest. 7:131–138.
Gruidl, M. E., Smith, P. A., Kuznicki, K. A., McCrone, J. S., Kirchner, J., Roussell, D. L., Strome, S., and Bennett, K. L. (1996). Multiple potential germ-line helicases are components of the germ-line/specific P granules of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93:13837–13842.
Hay, B., Jan, L. Y., and Jan, Y. N. (1988). A protein component of Drosophila polar granules is encoded by vasa and has extensive sequence similarity to ATP-dependent helicases. Cell 55:577–587.
Howley, C., and Ho, R. K. (2000). mRNA localization patterns in zebrafish oocytes. Mech. Dev. 92:305–309.
Hua, C., and Martin, M. M. (2001). Smad5 is required for mouse primordial germ cell development. Mech. Dev. 104:61–67.
Ikenishi, K., and Tanaka, T. S. (1997). Involvement of the protein of Xenopus vasa homolog (Xenopus vasa-like gene 1, XVLG1) in the differentiation of primordial germ cells. Dev. Growth Differ. 39:625–633.
Kimura, M. (1983). The Neutral Theory of Molecular Evolution, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Knaut, H., Steinbeisser, H., Schwarz, H., and Nusslein Volhard, C. (2002). An evolutionary conserved region in the vasa 3′ UTR targets RNA translation to the germ cells in the zebrafish. Curr. Biol. 12:454–466.
Kobayashi, T., Kajiura-Kobayashi, H., and Nagahama, Y. (2000). Differential expression of vasa homolog gene in the germ cells during oogenesis and spermatogenesis in a teleost fish, tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Mech. Dev. 99:139–142.
Komiya, T., Itoh, K., Ikenishi, K., and Furusawa, M. (1994). Isolation and characterization of a novel gene of the DEAD box protein family which is specifically expressed in germ cells of Xenopus laevis. Dev. Biol. 162:354–363.
Kühholzer, B., Baguisi, A., and Overstrom, E. W. (2000). Long-term culture and characterization of goat primordial germ cells. Theriogenology 53:1071–1079.
Kuznicki, K. A., Smith, P. A., Leung-Chiu, W. M., Estevez, A. O., Scott, H. C., and Bennett K. L. (2000). Combinatorial RNA interference indicates GLH-4 can compensate for GLH-1: These two P granule components are critical for fertility in C. elegans. Development 127(13):2907–2916.
Lasko, F., and Ashburner, M. (1988). The product of the Drosophila gene vasa is very similar to eucaryotic initiation factor-4A. Nature 335:611–617.
Liang, L., Diehl-Jones, W., and Lasko, P. (1994). Localization of Vasa protein to the Drosophila pole plasm is independent of its RNA-binding and helicase activities. Development 120:1201–1211.
Liu, R., Wan, H., Su, B., Zhang, F., and Han D. (1987). Relationship between sex reversal and serum proteins in Monopterus. Acta Hydrobiol. Sin. 11:22–28.
Liu, Y.-G., and Whittier, R. F. (1995). Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: Automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from P1 and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25(3):674–681.
Lu, H., Cheng, H., Guo, Y., and Zhou, R. (2003). Two alleles of the Sox9a2 in the rice field eel. J. Exp. Zool. (Mol. Dev. Evol.) 299B:36–40.
Lv Daoyuan, Song Ping, Chen Yungui, Gong Wuming, and Mo Saijun. (2005). Cloning and characterization of full-length of a novel zebrafish gene Zsrg abundantly expressed in the germline stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329:632–637.
Olsen, L. C., Aasland, R., and Fjose, A. (1997). A vasa-like gene in zebrafish identifies putative primordial germ cells. Mech. Dev. 66:95–105.
Pennetier, S., Uzbekova, S., Perreau, C., Papillier, P., Mermillod, P., and Dalbies-Tran, R. (2004). Spatio-temporal expression of the germ cell marker genes MATER,ZAR1, GDF9, BMP15,and VASA in adult bovine tissues, oocytes, and preimplantation embryos. Biol. Reprod. 71:1359–1366.
Roussell, D., and Bennett, K. L. (1993). glh-1, a germ-line putative RNA helicase from Caenorhabditis has four zinc fingers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90:9300–9304.
Schmid, S. R., and Linder, P. (1992). D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol. Microbiol. 6:283–292.
Schu, P., Bach, T., and Wieschaus, E. (1986). Maternal-effect mutations altering the anterior-posterior pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Roux’s Arch. Dev. Biol. 195:302–317.
Shibata, N., Umesono, Y., Orii, H., Sakurai, T., Watanabe, K., and Agata, K. (1999). Expression of vasa(vas)-related genes in germline cells and totipotent somatic stem cells of planarians. Dev. Biol. 206:73–87.
Shimomiya, A., Tanak, M., Kobayashi, T., Nagahama, Y., and Hamaguchi, S. (2000). The vasa-like gene, olvas, identifies the migration path of primordial germ cells during embryonic body formation stage in the medaka, Oryzias latipes. Dev. Growth Differ. 42:317–326.
Song, P., Malhotra, P., Tuteja, N., and Chauhan, V. S. (1999). RNA helicase-related genes of Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium cynomolgi. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 255:312–316.
Styhler, S., Nakamura, A., Swan, A., Suter, B., and Lasko, P. (1998). vasa is required for GURKEN accumulation in the oocyte, and is involved in oocyte differentiation and germline cyst development. Development 125:1569–1578.
Thompson, J. D., Gibson, T. J., Plewniak, F., Jeanmougin, F., and Higgins, D. G. (1997). The ClustalX Windows interface: Flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:4876–4882.
Tomancak, P., Guichet, A., Zavorszky, P., and Ephrussi, A. (1998). Oocyte polarity depends on regulation of gurken by Vasa. Development 125:1723–1732.
Tsunekawa, N., Naito, M., Sakai, Y., Nishida, T., and Noce, T. (2000). Isolation of chicken vasa homolog gene and tracing the origin of primordial germ cells. Development 127:2741–2750.
Wang, R., Cheng, H., Xia, L., Guo, Y., Huang, X., and Zhou, R. (2003). Molecular cloning and expression of Sox17 in gonads during sex reversal in the rice field eel, a teleost fish with a characteristic of natural sex transformation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 303:452–457.
Xia, L., Cheng, H., Yu, H., Guo, Y., and Zhou, R. (2004). Molecular cloning and expression of the osteoclast-stimulating-factor-like gene from the rice field eel. J. Exp. Zool. (Mol. Dev. Evol.) 302B:174–181.
Xiao, Y. (1993). Study on the reproductive biology of Monopterus albus (Zuiew) 1: Early gonadogenesis and structure change Monopterus albus. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Norm. Hunan 16:346–349.
Xiao, Y. (1995). Study on the reproductive biology of Monopterus albus (Zuiew) 2: Female development of Monopterus albus. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Norm. Hunan 18:45–51.
Xiao, Y., and Liu, Y. (1995). Study on the histology in sex changing from intersex to male of Monopterus albus. J. Fish. China 19:297–304.
Xu, H., Gui, J., and Hong, Y. (2005). Differential expression of vasa RNA and protein during spermatogenesis and oogenesis in the gibel carp (Carassius auratus gibelio), a bisexually and gynogenetically reproducing vertebrate. Dev. Dyn. 233:872–882.
Yoon, C., Kawakami, K., and Hopkins, N. (1997). Zebrafish vasa homolog RNA is localized to the cleavage planes of 2- and 4-cell-stage embryos and is expressed in the primordial germ cells. Development 124:3157–3166.
Yoshizaki, G., Sakatani, S., Tominaga, H., and Takeuchi, T. (2000). Cloning and characterization of a vasa-like gene in rainbow trout and its expression in the germ cell lineage. Mol. Rep. Dev. 55:364–371.
Yu, H., Cheng, H., Guo, Y., Xia, L., and Zhou, R. (2003). Alternative splicing and differential expression of P450c17 (CYP17) in gonads during sex transformation in the rice field eel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 307:165–171.
Zhou, R., Cheng, H., and Tiersch, R. T. (2002). Differential genome duplication and fish diversity. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 11:331–337.
Zhou, R., Liu, L., Guo, Y., Yu, H., Cheng, H., Huang, X., Tiersch, E. R., and Berta, P. (2003). Similar gene structure of two Sox9a genes and their expression patterns during gonadal differentiation in a teleost fish, rice field eel (Monopterus albus). Mol. Rep. Dev. 66:211–217.
Zou, J. (2000). Analysis of the relationship between sexual reversal and serum proteins. Chin. J. Irrigation Fish. 20:13–15.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by grants from the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology (CRP/CHN02-01), National 973 Project (No. 2004CB117400), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 30270675 and 30150005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, D., Lv, D., Song, P. et al. Cloning and Characterization of a Rice Field Eel vasa-Like Gene cDNA and Its Expression in Gonads During Natural Sex Transformation. Biochem Genet 45, 211–224 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9066-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-006-9066-6