Abstract
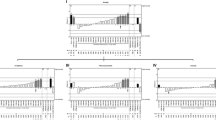
The expression of motor activity levels in response to novel situations is under complex genetic and environmental control. Several genetic loci have been implicated in the regulation of this behavioral phenotype, but their relationship to epigenetic and epistatic interactions is relatively unknown. Here, we report on a quantitative trait locus (QTL) on mouse chromosome 1 for novelty-induced motor activity in the open field, using chromosome substitution strains derived from a high active host strain (C57BL/6J) and a low active donor strain (A/J). The QTL for open field (horizontal distance moved) peaked at the location of Kcnj9, however, QTL detection was initially masked by an interplay of both grandparent genetic origin and genetic co-factors influencing behavior on chromosome 1. Our findings indicate that epigenetic interactions can play an important role in the identification of behavioral QTLs and must be taken into consideration when applying behavioral genetic strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisman H, Zaharia MD, Meaney MJ, Merali Z (1998) Do early-life events permanently alter behavioral and hormonal responses to stressors? Int J Dev Neurosci 16:149–164. doi:10.1016/S0736-5748(98)00025-2
Calatayud F, Coubard S, Belzung C (2004) Emotional reactivity in mice may not be inherited but influenced by parents. Physiol Behav 80:465–474. doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2003.10.001
Constancia M, Pickard B, Kelsey G, Reik W (1998) Imprinting mechanisms. Genome Res 8:881–900
Cowley DE, Pomp D, Atchley WR, Eisen EJ, Hawkins-Brown D (1989) The impact of maternal uterine genotype on postnatal growth and adult body size in mice. Genetics 122:193–203
de Ledesma AM, Desai AN, Bolivar VJ, Symula DJ, Flaherty L (2006) Two new behavioral QTLs, Emo4 and Reb1, map to mouse Chromosome 1: Congenic strains and candidate gene identification studies. Mamm Genome 17:111–118. doi:10.1007/s00335-005-0107-y
Flint J, Corley R, DeFries JC, Fulker DW, Gray JA, Miller S, Collins AC (1995) A simple genetic basis for a complex psychological trait in laboratory mice. Science 269:1432–1435. doi:10.1126/science.7660127
Francis DD, Szegda K, Campbell G, Martin WD, Insel TR (2003) Epigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice. Nat Neurosci 6:445–446
Gershenfeld HK, Paul SM (1997) Mapping quantitative trait loci for fear-like behaviors in mice. Genomics 46:1–8. doi:10.1006/geno.1997.5002
Gill KJ, Boyle AE (2005) Quantitative trait loci for novelty/stress-induced locomotor activation in recombinant inbred (RI) and recombinant congenic (RC) strains of mice. Behav Brain Res 161:113–124. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2005.01.013
Henderson ND, Turri MG, DeFries JC, Flint J (2004) QTL analysis of multiple behavioral measures of anxiety in mice. Behav Genet 34:267–293. doi:10.1023/B:BEGE.0000017872.25069.44
Hitzemann R, Demarest K, Koyner J, Cipp L, Patel N, Rasmussen E, McCaughran J Jr (2000) Effect of genetic cross on the detection of quantitative trait loci and a novel approach to mapping QTLs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 67:767–772. doi:10.1016/S0091-3057(00)00421-4
Hitzemann R, Malmanger B, Reed C, Lawler M, Hitzemann B, Coulombe S, Buck K, Rademacher B, Walter N, Polyakov Y, Sikela J, Gensler B, Burgers S, Williams RW, Manly K, Flint J, Talbot C (2003) A strategy for the integration of QTL, gene expression, and sequence analyses. Mamm Genome 14:733–747. doi:10.1007/s00335-003-2277-9
Holmes A, le Guisquet AM, Vogel E, Millstein RA, Leman S, Belzung C (2005) Early life genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors shaping emotionality in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1335–1346. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2005.04.012
Ikeda K, Onaka T, Yamakado M, Nakai J, Ishikawa TO, Taketo MM, Kawakami K (2003) Degeneration of the amygdala/piriform cortex and enhanced fear/anxiety behaviors in sodium pump alpha2 subunit (Atp1a2)-deficient mice. J Neurosci 23:4667–4676
Isles AR, Holland AJ (2005) Imprinted genes and mother-offspring interactions. Early Hum Dev 81:73–77. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2004.10.006
Jansen RC (1994) Controlling the type I and type II errors in mapping quantitative trait loci. Genetics 138:871–881
Kas MJ, Van Ree JM (2004) Dissecting complex behaviours in the post-genomic era. Trends Neurosci 27:366–369. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2004.04.011
Kas MJ, de Mooij-van Malsen AJ, Olivier B, Spruijt BM, Van Ree JM (2008a) Differential genetic regulation of motor activity and anxiety-related behaviors in mice using an automated home cage task. Behav Neurosci 122:769–776. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.122.4.769
Kas MJ, Mooij-van Malsen A, de Krom M, van Gassen KL, van Lith HA, Olivier B, Oppelaar H, Hendriks J, de Wit M, Groot Koerkamp MJ, Holstege FC, van Oost BA, de Graan PN (2008b) High resolution genetic mapping of mammalian motor activity levels in mice. Genes Brain Behav. doi:10.1111/j.1601-183X.2008.00435.x
Kelly MA, Low MJ, Phillips TJ, Wakeland EK, Yanagisawa M (2003) The mapping of quantitative trait loci underlying strain differences in locomotor activity between 129S6 and C57BL/6J mice. Mamm Genome 14:692–702. doi:10.1007/s00335-003-2273-0
Lander ES, Botstein D (1989) Mapping mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkage maps. Genetics 121:185–199
Leygraf A, Hohoff C, Freitag C, Willis-Owen SA, Krakowitzky P, Fritze J, Franke P, Bandelow B, Fimmers R, Flint J, Deckert J (2006) Rgs 2 gene polymorphisms as modulators of anxiety in humans? J Neural Trans 113:1921–1925. doi:10.1007/s00702-006-0484-8
Liu Y, Zeng ZB (2000) A general mixture model approach for mapping quantitative trait loci from diverse cross designs involving multiple inbred lines. Genet Res 75:345–355. doi:10.1017/S0016672300004493
Mott R, Talbot CJ, Turri MG, Collins AC, Flint J (2000) A method for fine mapping quantitative trait loci in outbred animal stocks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:12649–12654. doi:10.1073/pnas.230304397
Nadeau JH, Singer JB, Matin A, Lander ES (2000) Analysing complex genetic traits with chromosome substitution strains. Nat Genet 24:221–225. doi:10.1038/73427
Rosen GD, Chesler EJ, Manly KF, Williams RW (2007) An informatics approach to systems neurogenetics. Methods Mol Biol 401:287–303 Clifton
Singer JB, Hill AE, Burrage LC, Olszens KR, Song J, Justice M, O’Brien WE, Conti DV, Witte JS, Lander ES, Nadeau JH (2004) Genetic dissection of complex traits with chromosome substitution strains of mice. Science 304:445–448. doi:10.1126/science.1093139
Singer JB, Hill AE, Nadeau JH, Lander ES (2005) Mapping quantitative trait Loci for anxiety in chromosome substitution strains of mice. Genetics 169:855–862. doi:10.1534/genetics.104.031492
Talbot CJ, Nicod A, Cherny SS, Fulker DW, Collins AC, Flint J (1999) High-resolution mapping of quantitative trait loci in outbred mice. Nat Genet 21:305–308. doi:10.1038/6825
Turri MG, Talbot CJ, Radcliffe RA, Wehner JM, Flint J (1999) High-resolution mapping of quantitative trait loci for emotionality in selected strains of mice. Mamm Genome 10:1098–1101. doi:10.1007/s003359901169
Turri MG, Henderson ND, DeFries JC, Flint J (2001) Quantitative trait locus mapping in laboratory mice derived from a replicated selection experiment for open-field activity. Genetics 158:1217–1226
Tycko B, Morison IM (2002) Physiological functions of imprinted genes. J Cell Physiol 192:245–258. doi:10.1002/jcp.10129
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JOINMAP 3.0 software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Van Ooijen JW, Boer MP, Jansen RC, Maliepaard C (2002) MAPQTL 4.0 software for the calculation of QTL positions on genetic maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Yalcin B, Willis-Owen SA, Fullerton J, Meesaq A, Deacon RM, Rawlins JN, Copley RR, Morris AP, Flint J, Mott R (2004) Genetic dissection of a behavioral quantitative trait locus shows that Rgs2 modulates anxiety in mice. Nat Genet 36:1197–1202. doi:10.1038/ng1450
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Tamara Phillips.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Mooij-van Malsen, J.G., van Lith, H.A., Oppelaar, H. et al. Evidence for Epigenetic Interactions for Loci on Mouse Chromosome 1 Regulating Open Field Activity. Behav Genet 39, 176–182 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-008-9243-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-008-9243-y