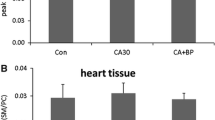
Changes in the phospholipid composition of cardiomyocyte plasma membranes during hemorrhagic shock suggest that disturbances in phosphatidylethanolamine metabolism serve as one of the major factors for myocardial alteration in shock. Depletion of membrane phosphatidylcholine causes destruction of cardiomyocytes. The enhanced breakdown of membrane sphingomyelin at the late stage of hemorrhagic shock is considered as a mechanism, which induces apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and Ca2+ accumulation in these cells. A simultaneous increase in the content of membrane phosphatidylserine is the mechanism of activation of opioid receptors, which plays a compensatory role.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O. S. Belokoneva and S. V. Zaitsev, Biokhimiya, 58, No. 1, 1685–1708 (1993).
A. A. Vartanyan, G. V. Aprikyan, and B. F. Vanyushin, Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR. Ser. Biol., No. 5, 786–789 (1990).
A. A. Dizhe, A. I. Levshankov, I. E. Krasovskaya, et al., Anest. Reanim., No. 4, 40–43 (2001).
V. T. Dolgikh, Damage and Protection of the Heart during Acute Fatal Blood Loss [in Russian], Omsk (2002).
L. N. Maslov, Yu. B. Lishmanov, G. D. Gross, et al., Vestn. Aritmol., No. 28, 67–78 (2002).
V. S. Orlov, Mechanisms of Vesicular Transport [in Russian], Moscow (1995).
V. E. Benediktsdóttir, J. Curvers, and S. Gudbjarnason, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 31, No. 5, 1105–1115 (1999).
Y. A. Hannun, C. Luberto, and K. M. Argraves, Biochemistry, 40, No. 16, 4893–4903 (2001).
A. M. Kidwai, M. A. Radcliffe, G. Duchon, and E. E. Daniel, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 45, No. 4, 901–910 (1971).
S. Persad and V. Panagia, J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 27, No. 1, 579–587 (1995).
Y. Sang, D. Cui, and X. Wang, Plant Physiol., 126, No. 4, 1449–1458 (2001).
S. Seraskeris, C. Gaitanaki, and A. Lazou, Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 392, No. 1, 117–122 (2001).
M. Soliman and A. M. Al-Drees, Pak. J. Med. Sci., 25, 289–292 (2009).
K. Törnquist, T. Blom, R. Shariatmadari, and M. Pasternack, Biochem. J., 380, Pt. 3, 661–668 (2004).
C. R. Winter and R. C. Baker, Life Sci., 57, No. 21, 1925–1934 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Byulleten’ Eksperimental’noi Biologii i Meditsiny, Vol. 151, No. 3, pp. 255-258, March, 2011
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leskova, G.F., Kryzhanovsky, G.N. Changes in Phospholipid Composition of Cardiomyocyte Plasma Membranes during Hemorrhagic Shock. Bull Exp Biol Med 151, 284–287 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1310-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10517-011-1310-3