Abstract
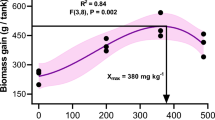
The experiment was conducted to investigate the effects of prepared hairtail protein hydrolysate–Fe2+ (PH–Fe2+) complexes on growth and non-specific immune responses of crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). The diets with five different levels of PH–Fe2+ (200, 400, 600, 800, and 1000 mg/kg) were fed to crayfish for 60 days. The results indicated that the survival rate, weight gain percentage, specific growth rate, and muscle index of crayfish with 400–1000 mg/kg of PH–Fe2+ feeding were significantly higher, 9.94–10.10, 8.55–8.72, 0.24–0.29 %/day, and 2.39–3.05 %, respectively, than the control values after 60 days of feeding. Additionally, after 30 days of feeding, 200–400 mg/kg of PH–Fe2+ showed no significant (P > 0.05) improvement effect on activities of superoxide dismutase (SOD), phenoloxidase (PO), lysozyme (LSZ), and acid phosphatase (ACP) in serum or hepatopancreas of crayfish. However, significant improvement effects were observed in 800–1000 mg/kg groups. After 60 days of feeding, 400–600 mg/kg of PH–Fe2+ significantly (P < 0.05) improved the activity of SOD and LSZ, but did not affect the activity of PO and ACP significantly (P > 0.05). Moreover, the activities of SOD, PO, LSZ, and ACP in serum and hepatopancreas were all significantly enhanced upon treatment with 800–1000 mg/kg of PH–Fe2+. For these reasons, PH–Fe2+ can be recommended as a supplement in crayfish feed to increase the growth and immunity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis, 15th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemists Inc, Virginia
Apines-Amar MJS, Satoh S, Caipang CMA, Kiron V, Watanabe T, Aoki T (2004) Amino acid-chelate: a better source of Zn, Mn and Cu for rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquaculture 240(1):345–358
Chaud MV, Izumi C, Nahaal Z, Shuhama T, Bianchi MLP (2002) Iron derivatives from casein hydrolysates as a potential source in the treatment of iron deficiency. J Agric Food Chem 50(4):871–877
De la Hoz L, Nunes da Silva VS, Morgano MA, Pacheco MTB (2014) Small peptides from enzymatic whey hydrolyzates increase dialyzable iron. Int Dairy J 38:145–147
Deng SG, Huo JC, Xie C (2008) Preparation by enzymolysis and bioactivity of iron complex of fish protein hydrolysate (Fe-FPH) from low value fish. Chin J Oceanol Limnol 26:300–306
Dörr AJM, Abete MC, Prearo M, Pacini N, Porta GL, Natali M, Elia AC (2013) Effects of selenium supplemented diets on growth and condition indexes in juvenile red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii. Environ Toxicol Phar 36(2):484–492
Gollas-Galván T, Hernández-López J, Vargas-Albores F (1999) Prophenoloxidase from brown shrimp (Penaeus californiensis) hemocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol B 122(1):77–82
Guo CR, Guo QQ, Fang XJ, Zeng QZ, Li GL (2010) Effect of peptides chelating zinc on the growth and serum biochemical performance of Tilapiagalilaea (Oreochromis niloticus). China Feed 23:35–37
Guo L, Harnedy PA, Li B, Hou H, Zhang Z, Zhao X, FitzGerald RJ (2014) Food protein-derived chelating peptides: biofunctional ingredients for dietary mineral bioavailability enhancement. Trends Food Sci Technol 37(2):92–105
Jiravanichpaisal P, Lee BL, Söderhäll K (2006) Cell-mediated immunity in arthropods: hematopoiesis, coagulation, melanization and opsonization. Immunobiology 211(4):213–236
Lin RH, Pan Y, Luo L, Ma X, Zhan RR, Mao SH (2011) Effects of different sources of iron, zinc, manganese and copper on growth, metabolism and non-specific immunity of Tilapia (Oreochrom isniloticus). Chin J Anim Nutr 23(5):763–770
Lin HM, Zhang B, Deng SG, Tang Y, Chen DJ (2012) Free radical scavenging activities and antibacterial activity of enzymatic hydrolysates protein ferrous chelates peptides from several low value fish of Zhoushan sea area. J Chin Inst Food Sci Technol 12(1):19–24
Lv Y, Bao XL, Yang BC, Ren CG, Guo ST (2008) Effect of soluble soybean protein hydrolysate-calcium complexes on calcium uptake by Caco-2 cells. J Food Sci 73(7):168–173
Pan JX, Lin XT, Cheng WX, Lin JH, Zhang CH (2007) The effect of shrimp-head extract on growth and immune factors of Litopenaeus vannamei. Ecol Sci 224(6):763–767
Ren XF, Zhou X, Zhao CY, Shui Y, Xu ZH, Shen HS, Zhang P, Bo AX (2013) Effects of dietary chitosan supplementation on growth, non-specific immune factors, muscle compositions and activities of digestive enzymes in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkia. J Dalian Ocean Univ 28(5):468–474
Roslan J, Yunos KFM, Abdullah N, Kama SM (2014) Characterization of fish protein hydrolysate from Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by-product. Agric Agric Sci Proced 2:312–319
Sang HM, Fotedar R, Filer K (2011) Effects of dietary mannan oligosaccharide on the survival, growth, immunity and digestive enzyme activity of freshwater crayfish, Cherax destructor Clark (1936). Aquac Nutr 17(2):e629–e635
Shi XZ, Zhao XF, Wang JX (2014) A new type antimicrobial peptide astacidin functions in antibacterial immune response in red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Dev Comp Immunol 43(1):121–128
Wang JG, Lu HD (2011) Changes of the activities of nonspecific immunity factors of Procambarus clarkii exposed to zinc sulphate. Jiangsu J Agric Sci 27(1):129–136
Xie LF, Xiao D, Yin D, Wu ZX, Chen XX (2007) Effects of Bacillus subtilis on immune functions of Procambarus clarkia. Freshw Fish 37(6):24–27
Xu QL, Zeng QZ, Yan L, Lin JY, Gu CQ, Zhan Y, Fan YM, Huang RQ (2010) Preparation and biological activities of Zn(II)-Tilapia peptide complexes. Food Sci 31(10):75–79
Yang C, Kong J, Wang Q, Liu Q, Tian Y, Luo K (2007) Heterosis of haemolymph analytes of two geographic populations in Chinese shrimp Fenneropenaeus chinensis. Fish Shellfish Immun 23(1):62–70
Zhang B, Deng SG, Lin HM (2011) Preparation and application of an agent (protein hydrolysate-Fe2+ complex) used for removal of heavy metals from the living aquatic species. China Patent ZL 201110197874.7. Accessed 13 July 2011
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Fund project, China (Grant No. 31201452), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang province (Grant No. LY14C 200002), and Science and technology project of Zhoushan (Grant Nos. 2013C11007 and 2013C41015). We thank LetPub for its linguistic assistance during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Shi, Zr., Wang, Xl. et al. The effects of hairtail protein hydrolysate–Fe2+ complexes on growth and non-specific immune response of red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Aquacult Int 24, 1039–1048 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-9969-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-016-9969-0