Abstract
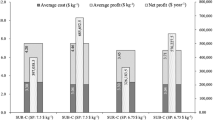
Economic feasibility studies regarding aquaculture systems are relatively scarce, but they are important to potential investors and for the allocation of resources for research and technological development. This study evaluated the economic viability of cobia cage culture from the actual investment and operational costs of a large-scale operation off Recife, northeastern Brazil (industrial system; IS), and a family-run farm located in a near-shore area of Rio de Janeiro (familiar system; FS). The IS had twenty-four 1607 m3 floating cages deployed at a depth of 24 m, while the FS had six 75 m3 wooden cages installed in a sheltered 6- to 7-m-deep area. Analyses of profitability (gross revenue, operational profit, cost price and break-even production) and investment (net present value—NPV; and payback time) were performed. An analysis of sensitivity was also carried out. The IS required an initial investment of approximately US$ 1.5 million dollars and was more sensitive to FCR, selling price and productivity fluctuations than the FS. The FS required a relatively small initial investment (US$ 16,000 dollars), which makes it more flexible to variations in production parameters and market fluctuations. The NPV was positive for both systems, and the payback times were estimated to be 3.88 years for the IS and 2.07 years for the FS. Therefore, given the assumptions of this study, cage culture of cobia in Brazil may be considered economically feasible in offshore production systems and in near-shore, FSs. Governmental support through decreased import taxes is recommended as a way to accelerate the early development of the cage culture of marine fish in Brazil.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldisserotto B, Gomes LC (eds) (2010) Espécies nativas para a piscicultura no Brasil, 2nd edn. Editora da UFSM, Santa Maria
Benetti DD, Orhun MR, Sardenberg B, O’Hanlon B, Welch A, Hoenig R, Zink I, Rivera JA, Denlinger B, Bacoat D, Palmer K, Cavalin F (2008) Advances in hatchery and grow-out technology of cobia Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus). Aquac Res 39:701–711
Beveridge M (2004) Cage aquaculture, 3rd edn. Blackwell Science, London
Bombeo-Tuburan I, Coniza EB, Rodriguez EM, Agbayani RF (2001) Culture and economics of wild grouper (Epinephelus coioides) using three feed types in ponds. Aquaculture 201:229–240
Bostock J, McAndrew B, Richards R, Jauncey K, Telfer T, Lorenzen K, Little D, Ross L, Handisyde N, Gatward I, Corner R (2010) Aquaculture: global status and trends. Philos Trans R Soc B 365:2897–2912
Brazil (2012) Simples nacional e as responsabilidades na área rural - Projeto Cidadania Rural/Serviço Nacional de Aprendizagem Rural– SENAR, 1st edn. Receita Federal do Brasil, Brasília
Cavalli RO, Garcia AS (2012) Exigências nutricionais e alimentação do beijupirá. In: Fracalossi DM, Cyrino JEP (eds) NUTRIAQUA: nutrição e alimentação de espécies de interesse para a aquicultura brasileira, 2nd edn. AQUABIO, Florianópolis
Cavalli RO, Domingues EC, Hamilton S (2011) Desenvolvimento da produção de peixes em mar aberto no Brasil: possibilidades e desafios. Rev Bras Zootec 40:155–164
Costa-Bomfim CN, Pessoa WVN, Oliveira RLM, Farias JL, Domingues EC, Hamilton S, Cavalli RO (2013) The effect of feeding frequency on growth performance of juvenile cobia, Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus, 1766). J Appl Ichthyol 30:135–139
Domingues EC, Hamilton S, Bezerra TRQ, Cavallli RO (2014) Viabilidade econômica da criação do beijupirá em mar aberto em Pernambuco. Bol Inst Pesca 40(2):237–249
Drumm A (2010) Evaluation of the promotion of offshore aquaculture through a technology platform (OATP). Marine Institute, Galway
FAO (2015) Cultured aquatic species information programme—Rachycentron canadum. http://www.fao.org/fishery/culturedspecies/Rachycentron_canadum/en. Cited 02 Sep 2015
Figueiredo JL, Menezes NA (1980) Manual de peixes marinhos do sudeste do Brasil. III. Teleostei (2). Museu de Zoologia da USP, São Paulo
Firretti R, Sales DS, Garcia SM (2007) Lucro com tilápia é para profissionais. Anualpec 2007. Anuário da Pecuária Brasileira. Instituto FNP, São Paulo
Fraser TWK, Davies SJ (2009) Nutritional requirements of cobia, Rachycentron canadum (Linnaeus): a review. Aquac Res 40:1219–1234
Holt GJ, Faulk C, Schwarz M (2007) A review of the larviculture of cobia Rachycentrom canadum, a warmwater marine fish. Aquaculture 268:181–187
Huang C, Miao S, Nan F, Jung S (2011) Study on regional production and economy of cobia (Rachycentron canadum) commercial cage culture. Aquacult Int 19:649–664
Huguenin JE (1997) The design, operations and economics of cage culture systems. Aquacult Eng 16:167–203
Kaiser MJ, Yu Y, Snyder B (2010) Economic feasibility of using offshore oil and gas structures in the Gulf of Mexico for platform-based aquaculture. Mar Policy 34:699–707
Kam LE, Leung PS (2008) Financial risk analysis in aquaculture. In: Bondad-Reantaso MG, Arthur JR, Subasinghe RP (eds) Understanding and applying risk analysis in aquaculture. FAO fisheries and aquaculture technical paper. No. 519. FAO, Rome
Kam LE, Leung PS, Ostrowski AC (2003) Economics of offshore aquaculture of Pacific threadfin (Polydactylus sexfilis) in Hawaii. Aquaculture 223:63–87
Kapetsky JM, Aguilar-Manjarrez J, Jenness J (2013) A global assessment of offshore mariculture potential from a spatial perspective. FAO fisheries and aquaculture technical paper no. 549. FAO, Rome
Kim JH, Gomez DK, Choresca CH Jr, Park SC (2007) Detection of major bacterial and viral pathogens in trash fish used to feed cultured flounder in Korea. Aquaculture 272:105–110
Liao IC, Leaño EM (2007) Cobia aquaculture: research, development and commercial production, 1st edn. Asian Fisheries Society, Taiwan
Liao IC, Huang T, Tsai W, Hsueh C, Chang S, Leaño EM (2004) Cobia culture in Taiwan: current status and problems. Aquaculture 237:155–165
Lima F (2009) Estado realiza operação pioneira. J Commer Recife Econ 25(10):8
Lipton DW, Kim DH (2007) Assessing the economic viability of offshore aquaculture in Korea: an evaluation based on rock bream, Oplegnathus fasciatus, production. J World Aquac Soc 38:506–515
Lisac D, Muir J (2000) Comparative economics of offshore and mariculture facilities. In: Muir J, Basurco B (eds) Mediterranean offshore mariculture. CIHEAM, Zaragoza
Martin NB, Serra R, Oliveira MDM, Angelo JA, Okawa H (1997) Sistema “CUSTAGRI”: sistema integrado de custos agropecuários. IEA/SAA, São Paulo
Matsunaga M, Bemelmans PF, Toledo PEN (1976) Metodologia de custo utilizada pelo IEA. Agricultura em São Paulo 23:123–139
Megliorini E, Vallim MA (2009) Administração financeira: uma abordagem brasileira, 1st edn. Pearson Prentice Hall, São Paulo
Miao S, Tang HC (2002) Bioeconomic analysis of improving management productivity regarding grouper Epinephelus malabaricus farming in Taiwan. Aquaculture 211:151–169
Miao S, Jen CC, Huang CT, Hu SH (2009) Ecological and economic analysis for cobia Rachycentron canadum commercial cage culture in Taiwan. Aquacult Int 17:125–141
MPA - Ministério da Pesca e Aquicultura (2013) Boletim estatístico da pesca e aquicultura—2011. http://www.mpa.gov.br/images/Docs/Informacoes_e_Estatisticas/Boletim%20MPA%202011FINAL3.pdf. Cited on 05 Jan 2014
Natale F, Fiore G, Hofherr J (2011) Mapping the research on aquaculture. A bibliometric analysis of aquaculture literature. Scientometrics 90:983–999
Nguyen QH, Sveier H, Bui VH, Le AT, Nhu VC, Tran MT, Svennevig N (2008) Growth performance of cobia, Rachycentron canadum, in sea cages using extruded fish feed or trash fish. In: Yang Y, Vu XZ, Zhou YQ (eds) Cage aquaculture in Asia: proceeding of the second international symposium on cage aquaculture in Asia. Asian Fishery Society, Manila
Nhu VC, Nguyen QH, Le TL, Tran MT, Sorgeloos P, Dierckens K, Reinertsen H, Kjorsvik E, Svennevig N (2011) Cobia Rachycentron canadum aquaculture in Vietnam: recent developments and prospects. Aquaculture 315:20–25
Petersen EH, Luan TD, Chinn DTM, Tuan VA, Bihn TQ, Truc LV, Glencross BD (2014) Bioeconomics of cobia, Rachycentron canadum, aquaculture in Vietnam. Aquac Econ Manag 18:28–44
Posadas BC, Hanson TR (2006) Economics of integrating nursery systems into indoor biosecure recirculating saltwater shrimp grow-out systems. In: Leung PS, Engle C (eds) Shrimp culture: economics, market, and trade. Blackwell Publishing, Ames
Rombenso AN, Moreira CB, Miranda-Filho KC, Sampaio L (2009) Avaliação do crescimento de bijupirá Rachycentron canadum alimentados com uma dieta comercial e peixe fresco. In: Proceedings of the 2ª Conferência Latino Americana sobre Cultivo de Peces Nativos, Chascomús, Argentina, 2–6 November 2009
Sampaio LAN, Tesser MB, Wasielesky W Jr (2010) Avanços da maricultura na primeira década do século XXI: piscicultura e carcinocultura marinha. Rev Bras Zootec 39:102–111
Sampaio LAN, Moreira CB, Miranda-Filho KC, Rombenso AN (2011) Culture of cobia Rachycentron canadum (L.) in near-shore cages off the Brazilian coast. Aquac Res 42:832–834
Sarker PK, Bureau DP, Hua K, Drew MD, Forster I, Were K, Hicks B, Vandenberg GW (2013) Sustainability issues related to feeding salmonids: a Canadian perspective. Rev Aquac 5:1–21
Schmittou HR (1993) High density fish culture in low volume cages, 1st edn. American Soybean Association, Singapore
Su MS, Chien YH, Liao IC (2000) Potential of marine cage aquaculture in Taiwan: cobia culture. In: Liao IC, Lin CK (eds) Cage aquaculture in Asia—Proceedings of the first international symposium on cage aquaculture in Asia. Asian Fisheries Society, Taiwan, pp 97–109
Whitmarsh DJ, Cook EJ, Black KD (2006) Searching for sustainability in aquaculture: an investigation into the economic prospects for an integrated salmon–mussel production system. Mar Policy 30:293–298
Xie J, Kinnucan HW, Myrland O (2009) Demand elasticities for farmed salmon in world trade. Eur Rev Agric Econ 36:425–445
Zimmermann S, Fitzsimmons K (2004) Tilapicultura intensiva. In: Cyrino JEP, Urbinati EC, Fracalossi DM, Castagnolli N (eds) Tópicos especiais em piscicultura de água doce tropical intensiva. AQUABIO, São Paulo
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ministry of Fisheries and Aquaculture—MPA and the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development—CNPq (559.759/2009-6 and 559.741/2009-0). Thanks to the MPA for the financial resources that allowed the operation of the offshore farm. T.R.Q. Bezerra acknowledges a Ph.D. scholarship from Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—CAPES (Edital Ciências do Mar), and A.N. Rombenso from CNPq/Science without Borders (238.105/2012-1). R.O. Cavalli is a research fellow of CNPq (308.139/2012-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Bezerra, T.R.Q., Domingues, E.C., Maia Filho, L.F.A. et al. Economic analysis of cobia (Rachycentron canadum) cage culture in large- and small-scale production systems in Brazil. Aquacult Int 24, 609–622 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9951-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10499-015-9951-2