Abstract
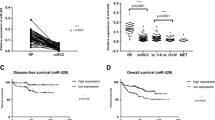
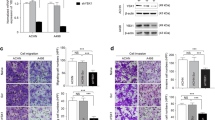
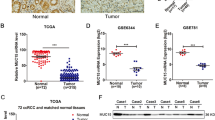
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) is the third most common urological cancer with highly metastatic potential. MAGI1 plays an important role in stabilization of the adherens junctions and has been confirmed to suppress invasiveness and metastasis in multiple cancers in clinic. However, its expression and anti-metastatic ability in RCC are still unclear. In this study, we demonstrated that MAGI1 was markedly decreased in the RCC and indicated poor survival. Furthermore, we found that MAGI1 suppressed the invasion and migration of human RCC cells. Mechanistic investigations revealed that MAGI1 stabilized the PTEN/MAGI1/β-catenin complex to inhibit β-catenin signaling pathway. Moreover, MAGI1 was targeted by miR-520h which was transcriptionally activated by c-Myb. Collectively, our findings suggested that MAGI1mediated tumor metastasis through c-Myb/miR-520h/MAGI1 signaling pathway in RCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424
Barata PC, Rini BI (2017) Treatment of renal cell carcinoma: current status and future directions. CA Cancer J Clin 67(6):507–524
Dabestani S, Thorstenson A, Lindblad P, Harmenberg U, Ljungberg B, Lundstam S (2016) Renal cell carcinoma recurrences and metastases in primary non-metastatic patients: a population-based study. World J Urol 34(8):1081–1086
Lalani AA, McGregor BA, Albiges L, Choueiri TK, Motzer R, Powles T et al (2019) Systemic treatment of metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma in 2018: current paradigms, use of immunotherapy, and future directions. Eur Urol 75(1):100–110
Hakimi AA, Voss MH, Kuo F, Sanchez A, Liu M, Nixon BG et al (2019) Transcriptomic profiling of the tumor microenvironment reveals distinct subgroups of clear cell renal cell cancer: data from a randomized phase III trial. Cancer Discov 9(4):510–525
Knights AJ, Funnell AP, Crossley M, Pearson RC (2012) Holding tight: cell junctions and cancer spread. Trends Cancer Res 8:861–869
Friedl P, Mayor R (2017) Tuning collective cell migration by cell-cell junction regulation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 9(4):a029199
Woodcock SA, Rooney C, Liontos M, Connolly Y, Zoumpourlis V, Whetton AD et al (2009) Src-induced disassembly of adherens junctions requires localized phosphorylation and degradation of the rac activator Tiam1. Mol Cell 33(5):639–653
Abe JI, Ko KA, Kotla S, Wang Y, Paez-Mayorga J, Shin IJ et al (2019) MAGI1 as a link between endothelial activation and ER stress drives atherosclerosis. JCI Insight 4(7):e125570
Feng X, Jia S, Martin TA, Jiang WG (2014) Regulation and involvement in cancer and pathological conditions of MAGI1, a tight junction protein. Anticancer Res 34(7):3251–3256
Zhang G, Wang Z (2011) MAGI1 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma via regulating PTEN. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 36(5):381–385
Zaric J, Joseph JM, Tercier S, Sengstag T, Ponsonnet L, Delorenzi M et al (2012) Identification of MAGI1 as a tumor-suppressor protein induced by cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors in colorectal cancer cells. Oncogene 31(1):48–59
Jia S, Lu J, Qu T, Feng Y, Wang X, Liu C et al (2017) MAGI1 inhibits migration and invasion via blocking MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer Res 29(1):25–35
Kotelevets L, van Hengel J, Bruyneel E, Mareel M, van Roy F, Chastre E (2005) Implication of the MAGI-1b/PTEN signalosome in stabilization of adherens junctions and suppression of invasiveness. FASEB J 19(1):115–117
Wen JL, Wen XF, Li RB, Jin YC, Wang XL, Zhou L et al (2015) UBE3C promotes growth and metastasis of renal cell carcinoma via activating Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0115622
Buttrick GJ, Wakefield JG (2008) PI3-K and GSK-3: Akt-ing together with microtubules. Cell Cycle 7(17):2621–2625
Wu D, Pan W (2010) GSK3: a multifaceted kinase in Wnt signaling. Trends Biochem Sci 35(3):161–168
Zhou BP, Deng J, Xia W, Xu J, Li YM, Gunduz M et al (2004) Dual regulation of Snail by GSK-3beta-mediated phosphorylation in control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 6(10):931–940
Mittal V (2018) Epithelial mesenchymal transition in tumor metastasis. Annu Rev Pathol 13:395–412
Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ (2017) Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med 376(4):354–366
Nguyen MM, Nguyen ML, Caruana G, Bernstein A, Lambert PF, Griep AE (2003) Requirement of PDZ-containing proteins for cell cycle regulation and differentiation in the mouse lens epithelium. Mol Cell Biol 23(24):8970–8981
Ghimire K, Zaric J, Alday-Parejo B, Seebach J, Bousquenaud M, Stalin J et al (2019) MAGI1 mediates eNOS activation and NO production in endothelial cells in response to fluid shear stress. Cells 8(5):388
Sakurai A, Fukuhara S, Yamagishi A, Sako K, Kamioka Y, Masuda M et al (2006) MAGI-1 is required for Rap1 activation upon cell-cell contact and for enhancement of vascular endothelial cadherin-mediated cell adhesion. Mol Biol Cell 17(2):966–976
Ma J, Guo X, Zhang J, Wu D, Hu X, Li J et al (2017) PTEN gene induces cell invasion and migration via regulating AKT/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human gastric cancer. Dig Dis Sci 62(12):3415–3425
Lu Z, Ghosh S, Wang Z, Hunter T (2003) Downregulation of caveolin-1 function by EGF leads to the loss of E-cadherin, increased transcriptional activity of beta-catenin, and enhanced tumor cell invasion. Cancer Cell 4(6):499–515
Liu H, Yin J, Wang H, Jiang G, Deng M, Zhang G et al (2015) FOXO3a modulates WNT/beta-catenin signaling and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal 27(3):510–518
Wang Y, Bu F, Royer C, Serres S, Larkin JR, Soto MS et al (2014) ASPP2 controls epithelial plasticity and inhibits metastasis through beta-catenin-dependent regulation of ZEB1. Nat Cell Biol 16(11):1092–1104
Gurtan AM, Sharp PA (2013) The role of miRNAs in regulating gene expression networks. J Mol Biol 425(19):3582–3600
Pencheva N, Tavazoie SF (2013) Control of metastatic progression by microRNA regulatory networks. Nat Cell Biol 15(6):546–554
Liao R, Sun J, Zhang L, Lou G, Chen M, Zhou D et al (2008) MicroRNAs play a role in the development of human hematopoietic stem cells. J Cell Biochem 104(3):805–817
Zhang J, Liu W, Shen F, Ma X, Liu X, Tian F et al (2018) The activation of microRNA-520h-associated TGF-beta1/c-Myb/Smad7 axis promotes epithelial ovarian cancer progression. Cell Death Dis 9(9):884
Su CM, Wang MY, Hong CC, Chen HA, Su YH, Wu CH et al (2016) miR-520h is crucial for DAPK2 regulation and breast cancer progression. Oncogene 35(9):1134–1142
Wang F, Xue X, Wei J, An Y, Yao J, Cai H et al (2010) hsa-miR-520h downregulates ABCG2 in pancreatic cancer cells to inhibit migration, invasion, and side populations. Br J Cancer 103(4):567–574
Ding M, Lu X, Wang C, Zhao Q, Ge J, Xia Q et al (2018) The E2F1-miR-520/372/373-SPOP axis modulates progression of renal carcinoma. Cancer Res 78(24):6771–6784
Ramsay RG, Gonda TJ (2008) MYB function in normal and cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer 8(7):523–534
Li Y, Jin K, van Pelt GW, van Dam H, Yu X, Mesker WE et al (2016) c-Myb enhances breast cancer Invasion and metastasis through the Wnt/beta-Catenin/Axin2 pathway. Cancer Res 76(11):3364–3375
Chen RX, Xia YH, Xue TC, Ye SL (2010) Transcription factor c-Myb promotes the invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via increasing osteopontin expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 29:172
Lan T, Yuan K, Yan X, Xu L, Liao H, Hao X et al (2019) LncRNA SNHG10 facilitates hepatocarcinogenesis and metastasis by modulating its homolog SCARNA13 via a positive feedback loop. Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-4044
Acknowledgements
The work was supported by grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21300005131323).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW and TZ conceived and designed the experiments; WW, YY and XC performed the experiments; WW, SS and SH analyzed the data; WW and TZ wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Yang, Y., Chen, X. et al. MAGI1 mediates tumor metastasis through c-Myb/miR-520h/MAGI1 signaling pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Apoptosis 24, 837–848 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01562-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01562-8