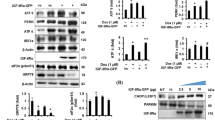
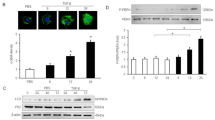
Abstract
Cardiomyocyte apoptosis is a major process in pathogenesis of a number of heart diseases, including ischemic heart diseases and cardiac failure. Ensuring survival of cardiac cells by blocking apoptotic events is an important strategy to improve cardiac function. Although the role of ER disruption in inducing apoptosis has been demonstrated, we do not yet fully understand how it influences the mitochondrial apoptotic machinery in cardiac cell models. Recent investigations have provided evidences that the prosurvival protein HCLS1-associated protein X-1 (Hax1) protein is intimately associated with the pathogenesis of heart disease, mitochondrial biology, and protection from apoptotic cell death. To study the role of Hax1 upon ER stress induction, Hax1 was overexpressed in cardiac cells subjected to ER stress, and cell death parameters as well as mitochondrial alterations were examined. Our results demonstrated that the Hax1 is significantly downregulated in cardiac cells upon ER stress induction. Moreover, overexpression of Hax1 protected from apoptotic events triggered by Tunicamycin-induced ER stress. Upon treatment with Tunicamycin, Hax1 protected from mitochondrial fission, downregulation of mitofusins 1 and 2 (MFN1 and MFN2), loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (∆Ψm), production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptotic cell death. Taken together, our results suggest that Hax1 inhibits ER stress-induced apoptosis at both the pre- and post-mitochondrial levels. These findings may offer an opportunity to develop new agents that inhibit cell death in the diseased heart.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
van Empel VP, Bertrand AT, Hofstra L, Crijns HJ, Doevendans PA, De Windt LJ (2005) Myocyte apoptosis in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 67:21–29
Wang Y, Huang S, Sah VP, Ross J Jr, Brown JH, Han J et al (1998) Cardiac muscle cell hypertrophy and apoptosis induced by distinct members of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase family. J Biol Chem 273:2161–2168
Mel’nikova NP, Timoshin SS, Jivotova EY, Pelliniemi LJ, Jokinen E, Abdelwahid E (2006) Angiotensin-II activates apoptosis, proliferation and protein synthesis in the left heart ventricle of newborn albino rats. Int J Cardiol 112:219–222
Abdelwahid E, Smith G (2007) Apoptosis in chronic heart failure. Int J Cardiol 114:375
Abdelwahid E, Petrovic D, Feng Q, Mistiaen WP (2007) Molecular mechanisms and new developments in the regulation of programmed cell death (apoptosis) and its role in pathogenesis of heart diseases. Nova Science Publishers, Inc, New York
Abdelwahid E, Rolland S, Teng X, Conradt B, Hardwick JM, White K (2011) Mitochondrial involvement in cell death of non-mammalian eukaryotes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:597–607
Abdelwahid E, Yokokura T, Krieser RJ, Balasundaram S, Fowle WH, White K (2007) Mitochondrial disruption in Drosophila apoptosis. Dev Cell 12:793–806
Yu T, Sheu SS, Robotham JL, Yoon Y (2008) Mitochondrial fission mediates high glucose-induced cell death through elevated production of reactive oxygen species. Cardiovasc Res 79:341–351
Youle RJ, Karbowski M (2005) Mitochondrial fission in apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:657–663
Su B, Wang X, Bonda D, Perry G, Smith M, Zhu X (2010) Abnormal mitochondrial dynamics–a novel therapeutic target for Alzheimer’s disease? Mol Neurobiol 41:87–96
Kaufman RJ (2002) Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J Clin Invest 110:1389–1398
Ruddock LW, Molinari M (2006) N-glycan processing in ER quality control. J Cell Sci 119:4373–4380
Ono Y, Shimazawa M, Ishisaka M, Oyagi A, Tsuruma K, Hara H (2012) Imipramine protects mouse hippocampus against Tunicamycin-induced cell death. Eur J Pharmacol 696:83–88
Gorlach A, Klappa P, Kietzmann T (2006) The endoplasmic reticulum: folding, calcium homeostasis, signaling, and redox control. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:1391–1418
Sidrauski C, Chapman R, Walter P (1998) The unfolded protein response: an intracellular signalling pathway with many surprising features. Trends Cell Biol 8:245–249
Urano F, Bertolotti A, Ron D (2000) IRE1 and efferent signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 21):3697–3702
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, Li E, Xu J, Yankner BA et al (2000) Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature 403:98–103
Puthalakath H, O’Reilly LA, Gunn P, Lee L, Kelly PN, Huntington ND et al (2007) ER stress triggers apoptosis by activating BH3-only protein Bim. Cell 129:1337–1349
Kornmann B, Walter P (2010) ERMES-mediated ER-mitochondria contacts: molecular hubs for the regulation of mitochondrial biology. J Cell Sci 123:1389–1393
Pizzo P, Pozzan T (2007) Mitochondria-endoplasmic reticulum choreography: structure and signaling dynamics. Trends Cell Biol 17:511–517
Csordas G, Varnai P, Golenar T, Roy S, Purkins G, Schneider TG et al (2010) Imaging interorganelle contacts and local calcium dynamics at the ER-mitochondrial interface. Mol Cell 39:121–132
Pirot P, Ortis F, Cnop M, Ma Y, Hendershot LM, Eizirik DL et al (2007) Transcriptional regulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress gene chop in pancreatic insulin-producing cells. Diabetes 56:1069–1077
Suzuki Y, Demoliere C, Kitamura D, Takeshita H, Deuschle U, Watanabe T (1997) HAX-1, a novel intracellular protein, localized on mitochondria, directly associates with HS1, a substrate of Src family tyrosine kinases. J Immunol 158:2736–2744
Lam CK, Zhao W, Cai W, Vafiadaki E, Florea SM, Ren X et al (2013) Novel role of HAX-1 in ischemic injury protection involvement of heat shock protein 90. Circ Res 112:79–89
Han Y, Chen YS, Liu Z, Bodyak N, Rigor D, Bisping E et al (2006) Overexpression of HAX-1 protects cardiac myocytes from apoptosis through caspase-9 inhibition. Circ Res 99:415–423
Chao JR, Parganas E, Boyd K, Hong CY, Opferman JT, Ihle JN (2008) Hax1-mediated processing of HtrA2 by Parl allows survival of lymphocytes and neurons. Nature 452:98–102
Fadeel B, Grzybowska E (2009) HAX-1: a multifunctional protein with emerging roles in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1790:1139–1148
Boztug K, Ding XQ, Hartmann H, Ziesenitz L, Schaffer AA, Diestelhorst J et al (2010) HAX1 mutations causing severe congenital neuropenia and neurological disease lead to cerebral microstructural abnormalities documented by quantitative MRI. Am J Med Genet A 152 A:3157–3163
Lanciotti M, Indaco S, Bonanomi S, Coliva T, Mastrodicasa E, Caridi G et al (2010) Novel HAX1 gene mutations associated to neurodevelopment abnormalities in two Italian patients with severe congenital neutropenia. Haematologica 95:168–169
Koontz J, Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos A (2014) Competition through dimerization between antiapoptotic and proapoptotic HS-1-associated protein X-1 (Hax-1). J Biol Chem 289:3468–3477
Zhao W, Waggoner JR, Zhang ZG, Lam CK, Han P, Qian J et al (2009) The anti-apoptotic protein HAX-1 is a regulator of cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20776–20781
Grzybowska EA, Sarnowska E, Konopinski R, Wilczynska A, Sarnowski TJ, Siedlecki JA (2006) Identification and expression analysis of alternative splice variants of the rat Hax-1 gene. Gene 371:84–92
Jeyaraju DV, Cisbani G, De Brito OM, Koonin EV, Pellegrini L (2009) Hax1 lacks BH modules and is peripherally associated to heavy membranes: implications for Omi/HtrA2 and PARL activity in the regulation of mitochondrial stress and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 16:1622–1629
Gurgen D, Hegner B, Kusch A, Catar R, Chaykovska L, Hoff U et al (2011) Estrogen receptor-beta signals left ventricular hypertrophy sex differences in normotensive deoxycorticosterone acetate-salt mice. Hypertension 57:648–654
Santra M, Skorski T, Calabretta B, Lattime EC, Iozzo RV (1995) De novo decorin gene expression suppresses the malignant phenotype in human colon cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:7016–7020
Frank S, Gaume B, Bergmann-Leitner ES, Leitner WW, Robert EG, Catez F et al (2001) The role of dynamin-related protein 1, a mediator of mitochondrial fission, in apoptosis. Dev Cell 1:515–525
Liot G, Bossy B, Lubitz S, Kushnareva Y, Sejbuk N, Bossy-Wetzel E (2009) Complex II inhibition by 3-NP causes mitochondrial fragmentation and neuronal cell death via an NMDA- and ROS-dependent pathway. Cell Death Differ 16:899–909
Chou CH, Lin CC, Yang MC, Wei CC, Liao HD, Lin RC et al (2012) GSK3beta-mediated Drp1 phosphorylation induced elongated mitochondrial morphology against oxidative stress. PLoS One 7:e49112
Eura Y, Ishihara N, Yokota S, Mihara K (2003) Two mitofusin proteins, mammalian homologues of FZO, with distinct functions are both required for mitochondrial fusion. J Biochem 134:333–344
Yaglom JA, Ekhterae D, Gabai VL, Sherman MY (2003) Regulation of necrosis of H9c2 myogenic cells upon transient energy deprivation. Rapid deenergization of mitochondria precedes necrosis and is controlled by reactive oxygen species, stress kinase JNK, HSP72 and ARC. J Biol Chem 278:50483–50496
Shen M, Wang L, Wang B, Wang T, Yang G, Shen L et al (2014) Activation of volume-sensitive outwardly rectifying chloride channel by ROS contributes to ER stress and cardiac contractile dysfunction: involvement of CHOP through Wnt. Cell Death Dis 5:e1528
Li G, Scull C, Ozcan L, Tabas I (2010) NADPH oxidase links endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress, and PKR activation to induce apoptosis. J Cell Biol 191:1113–1125
Tanjore H, Lawson WE, Blackwell TS (2013) Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a pro-fibrotic stimulus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:940–947
Han C, Nam MK, Park HJ, Seong YM, Kang S, Rhim H (2008) Tunicamycin-induced ER stress upregulates the expression of mitochondrial HtrA2 and promotes apoptosis through the cytosolic release of HtrA2. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:1197–1202
Ngoh GA, Papanicolaou KN, Walsh K (2012) Loss of mitofusin 2 promotes endoplasmic reticulum stress. J Biol Chem 287:20321–20332
Korobova F, Ramabhadran V, Higgs HN (2013) An actin-dependent step in mitochondrial fission mediated by the ER-associated formin INF2. Science 339:464–467
Friedman JR, Lackner LL, West M, DiBenedetto JR, Nunnari J, Voeltz GK (2011) ER tubules mark sites of mitochondrial division. Science 334:358–362
Iwasawa R, Mahul-Mellier AL, Datler C, Pazarentzos E, Grimm S (2011) Fis1 and Bap31 bridge the mitochondria-ER interface to establish a platform for apoptosis induction. EMBO J 30:556–568
Ong SB, Subrayan S, Lim SY, Yellon DM, Davidson SM, Hausenloy DJ (2010) Inhibiting mitochondrial fission protects the heart against ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circulation 121:2012–2022
Grossmann J, Walther K, Artinger M, Kiessling S, Scholmerich J (2001) Apoptotic signaling during initiation of detachment-induced apoptosis (“anoikis”) of primary human intestinal epithelial cells. Cell Growth Differ 12:147–155
Grossmann J (2002) Molecular mechanisms of “detachment-induced apoptosis–Anoikis”. Apoptosis 7:247–260
Sun J, Sun G, Meng X, Wang H, Wang M, Qin M et al (2013) Ginsenoside RK3 Prevents Hypoxia-Reoxygenation Induced Apoptosis in H9c2 Cardiomyocytes via AKT and MAPK Pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013:690190
Abdelwahid E, Kalvelyte A, Stulpinas A, de Carvalho KA, Guarita-Souza LC, Foldes G (2016) Stem cell death and survival in heart regeneration and repair. Apoptosis 21:252–268
Abdelwahid E, Rice D, Pelliniemi LJ, Jokinen E (2001) Overlapping and differential localization of Bmp-2, Bmp-4, Msx-2 and apoptosis in the endocardial cushion and adjacent tissues of the developing mouse heart. Cell Tissue Res 305:67–78
Wang C, Li YZ, Wang XR, Lu ZR, Shi DZ, Liu XH (2012) Panax quinquefolium saponins reduce myocardial hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by inhibiting excessive endoplasmic reticulum stress. Shock 37:228–233
Wu XD, Zhang ZY, Sun S, Li YZ, Wang XR, Zhu XQ et al (2013) Hypoxic preconditioning protects microvascular endothelial cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Apoptosis 18:85–98
Lam CK, Zhao W, Liu GS, Cai WF, Gardner G, Adly G et al (2015) HAX-1 regulates cyclophilin-D levels and mitochondria permeability transition pore in the heart. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E6466–E6475
Lam AK, Galione A, Lai FA, Zissimopoulos S (2013) Hax-1 identified as a two-pore channel (TPC)-binding protein. FEBS Lett 587:3782–3786
Radhika V, Onesime D, Ha JH, Dhanasekaran N (2004) Galpha13 stimulates cell migration through cortactin-interacting protein Hax-1. J Biol Chem 279:49406–49413
Kawaguchi Y, Nakajima K, Igarashi M, Morita T, Tanaka M, Suzuki M et al (2000) Interaction of Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen leader protein (EBNA-LP) with HS1-associated protein X-1: implication of cytoplasmic function of EBNA-LP. J Virol 74:10104–10111
Vasquez-Trincado C, Garcia-Carvajal I, Pennanen C, Parra V, Hill JA, Rothermel BA et al (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy and cardiovascular disease. J Physiol 594:509–525
Kane LA, Youle RJ (2010) Mitochondrial fission and fusion and their roles in the heart. J Mol Med (Berl) 88:971–979
Hom J, Sheu SS (2009) Morphological dynamics of mitochondria–a special emphasis on cardiac muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 46:811–820
Ong SB, Hausenloy DJ (2010) Mitochondrial morphology and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 88:16–29
Chen H, Detmer SA, Ewald AJ, Griffin EE, Fraser SE, Chan DC (2003) Mitofusins Mfn1 and Mfn2 coordinately regulate mitochondrial fusion and are essential for embryonic development. J Cell Biol 160:189–200
Papanicolaou KN, Ngoh GA, Dabkowski ER, O’Connell KA, Ribeiro RF Jr, Stanley WC et al (2012) Cardiomyocyte deletion of mitofusin-1 leads to mitochondrial fragmentation and improves tolerance to ROS-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cell death. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302:H167–H179
Chen Y, Liu Y, Dorn GW 2nd (2011) Mitochondrial fusion is essential for organelle function and cardiac homeostasis. Circ Res 109:1327–1331
Skulachev VP (2001) Mitochondrial filaments and clusters as intracellular power-transmitting cables. Trends Biochem Sci 26:23–29
Narula J, Pandey P, Arbustini E, Haider N, Narula N, Kolodgie FD et al (1999) Apoptosis in heart failure: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria and activation of caspase-3 in human cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8144–8149
Papanicolaou KN, Khairallah RJ, Ngoh GA, Chikando A, Luptak I, O’Shea KM et al (2011) Mitofusin-2 maintains mitochondrial structure and contributes to stress-induced permeability transition in cardiac myocytes. Mol Cell Biol 31:1309–1328
Shi Y (2002) Mechanisms of caspase activation and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell 9:459–470
Olsson M, Zhivotovsky B (2011) Caspases and cancer. Cell Death Differ 18:1441–1449
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2002) Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem 277:13430–13437
Enoksson M, Robertson JD, Gogvadze V, Bu P, Kropotov A, Zhivotovsky B et al (2004) Caspase-2 permeabilizes the outer mitochondrial membrane and disrupts the binding of cytochrome c to anionic phospholipids. J Biol Chem 279:49575–49578
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Luca Pellegrini (Faculty of Medicine, Université Laval, Quebec, QC, Canada) for Hax1 overexpression construct, Dr. Thomas Simmen for discussion and Dr. Aikaterini Kontrogianni-Konstantopoulos for kindly sharing information on Hax1 expression. We are grateful to Mr. Denislam Zaripov for art drawing. E.A. was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NIH/NHLBI), Grant SP0012613. X.L. was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81272278). K.A.T.C was supported by Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (CAPES) of Brazil, Grant PE 1711.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdelwahid, E., Li, H., Wu, J. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress triggers Hax1-dependent mitochondrial apoptotic events in cardiac cells. Apoptosis 21, 1227–1239 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1286-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-016-1286-6