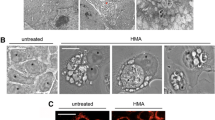
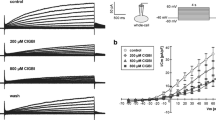
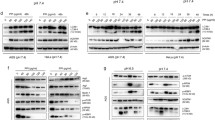
Abstract
Amiloride derivatives are a class of new promising chemotherapeutic agents. A representative member of this family is the sodium–hydrogen antiporter inhibitor HMA (5-(N,N-hexamethylene amiloride), which has been demonstrated to induce cellular intracytosolic acidification and cell death through the apoptotic pathway(s). This work aims at characterizing drug response of human cancer cell lines to HMA. After a first screening revealing that HMA interferes with cancer cell survival, we focused our attention on SW613-B3 colon carcinoma cells, which are intrinsically resistant to a panel of drugs. Searching for the activation of canonical apoptosis, we found that this process was abortive, given that the final steps of this process, i.e. PARP-1 cleavage and DNA ladder, were not detectable. Thus, we addressed caspase-independent paradigms of cell death and we observed that HMA promotes the induction of the LEI/L-DNase II pathway as well as of parthanatos. Finally, we explored the possible impact of autophagy of cell response to HMA, providing the evidence that autophagy is activated in our experimental system. On the whole, our results defined the biochemical reactions triggered by HMA, and elucidated its multiple effects, thus adding further complexity to the intricate network leading to drug resistance.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giansanti V, Torriglia A, Scovassi AI (2011) Conversation between apoptosis and autophagy: “Is it your turn or mine?”. Apoptosis 16:321–333
Giansanti V, Tillhon M, Mazzini G, Prosperi E, Lombardi P, Scovassi AI (2011) Killing of tumor cells: a drama in two acts. Biochem Pharmacol 82:1304–1310
Aredia F, Scovassi AI (2013) Manipulation of autophagy in cancer cells: an innovative strategy to fight drug resistance. Future Med Chem 5:1009–1021
Swartz MA, Iida N, Roberts EW, Sangaletti S, Wong MH, Yull FE, Coussens LM, DeClerck YA (2012) Tumor microenvironment complexity: emerging roles in cancer therapy. Cancer Res 72:2473–2480
Daniel C, Bell C, Burton C, Harguindey S, Reshkin SJ, Rauch C (2013) The role of proton dynamics in the development and maintenance of multidrug resistance in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832:606–617
Giansanti V, Santamaria G, Torriglia A, Aredia F, Scovassi AI, Bottiroli G, Croce AC (2012) Fluorescence properties of the Na+/H+ exchanger inhibitor HMA (5-(N,N-hexamethylene)amiloride) are modulated by intracellular pH. Eur J Histochem 56:e3
Rich IN, Worthington-White D, Garden OA, Musk P (2000) Apoptosis of leukemic cells accompanies reduction in intracellular pH after targeted inhibition of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger. Blood 95:1427–1434
Coakley RJ, Taggart C, McElvaney NG, O’Neill SJ (2002) Cytosolic pH and the inflammatory microenvironment modulate cell death in human neutrophils after phagocytosis. Blood 100:3383–3391
Altairac S, Zeggai S, Perani P, Courtois Y, Torriglia A (2003) Apoptosis induced by Na+/H+ antiport inhibition activates the LEI/L- DNase II pathway. Cell Death Differ 10:548–557
Giansanti V, Rodriguez GE, Savoldelli M, Gioia R, Forlino A, Mazzini G, Pennati M, Zaffaroni N, Scovassi AI, Torriglia A (2013) Characterization of stress response in human retinal epithelial cells. J Cell Mol Med 17:103–115
Torriglia A, Leprêtre C (2009) LEI/L-DNase II: interplay between caspase-dependent and independent pathways. Front Biosci 14:4836–4847
Wang Y, Dawson VL, Dawson TM (2009) Poly(ADP-ribose) signals to mitochondrial AIF: a key event in parthanatos. Exp Neurol 218:193–202
Klionsky DJ, Abdalla FC, Abeliovich H et al (2012) Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy. Autophagy 8:445–554
Lavialle C, Modjtahedi N, Cassingena R, Brison O (1988) High c-myc amplification level contributes to the tumorigenic phenotype of the human breast carcinoma cell line SW 613-S. Oncogene 3:335–339
Donzelli M, Bernardi R, Negri C, Prosperi E, Padovan L, Lavialle C, Brison O, Scovassi AI (1999) Apoptosis-prone phenotype of human colon carcinoma cells with a high level amplification of the c-myc gene. Oncogene 18:439–448
Bottone MG, Soldani C, Tognon G, Gorrini C, Lazzè MC, Brison O, Ciomei M, Pellicciari C, Scovassi AI (2003) Multiple effects of paclitaxel are modulated by a high c-myc amplification level. Exp Cell Res 290:49–59
Gorrini C, Donzelli M, Torriglia A, Supino R, Brison O, Bernardi R, Negri C, Denegri M, Counis MF, Ranzani GN, Scovassi AI (2003) Effect of apoptogenic stimuli on colon carcinoma cell lines with a different c-myc expression level. Int J Mol Med 11:737–742
Parks M, Tillhon M, Donà F, Prosperi E, Scovassi AI (2011) 2-Methoxyestradiol: new perspectives in colon carcinoma treatment. Mol Cell Endocrinol 331:119–128
Torriglia A, Negri C, Chaudun E, Prosperi E, Courtois Y, Counis MF, Scovassi AI (1999) Differential involvement of DNases in HeLa cell apoptosis induced by etoposide and long term-culture. Cell Death Differ 6:234–244
Giansanti V, Camboni T, Piscitelli F, Prosperi E, La Regina G, Lazzè MC, Santin G, Silvestri R, Scovassi AI (2009) Study of the effects of a new pyrazolecarboxamide: changes in mitochondria and induction of apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1890–1898
Santin G, Scietti L, Veneroni P, Barni S, Bernocchi G, Bottone MG (2012) Effects of Cisplatin in neuroblastoma rat cells: damage to cellular organelles. Int J Cell Biol 2012:424072
Donà F, Prosperi E, Savio M, Coppa T, Scovassi AI, Mondello C (2008) Loss of histone H2AX increases sensitivity of immortalized mouse fibroblasts to the topoisomerase II inhibitor etoposide. Int J Oncol 33:613–631
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 7:321–328
Torriglia A, Leprêtre C, Padrón-Barthe L, Chahory S, Martin E (2008) Molecular mechanism of L-DNase II activation and function as a molecular switch in apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 76:1490–1502
Leprêtre C, Tchakarska G, Blibech H, Lebon C, Torriglia A (2013) Apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and leukocyte elastase inhibitor/L-DNase II (LEI/LDNaseII), can interact to conduct caspase-independent cell death. Apoptosis 18:1048–1059
Matthews H, Ranson M, Kelso MJ (2011) Anti-tumour/metastasis effects of the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride: an orally active anti-cancer drug waiting for its call-of-duty? Int J Cancer 129:2051–2061
Park KS, Poburko D, Wollheim CB, Demaurex N (2009) Amiloride derivatives induce apoptosis by depleting ER Ca(2+) stores in vascular endothelial cells. Br J Pharmacol 156:1296–1304
Bourge M, Tlili A, Dupré-Crochet S, Nüsse O, Sulpice JC (2010) Amiloride derivatives modulate PS externalization in neutrophil-like PLB-985 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 80:1012–1020
Pennati M, Millo E, Gandellini P, Folini M, Zaffaroni N (2012) RNA interference-mediated validation of survivin and Apollon/BRUCE as new therapeutic targets for cancer therapy. Curr Top Med Chem 12:69–78
Feng R, Han J, Ziegler J, Yang M, Castranova V (2012) Apaf-1 deficiency confers resistance to ultraviolet-induced apoptosis in mouse embryonic fibroblasts by disrupting reactive oxygen species amplification production and mitochondrial pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 52:889–897
Leprêtre C, Sidoli G, Scovassi AI, Torriglia A (2009) Leukocyte elastase inhibitor: a new regulator of PARP-1. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1171:25–31
Leprêtre C, Scovassi AI, Shah GM, Torriglia A (2009) Regulation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 functions by leukocyte elastase inhibitor/LEI-derived DNase II during caspase-independent apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:1046–1054
Chahory S, Keller N, Martin E, Omri B, Crisanti P, Torriglia A (2010) Light induced retinal degeneration activates a caspase-independent pathway involving cathepsin D. Neurochem Int 57:278–287
Hangen E, Blomgren K, Bénit P, Kroemer G, Modjtahedi N (2010) Life with or without AIF. Trends Biochem Sci 35:278–287
Wu WK, Coffelt SB, Cho CH, Wang XJ, Lee CW, Chan FK, Yu J, Sung JJ (2012) The autophagic paradox in cancer therapy. Oncogene 31:939–953
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to Maria Grazia Bottone for cytoskeleton immunofluorescence, Roberta Gioia for qPCR analysis and Marzia Pennati for survivin experiments. Research was partially granted by Italian Regione Lombardia (Project Plant Cell to A.I.S) and Cariplo (Project 2011-0270 to A.F.). F.A. is a PhD student (Dottorato in Genetica, Biologia Cellulare e Molecolare, University of Pavia, Italy). L.M.G.O. is a PhD student (Dottorato in Genetica, Biologia Cellulare e Molecolare, University of Pavia, Italy) supported by SENESCYT (Quito, Ecuador) and UTPL (Loja, Ecuador). I.J. is supported by an ADEME grant to A.T.
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aredia, F., Giansanti, V., Mazzini, G. et al. Multiple effects of the Na+/H+ antiporter inhibitor HMA on cancer cells. Apoptosis 18, 1586–1598 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0898-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0898-3