Abstract
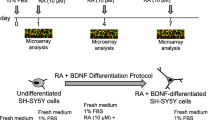
Bilobalide, a sesquiterpene trilactone constituent of Ginkgo biloba leaf extracts, has been proposed to exert protective and trophic effects on neurons. However, mechanisms underlying the protective effects of bilobalide remain unclear. Using human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells and primary hippocampal neurons, this study investigated the neuroprotective effects of bilobalide. We mimicked aging-associated neuronal impairments by applying external factors (beta amyloid protein (Aβ) 1-42, H2O2 and serum deprivation) consequently inducing cell apoptosis. As markers for apoptosis, cell viability, DNA fragmentation, mitochondrial membrane potential and levels of cleaved caspase 3 were measured. We found that, bilobalide prevented Aβ 1-42-, H2O2- and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. To better understand the neuroprotective effects of bilobalide, we also tested the ability of bilobalide to modulate pro-survival signaling pathways such as protein kinase C (PKC), extracellular-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathways. It was found that, bilobalide dose-dependently increased PI3K activity and levels of phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt Ser473 and Thr308), which could be maintained up to at least 2 h after bilobalide withdrawal in cells treated with or without Aβ 1-42, H2O2 or serum-free medium. In addition, application of PI3K/Akt inhibitor LY294002 could abrogate both the protective effects of bilobalide against Aβ 1-42-, H2O2- and serum deprivation-induced apoptotic cell damage and bilobalide-induced increase in PI3K activity and levels of p-Akt (Ser473 and Thr308). In contrast, application of PKC inhibitor staurosporine (STS) did not affect the protective effects of bilobalide. Moreover, no change in levels of phosphorylated ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) was observed in bilobalide-treated cells. These results further suggested that the PI3K/Akt pathway might be involved in the protective effects of bilobalide. Since modern technology allows production of purified bilobalide with high bioavailability, bilobalide may be useful in developing therapy for diseases involving age-associated neurodegeneration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rossi R, Basilico F, Rossoni G, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Mauri PL (2009) Liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization ion trap mass spectrometry of bilobalide in plasma and brain of rats after oral administration of its phospholipidic complex. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:224–227. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2009.04.026
Bruno C, Cuppini R, Sartini S, Cecchini T, Ambrogini P, Bombardelli E (1993) Regeneration of motor nerves in bilobalide-treated rats. Planta Med 59:302–307. doi:10.1055/s-2006-959686
DeFeudis FV (2002) Bilobalide and neuroprotection. Pharmacol Res 46:565–568. doi:10.1016/S1043-6618(02)00233-5
Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J (2003) Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:1779–1792. doi:10.1007/s00018-003-3080-1
Ahlemeyer B, Krieglstein J (2003) Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacopsychiatry 36(Suppl 1):S8–S14. doi:10.1055/s-2003-40454
Zhou LJ, Song W, Zhu XZ, Chen ZL, Yin ML, Cheng XF (2000) Protective effects of bilobalide on amyloid beta-peptide 25–35-induced PC12 cell cytotoxicity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 21:75–79
Zhou LJ, Zhu XZ (2000) Reactive oxygen species-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and protective effect of bilobalide. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:982–988
Tchantchou F, Lacor PN, Cao Z, Lao L, Hou Y, Cui C, Klein WL, Luo Y (2009) Stimulation of neurogenesis and synaptogenesis by bilobalide and quercetin via common final pathway in hippocampal neurons. J Alzheimers Dis. doi:10.3233/JAD-2009-1189
Xu Y, Cui C, Pang C, Christen Y, Luo Y (2007) Restoration of impaired phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element-binding protein (CREB) by EGb 761 and its constituents in Abeta-expressing neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Neurosci 26:2931–2939. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05905.x
Nuutinen U, Postila V, Mättö M, Eeva J, Ropponen A, Eray M, Riikonen P, Pelkonen J (2006) Inhibition of PI3-kinase-Akt pathway enhances dexamethasone-induced apoptosis in a human follicular lymphoma cell line. Exp Cell Res 312:322–330. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2005.10.023
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME (1999) Cellular survival: a play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13:2905–2927. doi:10.1101/gad.13.22.2905
Cross TG, Scheel-Toellner D, Henriquez NV, Deacon E, Salmon M, Lord JM (2000) Serine/threonine protein kinases and apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 256:34–41. doi:10.1006/excr.2000.4836
O’Gorman DM, Cotter TG (2001) Molecular signals in anti-apoptotic survival pathways. Leukemia 15:21–34. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2401998
Bonni A, Brunet A, West AE, Datta SR, Takasu MA, Greenberg ME (1999) Cell survival promoted by the Ras-MAPK signaling pathway by transcription-dependent and independent mechanisms. Science 286:1358–1362. doi:10.1126/science.286.5443.1358
Shimoke K, Chiba H (2001) Nerve growth factor prevents 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced cell death via the Akt pathway by suppressing caspase 3-like activity using PC12 cells relevance to therapeutical application for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci Res 63:402–409. doi:10.1002/1097-4547(20010301)63:5<402:AID-JNR1035>3.0.CO;2-F
Yu XR, Jia GR, Gao GD, Wang SH, Han Y, Cao W (2006) Neuroprotection of insulin against oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cultured retinal neurons involvement of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signal pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 38:241–248. doi:10.1111/j.1745-7270.2006.00152.x
Shi C, Zhao L, Zhu B, Li Q, Yew DT, Yao Z, Xu J (2009) Dosage effects of EGb761 on hydrogen peroxide-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact 180:389–397. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.04.008
Shi C, Zhao L, Zhu B, Li Q, Yew DT, Yao Z, Xu J (2009) Protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb761) and its constituents quercetin and ginkgolide B against beta-amyloid peptide-induced toxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Chem Biol Interact 181:115–123. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2009.05.010
Du K, Montminy M (1998) CREB is a regulatory target for the protein kinase Akt/PKB. J Biol Chem 273:32377–32379. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.49.32377
Aakalu G, Smith WB, Nguyen N, Jiang C, Schuman EM (2001) Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 30:489–502. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(01)00295-1
Kobayashi MS, Han D, Packer L (2000) Antioxidants and herbal extracts protect HT-4 neuronal cells against glutamate-induced cytotoxicity. Free Radic Res 32:115–124. doi:10.1080/10715760000300121
Venkatesan B, Valente AJ, Reddy VS, Siwik DA, Chandrasekar B (2009) Resveratrol blocks interleukin-18-EMMPRIN cross-regulation and smooth muscle cell migration. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297:H874–H886. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00311.2009
Jacotot E, Costantini P, Laboureau E, Zamzami N, Susin SA, Kroemer G (1999) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization during the apoptotic process. Ann N Y Acad Sci 887:18–30. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb07919.x
Macdonald NJ, Delderfield SM, Zhang W, Taglialatela G (2003) Tumour necrosis factor-alpha vs. growth factor deprivation-promoted cell death: distinct converging pathways. Aging Cell 2:245–256. doi:10.1046/j.1474-9728.2003.00059.x
Shi C, Guo K, Yew DT, Yao Z, Forster EL, Wang H, Xu J (2008) Effects of ageing and Alzheimer’s disease on mitochondrial function of human platelets. Exp Gerontol 43:589–594. doi:10.1016/j.exger.2008.02.004
Shi C, Yao Z, Xu J, Yew DT (2009) Effects of Gingko Extract (EGb761) on oxidative damage under different conditions of serum supply. J Bioenerg Biomembr 41:61–69. doi:10.1007/s10863-009-9197-7
Ramassamy C (2006) Emerging role of polyphenolic compounds in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases: a review of their intracellular targets. Eur J Pharmacol 545:51–64. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.06.025
Luo Y, Smith JV, Paramasivam V, Burdick A, Curry KJ, Buford JP, Khan I, Netzer WJ, Xu H, Butko P (2002) Inhibition of amyloid-beta aggregation and caspase 3 activation by the Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:12197–12202. doi:10.1073/pnas.182425199
Vivanco I, Sawyers CL (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2:489–501. doi:10.1038/nrc839
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase 9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease. Cell 91:479–489. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80434-1
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80595-4
Nicholson KM, Anderson NG (2002) The protein kinase B/Akt signalling pathway in human malignancy. Cell Signal 14:381–395. doi:10.1016/S0898-6568(01)00271-6
Zhou BP, Hung MC (2002) Novel targets of Akt, p21(Cipl/WAF1), and MDM2. Semin Oncol 29:62–70. doi:10.1053/sonc.2002.34057
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L, Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M, Green DR (2004) Direct activation of Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 303:1010–1014. doi:10.1126/science.1092734
Gottlieb TM, Leal JF, Seger R, Taya Y, Oren M (2002) Cross-talk between Akt, p53 and Mdm2: possible implications for the regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 21:1299–1303. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205181
Ramljak D, Coticchia CM, Nishanian TG, Saji M, Ringel MD, Conzen SD, Dickson RB (2003) Epidermal growth factor inhibition of c-Myc-mediumted apoptosis through Akt and Erk involves Bcl-xL upregulation in mammary epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 287:397–410. doi:10.1016/S0014-4827(03)00135-6
Farrall AJ, Wardlaw JM (2009) Blood-brain barrier: ageing and microvascular disease—systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging 30:337–352. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.07.015
Popescu BO, Toescu EC, Popescu LM, Bajenaru O, Muresanu DF, Schultzberg M, Bogdanovic N (2009) Blood-brain barrier alterations in ageing and dementia. J Neurol Sci 283:99–106. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.02.321
Shi C, Fang L, Yew DT, Yao Z, Xu J (2010) Ginkgo biloba extract EGb761 protects against mitochondrial dysfunction in platelets and hippocampi in ovariectomized rats. Platelets 21:53–59. doi:10.3109/09537100903395180
Acknowledgments
Many thanks for support from the GuangDong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. 20090171110046) and Science Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (No. 9151008901000039).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Chun Shi and Fengming Wu contribute to this work equally and are listed as co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, C., Wu, F., Yew, D.T. et al. Bilobalide prevents apoptosis through activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway in SH-SY5Y cells. Apoptosis 15, 715–727 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0492-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-010-0492-x