Abstract
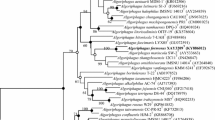
A Gram-stain negative, non-motile and short rod shaped bacterium, designated strain DSL-12T, was isolated from seawater of the East China Sea and characterised phylogenetically and phenotypically. Optimal growth was found to occur at 28 °C (range 4–40 °C), pH 7 (range 6–12) and with 3% (w/v) NaCl (range 0–8%). Phylogenetic analysis based on the 16S rRNA gene sequence showed that strain DSL-12T is related to members of the genus Algoriphagus and shares high sequence similarities with Algoriphagus boritolerans DSM 17298T (97.6%) and Algoriphagus alkaliphilus DSM 22703T (97.6%). The 16S rRNA gene sequence identities between strain DSL-12T and other current members of the genus Algoriphagus were below 96.4%. The digital DNA–DNA hybridization values between strain DSL-12T and the type strains A. boritolerans DSM 17298T and A. alkaliphilus DSM 22703T were found to be 21.2 ± 2.4% and 20.2 ± 2.4%, respectively. The average nucleotide identity (ANI) values between strain DSL-12T and A. boritolerans DSM 17298T and A. alkaliphilus DSM 22703T were found to be 83.2% and 82.8%, respectively. The sole respiratory quinone was identified as MK-7. The major polar lipids were identified as phosphatidylethanolamine, diphosphatidylglycerol, one unidentified phospholipid and two unidentified lipids. The major fatty acids identified as were iso-C15:0, summed feature 8 (C18:1ω7c and/or C18:1ω6c), C16:0, summed feature 3 (C16:1ω7c and/or C16:1ω6c) and iso-C17:0. The G+C content of the genomic DNA was determined to be 43.3 mol%. The combined genotypic and phenotypic data indicate that strain DSL-12T represents a novel species of the genus Algoriphagus, for which the name Algoriphagus litoralis sp. nov. is proposed, with the type strain DSL-12T (= KCTC 62647T = MCCC 1K03536T).

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- DDH:
-
DNA–DNA hybridization
- DPG:
-
Diphosphatidylglycerol
- PE:
-
Phosphatidylethanolamine
- PL:
-
Phospholipid
- PC:
-
Phosphatidylcholine
- AL:
-
Aminolipid
References
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007) Chimaereicella boritolerans sp. nov., a boron-tolerant and alkaliphilic bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:986–992
Bowman JP, Nichols CM, Gibson JA (2003) Algoriphagus ratkowskyi gen. nov., sp. nov., Brumimicrobium glaciale gen. nov., sp. nov., Cryomorpha ignava gen. nov., sp. nov. and Crocinitomix catalasitica gen. nov., sp. nov., novel flavobacteria isolated from various polar habitats. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 53:1343–1355
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, Da CM, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De MS (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA–DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Han JR, Geng QL, Wang FQ, Du ZJ, Chen GJ (2017a) Algoriphagus marinus sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment and emended description of the genus Algoriphagus. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:2412–2417
Han JR, Zhao JX, Wang ZJ, Chen GJ, Du ZJ (2017b) Algoriphagus resistens sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1275–1280
Jia X, Jia B, Kim KH, Jeon CO (2017) Algoriphagus aestuariicola sp. nov., isolated from estuary sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:914–919
Jung YT, Lee JS, Yoon JH (2015) Algoriphagus aestuarii sp. nov., a member of the Cyclobacteriaceae isolated from a tidal-flat sediment of the Yellow Sea in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:3439–3446
Kang H, Weerawongwiwat V, Jung MY, Myung SC, Kim W (2013) Algoriphagus chungangensis sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 63:648–653
Kim H, Joung Y, Joh K (2014a) Algoriphagus taeanensis sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat, and emended description of Algoriphagus hitonicola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:21–26
Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J (2014b) Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:346–351
Kumar S, Stecher G, Tamura K (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33:1870–1874
Lee DH, Kahng HY, Lee SB (2012) Algoriphagus jejuensis sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:409–413
Li Y, Yan S, Yang Q, Qi Z, Zhang XH, Fu YB (2011) Algoriphagus faecimaris sp. nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2856–2860
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Goker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinform 14:60
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Oh KH, Kang SJ, Lee SY, Park S, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2012) Algoriphagus namhaensis sp. nov., isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:575–579
Park S, Kang SJ, Oh KH, Oh TK, Yoon JH (2010) Algoriphagus lutimaris sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:200–204
Park S, Ha MJ, Yoon SY, Jung YT, Yoon JH (2016) Algoriphagus litorisediminis sp. nov., isolated from a tidal flat. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:5437–5443
Park S, Jung YT, Park JM, Yoon JH (2017a) Algoriphagus aquaemixtae sp. nov., isolated from water in an estuary environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3231–3236
Park S, Park JM, Yoon JH (2017b) Algoriphagus marisflavi sp. nov., isolated from water of an estuary environment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:4168–4174
Richter M, Rossello-Mora R (2009) Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:19126–19131
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids, MIDI Technical Note 101. MIDI Inc, Newark
Skerman V (1967) A guide to the identification of the genera of bacteria: with methods and digests of generic characteristics, 2nd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Stackebrandt E, Ebers J (2006) Taxonomic parameters revisited: tarnished gold standards. Microbiol Today 33:152–155
Sun QL, Sun L (2017) Description of Algoriphagus iocasae sp. nov., isolated from deep-sea sediment of Okinawa Trough. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:243–249
Thompson CC, Chimetto L, Edwards RA, Swings J, Stackebrandt E, Thompson FL (2013) Microbial genomic taxonomy. BMC Genom 14:913
Tiago I, Mendes V, Pires C, Morais PV, Veríssimo A (2006) Chimaereicella alkaliphila gen. nov., sp. nov., a Gram-negative alkaliphilic bacterium isolated from a nonsaline alkaline groundwater. Syst Appl Microbiol 29:100–108
Tindall BJ (1990) Lipid composition of Halobacterium lacusprofundi. FEMS Microbiol Lett 66:199–202
Tindall B, Sikorski J, Smibert R, Krieg N (2007) Phenotypic characterization and the principles of comparative systematics. In: Reddy CA, Beveridge TJ, Breznak JA, Marzluf GA, Schmidt TM, Snyder LR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology, 3rd edn. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 330–393
Wayne L, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 37:463–464
Wei Y, Fang J, Xu Y, Zhao W, Cao J (2018) Corynebacterium hadale sp. nov. isolated from hadopelagic water of the New Britain Trench. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:1474–1478
Ye MQ, Wang XT, Zhang J, Chen GJ, Du ZJ (2017) Algoriphagus formosus sp. nov., isolated from coastal sediment. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 111:913–920
Yoon JH, Lee MH, Kang SJ, Oh TK (2006) Algoriphagus terrigena sp. nov., isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:777–780
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, Chun J (2017) Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:1613–1617
Acknowledgements
This work is supported support by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41773069, 91328208 and 41373071 to JF). YLW acknowledges the Project Sponsored by the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars State Education Ministry (Grant No. D-8002-15-8004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical statement
This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Y., Mao, H., Wang, K. et al. Algoriphagus litoralis sp. nov., isolated from the junction between the ocean and a freshwater lake. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1545–1552 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01280-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01280-w