Abstract
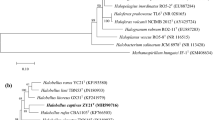
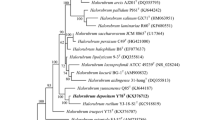
An extremely halophilic archaeon, designated strain GSM28T, was isolated from a subterranean halite deposit in a Yunnan salt mine, China. Cells of the strain were observed to be cocci, non-motile and Gram-variable, and to require at least 15% (w/v) NaCl for growth (optimum 20%). Growth was found to occur in the ranges of 20–45 °C (optimum 42 °C) and pH 6.0–8.5 (optimum 7.5). Cells did not lyse in distilled water. Phylogenetic analysis based on 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that this strain belongs to the genus Halalkalicoccus and shows 99.1% similarities with its close phylogenetic relative Halalkalicoccus paucihalophilus DSM 24557T. Genomic ANI analysis showed that the DNA–DNA relatedness between strain GSM28T and the closely related species Hac. paucihalophilus DSM 24557T and Halalkalicoccus jeotgali B3T was 83.7% and 83.1%, respectively. The major polar lipids were determined to be phosphatidylglycerol, phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester, phosphatidylglycerol sulfate, sulfated mannosyl-glucosyl-glycerol diether-1 and two unidentified glycolipids. The DNA G + C content was determined to be 61.8 mol %. On the basis of physiological, biochemical tests and phylogenetic differentiations, strain GSM28T is concluded to represent a novel species in the genus Halalkalicoccus, for which the name Halalkalicoccus subterraneus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is GSM28T (= CGMCC 1.16344T = NBRC 113432T).


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MES:
-
2-Morpholinoethanesulfonic acid
- PIPES:
-
1, 4-Piperazine bis (ethanesulfonic acid)
- CHES:
-
2-(Cyclohexylamino) ethanesulfonic acid
- CAPS:
-
N-Cyclohexyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid
- DMSO:
-
Dimethylsulfoxide
- OD:
-
Optical density
- ANI:
-
Average nucleotide identity
- MLSA:
-
Multilocus sequence analysis
- DDH:
-
DNA–DNA hybridization
- TLC:
-
Thin-layer chromatography
- PG:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol
- PGP-Me:
-
Phosphatidylglycerol phosphate methyl ester
- S-DGD-1:
-
Sulfated mannosyl-glucosyl-glycerol diether-1
References
Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, Rooney AP, Yi H, Xu XW, De Meyer S, Trujillo ME (2018) Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 68:461–466
Cui HL, Zhou PJ, Oren A, Liu SJ (2009) Intraspecific polymorphism of 16S rRNA genes in two halophilic archaeal genera, Haloarcula and Halomicrobium. Extremophiles 13:31–37
Dussault HP (1955) An improved technique for staining red halophilic bacteria. J Bacteriol 70:484–485
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gutiérrez C, González C (1972) Method for simultaneous detection of proteinase and esterase activities in extremely halophilic bacteria. Appl Microbiol 24:516–517
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hartmann R, Sickinger HD, Oesterhelt D (1980) Anaerobic growth of halobacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3821–3825
Kamekura M (1993) Lipids of extreme halophiles. In: Vreeland RH, Hochstein LI (eds) The biology of halophilic bacteria. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 135–161
Liu BB, Tang SK, Zhang YG, Lu XH, Li L, Cheng J, Zhang YM, Zhang LL, Li WJ (2013) Halalkalicoccus paucihalophilus sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from Lop Nur region in Xinjiang, northwest of China. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 103:1007–1014
Marmur J (1961) A procedure for the isolation of deoxyribonucleic acid from microorganisms. J Mol Biol 3:208–218
Minegishi H, Kamekura M, Itoh T, Echigo A, Usami R, Hashimoto T (2010) Further refinement of the phylogeny of the Halobacteriaceae based on the full-length RNA polymerase subunit B′ (rpoB′) gene. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:2398–2408
Mukhtar S, Mirza BS, Mehnaz S, Mirza MS, Mclean J, Malik KA (2018) Impact of soil salinity on the microbial structure of halophyte rhizosphere microbiome. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 34:136
Mwirichia R, Cousin S, Muigai AW, Boga HI, Stackebrandt E (2010) Archaeal diversity in the haloalkaline Lake Elmenteita in Kenya. Curr Microbiol 60:47–52
Nurk S, Bankevich A, Antipov D, Gurevich AA, Korobeynikov A, Lapidus A, Prjibelski AD, Pyshkin A, Sirotkin A, Sirotkin Y, Stepanauskas R, Clingenpeel SR, Woyke T, McLean JS, Lasken R, Tesler G, Alekseyev MA, Pevzner PA (2012) SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J Comput Biol 19:455–477
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:233–238
Ozcan B, Ozcengiz G, Coleri A, Cokmus C (2007) Diversity of halophilic archaea from six hypersaline environments in Turkey. J Microbiol Biotechnol 17:985–992
Papke RT, White E, Reddy P, Weigel G, Kamekura M, Minegishi H, Usami R, Ventosa A (2011) A multilocus sequence analysis approach to the phylogeny and taxonomy of the Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2984–2995
Roh SW, Nam YD, Chang HW, Sung Y, Kim KH, Oh HM, Bae JW (2007) Halalkalicoccus jeotgali sp. nov., a halophilic archaeon from shrimp jeotgal, a traditional Korean fermented seafood. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2296–2298
Rosenzweig WD, Peterson J, Woish J, Vreeland RH (2000) Development of a protocol to retrieve microorganisms from ancient salt crystals. Geomicrobiol J 17:185–192
Smibert RM, Krieg NR (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P (ed) Methods for general and molecular bacteriology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 607–654
Sun W, Li J, Jiang L, Sun Z, Fu M, Peng X (2015) Profiling microbial community structures across six large oilfields in China and the potential role of dominant microorganisms in bioremediation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 99:8751–8764
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Valenzuela-Encinas C, Neria-González I, Alcántara-Hernández RJ, Enríquez-Aragón JA, Estrada-Alvarado I, Hernández-Rodríguez C, Dendooven L, Marsch R (2008) Phylogenetic analysis of the archaeal community in an alkaline-saline soil of the former lake Texcoco (Mexico). Extremophiles 12:247–254
Xiao W, Wang ZG, Wang YX, Schneegurt MA, Li ZY, Lai YH, Zhang SY, Wen ML, Cui XL (2013) Comparative molecular analysis of the prokaryotic diversity of two salt mine soils in southwest China. J Basic Microbiol 53:942–952
Xue Y, Fan H, Ventosa A, Grant WD, Jones BE, Cowan DA, Ma Y (2005) Halalkalicoccus tibetensis gen. nov., sp. nov., representing a novel genus of haloalkaliphilic archaea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2501–2505
Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim JM, Kwon SJ, Chun J (2017) A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 110:1281–1286
Acknowledgements
We thank Professor Zhu L. Yang from the Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences for the help in sample collection, and we also thank Dr. Hao Yan from the College of Life Sciences, Anhui Normal University, for his technical assistance.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31460003), the Anhui Provincial Key Lab. of the Conservation and Exploitation of Biological Resources (591601), and the Department of Education Anhui Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SC conceived the project, analysed the data, and drafted the manuscript. SC, YX, SS and FC performed the study. YX and JL critically revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
No specific ethical or institutional permits were required to conduct sampling and the experimental studies did not involve endangered or protected species.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, S., Xu, Y., Sun, S. et al. Halalkalicoccus subterraneus sp. nov., an extremely halophilic archaeon isolated from a subterranean halite deposit. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 112, 1067–1075 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01241-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-019-01241-3