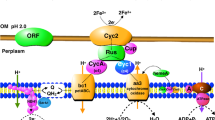
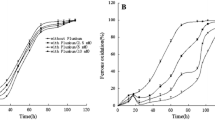
Abstract
In contrast to iron-oxidizing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans, A. ferrooxidans from a stationary phase elemental sulfur-oxidizing culture exhibited a lag phase in pyrite oxidation, which is similar to its behaviour during ferrous iron oxidation. The ability of elemental sulfur-oxidizing A. ferrooxidans to immediately oxidize ferrous iron or pyrite without a lag phase was only observed in bacteria obtained from growing cultures with elemental sulfur. However, these cultures that shifted to ferrous iron oxidation showed a low rate of ferrous iron oxidation while no growth was observed. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis was used for a quantitative proteomic analysis of the adaptation process when bacteria were switched from elemental sulfur to ferrous iron. A comparison of total cell lysates revealed 39 proteins whose increase or decrease in abundance was related to this phenotypic switching. However, only a few proteins were closely related to iron and sulfur metabolism. Reverse-transcription quantitative PCR was used to further characterize the bacterial adaptation process. The expression profiles of selected genes primarily involved in the ferrous iron oxidation indicated that phenotypic switching is a complex process that includes the activation of genes encoding a membrane protein, maturation proteins, electron transport proteins and their regulators.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amouric A, Appia-Ayme C, Yarzabal A, Bonnefoy V (2009) Regulation of the iron and sulfur oxidation pathways in the acidophilic Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Adv Mater Res 71–73:163–166
Appia-Ayme C, Quatrini R, Denis Y, Denizot F, Silver S, Roberto F, Veloso F, Valdes J, Cardenas JP, Esparza M, Orellana O, Jedlicki E, Bonnefoy V, Holmes DS (2006) Microarray and bioinformatic analyses suggest models for carbon metabolism in the autotroph Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 83:273–280
Bouchal P, Zdrahal Z, Helanova S, Janiczek O, Hallberg KB, Mandl M (2006) Proteomic and bioinformatic analysis of iron- and sulfur-oxidizing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans using immobilized pH gradients and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 6:4278–4285
Bruscella P, Appia-Ayme C, Levican G, Ratouchniak J, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2007) Differential expression of two bc 1 complexes in the strict acidophilic chemolithoautotrophic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans suggests a model for their respective roles in iron or sulfur oxidation. Microbiol-SGM 153:102–110
Cabrejos ME, Zhao HL, Guacucano M, Bueno S, Levican G, Garcia E, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS (1999) IST1 insertional inactivation of the resB gene: implications for phenotypic switching in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. FEMS Microbiol Lett 175:223–229
Ceskova P, Mandl M, Hubackova J (2000) Kinetic quantitation of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria adsorbed on sulfur. Biotechnol Lett 22:699–701
Chi A, Valenzuela L, Beard S, Mackey AJ, Shabanowitz J, Hunt DF, Jerez CA (2007) Periplasmic proteins of the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Mol Cell Proteomics 6:2239–2251
Felicio AP, de Oliveira E, Odena MA, Garcia O, Bertolini MC, Ferraz LFC, Ottoboni LMM, Novo MTM (2011) Differential proteomic analysis of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cells maintained in contact with bornite or chalcopyrite: proteins involved with the early bacterial response. Process Biochem 46:770–776
Holmes DS, Zhao HL, Levican G, Ratouchniak J, Bonnefoy V, Varela P, Jedlicki E (2001) ISAfe1, an ISL3 family insertion sequence from Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 19859. J Bacteriol 183:4323–4329
Ishihama Y, Oda Y, Tabata T, Sato T, Nagasu T, Rappsilber J, Mann M (2005) Exponentially modified protein abundance index (emPAI) for estimation of absolute protein amount in proteomics by the number of sequenced peptides per protein. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:1265–1272
Johnson DB (2010) The biogeochemistry of biomining. In: Barton L, Mandl M, Loy A (eds) Geomicrobiology: molecular and environmental perspective. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 401–426
Johnson DB, Hallberg KB (2009) Carbon, iron and sulfur metabolism in acidophilic micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol 54:201–255
Kucera J, Bouchal P, Cerna H, Potesil D, Janiczek O, Zdrahal Z, Mandl M (2012) Kinetics of anaerobic elemental sulfur oxidation by ferric iron in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and protein identification by comparative 2-DE-MS/MS. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 101:561–573
Kulpa CF Jr, Mjoli N, Roskey MT (1986) Comparison of iron and sulfur oxidation in Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: inhibition of iron oxidation by growth on sulfur. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 16:289–295
Landesman J, Duncan DW, Walden CC (1966) Oxidation of inorganic sulfur compounds by washed cell suspension of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Can J Microbiol 12:957–964
Lefimil C, Osorio H, Quatrini R, Holmes D, Jedlicki E (2009) Regulation of expression of the petI operon involved in iron oxidation in the biomining bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Adv Mater Res 71–73:199–202
Levican G, Bruscella P, Guacunano M, Inostroza C, Bonnefoy V, Holmes DS, Jedlicki E (2002) Characterization of the petI and res operons of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 184:1498–1501
Mandl M, Novakova O (1993) An ultraviolet method for the determination of oxidation of iron sulphide minerals by bacteria. Biotechnol Tech 7:573–574
Mandl M, Vyskovsky M (1994) Kinetics of arsenic(III) oxidation by iron(III) catalysed by pyrite in the presence of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Lett 16:1199–1204
Moura I, Lino AR (1994) Low-spin sulfite reductases. Methods Enzymol 243:296–301
Oliver DJ, VanSlyke JK (1988) Sulfur-dependent inhibition of protein and RNA synthesis by iron-grown Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Arch Biochem Biophys 263:369–377
Pakostova E, Mandl M, Omesova Pokorna B, Diviskova E, Lojek A (2013) Cellular ATP changes in Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans cultures oxidizing ferrous iron and elemental sulfur. Geomicrobiol J 30:1–7
Pfaffl MW (2001) A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 29:e45
Planeta J, Karasek P, Vejrosta J (2003) Development of packed capillary columns using carbon dioxide slurries. J Sep Sci 26:525–530
Pokorna B, Mandl M, Borilova S, Ceskova P, Markova R, Janiczek O (2007) Kinetic constant variability in bacterial oxidation of elemental sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 37:3752–3754
Ponce JS, Moinier D, Byrne D, Amouric A, Bonnefoy V (2012) Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans oxidizes ferrous iron before sulfur likely through transcriptional regulation by the global redox responding RegBA signal transducing system. Hydrometallurgy 127–128:187–194
Pott AS, Dahl C (1998) Sirohaem sulfite reductase and other proteins encoded by genes at the dsr locus of Chromatium vinosum are involved in the oxidation of intracellular sulfur. Microbiol-SGM 144:1881–1894
Quatrini R, Lefimil C, Holmes DS, Jedlicki E (2005) The ferric iron uptake regulator (Fur) from the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Microbiol-SGM 151:2005–2015
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Ratouchniak J, Veloso F, Valdes J, Lefimil C, Silver S, Roberto F, Orellana O, Denizot F, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2006) Insights into the iron and sulfur energetic metabolism of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by microarray transcriptome profiling. Hydrometallurgy 83:263–272
Quatrini R, Appia-Ayme C, Denis Y, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS, Bonnefoy V (2009) Extending the models for iron and sulfur oxidation in the extreme acidophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. BMC Genomics 10:394
Ramirez P, Guiliani N, Valenzuela L, Beard S, Jerez CA (2004) Differential protein expression during growth of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans on ferrous iron, sulfur compounds or metal sulfides. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4491–4498
Schippers A, Sand W (1999) Bacterial leaching of metal sulfides proceeds by two indirect mechanisms via thiosulfate or via polysulfides and sulfur. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:319–321
Silverman MP, Lungred DG (1959) Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol 77:642–647
Sugio T, Wada K, Mori M, Inagaki K, Tano T (1988) Synthesis of an iron-oxidizing system during growth of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans on sulfur-basal salts medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 54:150–152
Valdes J, Veloso F, Jedlicki E, Holmes DS (2003) Metabolic reconstruction of sulfur assimilation in the extremophile Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans based on genome analysis. BMC Genomics 4:51
Vera M, Guiliani N, Jerez CA (2003) Proteomic and genomic analysis of the phosphate starvation response of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 71:125–132
Vera M, Rohwerder T, Bellenberg S, Sand W, Denis Y, Bonnefoy V (2009) Characterization of biofilm formation by the bioleaching acidophilic bacterium Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans by a microarray transcriptome analysis. Adv Mater Res 71–73:175–178
Yarzabal A, Brasseur G, Ratouchniak J, Lund K, Lemesle-Meunier D, DeMoss JA, Bonnefoy V (2002) The high-molecular-weight cytochrome c Cyc2 of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans is an outer membrane protein. J Bacteriol 184:313–317
Yarzabal A, Dusquesne K, Bonnefoy V (2003) Rusticyanin gene expression of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans ATCC 33020 in sulfur- and in ferrous iron media. Hydrometallurgy 71:107–114
Yarzabal A, Appia-Ayme C, Ratouchniak J, Bonnefoy V (2004) Regulation of the expression of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans rus operon encoding two cytochromes c, a cytochrome oxidase and rusticyanin. Microbiol-SGM 150:2113–2123
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants 525/08/0697 from the Czech Science Foundation. The MS-based proteomic study (Z.Z. and D.P.) was supported by the project “CEITEC—Central European Institute of Technology” (CZ.1.05/1.1.00/02.0068) from the European Regional Development Fund. P.B. was partly supported by the European Regional Development Fund and the State Budget of the Czech Republic (RECAMO, CZ.1.05/2.1.00/03.0101).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kucera, J., Bouchal, P., Lochman, J. et al. Ferrous iron oxidation by sulfur-oxidizing Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and analysis of the process at the levels of transcription and protein synthesis. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 103, 905–919 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9872-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9872-2