Abstract
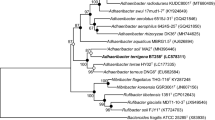
An orange-coloured, non-spore-forming, motile and coccus-shaped actinobacterium, designated YIM 75677T, was isolated from a soil sample collected from a dry-hot river valley in Dongchuan county, Yunnan Province, south-west China and its taxonomic position was investigated. Growth of strain YIM 75677T occurred at 12–55 °C, pH 6.0–9.0 and NaCl tolerance up to 2 % (w/v). Cells adhered to agar media and were agglutinated tightly together. The peptidoglycan contained meso-diaminopimelic acid, alanine and glutamic acid. The whole-cell hydrolysates mainly contained glucose, galactose, mannose and ribose. The predominant menaquinone was MK-9 (H2) and the major fatty acids were anteiso-C15:0 and iso-C15:0. Mycolic acids were not present. The DNA G+C content of strain YIM 75677T was 74.8 mol%. Phylogenetic analyses based on 16S rRNA gene sequence comparisons clearly revealed that strain YIM 75677T represents a novel member of the genus Kineococcus and is closely related to Kineococcus xinjiangensis S2-20T (level of similarity, 98.6 %). Meanwhile, the result of DNA–DNA hybridization between strain YIM 75677T and K. xinjiangensis S2-20T demonstrated that this isolate represented a different genomic species in the genus Kineococcus. On the basis of phylogenetic, phenotypic and chemotaxonomic characteristics, strain YIM 75677T represents a novel species of the genus Kineococcus, for which the name Kineococcus glutineturens sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is YIM 75677T (=CCTCC AA 209075T = JCM 18126T).

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Carlsohn MR, Groth I, Saluz HP, Schumann P, Stackebrandt E (2008) Fodinicola feengrottensis gen. nov., sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from a medieval mine. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:1529–1536
Christensen H, Angen O, Mutters R, Olsen JE, Bisgaard M (2000) DNA–DNA hybridization determined in micro-wells using covalent attachment of DNA. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1095–1102
Chun J, Lee JH, Jung Y, Kim M, Kim S, Kim BK, Lim YW (2007) EzTaxon: a web-based tool for the identification of prokaryotes based on 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2259–2261
Collins MD, Pirouz T, Goodfellow M, Minnikin DE (1977) Distribution of menaquinones in actinomycetes and corynebacteria. J Gen Microbiol 100:221–230
Dong XZ, Cai MY (2001) Manual of systematics and identification of general bacteria. Science Press, Beijing
Duangmal K, Thamchaipenet A, Ara I, Matsumoto A, Takahashi Y (2008) Kineococcus gynurae sp. nov., isolated from a Thai medicinal plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2439–2442
Ezaki T, Hashimoto Y, Yabuuchi E (1989) Fluorometric deoxyribonucleic acid–deoxyribonucleic acid hybridization in microdilution wells as an alternative to membrane filter hybridization in which radioisotopes are used to determine genetic relatedness among bacterial strains. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:224–229
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–789
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Garrity GM, Lilburn TG, Cole JR, Harrison SH, Euzeby J, Tindall BJ (2007) Part 10—The Bacteria: phylum Actinobacteria: class ‘Actinobacteria’. In: The taxonomic outline of the Bacteria and Archaea. Release 7.7. http://www.taxonomicoutline.org/index.php/toba/article/view/187/219
Gordon RE, Barnett DA, Handerhan JE, Pang CHN (1974) Nocardia coeliaca, Nocardia autotrophica, and the nocardin strain. Int J Syst Bacteriol 24:54–63
He L, Li W, Huang Y, Wang LM, Liu ZH, Lanoot BJ, Vancanneyt M, Swings J (2005) Streptomyces jietaisiensis sp. nov., isolated from soil in northern China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1939–1944
Jurado V, Laiz L, Martinez AO, Groth I, Jimenez CS (2011) Pseudokineococcus lusitanus gen. nov., sp. nov., and reclassification of Kineococcus marinus Lee 2006 as Pseudokineococcus marinus comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:2515–2519
Kelly KL (1964) Inter-Society Color Council–National Bureau of Standards color name charts illustrated with centroid colors. US Government Printing Office, Washington
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kimura M (1983) The neutral theory of molecular evolution. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Lee SD (2006) Kineococcus marinus sp. nov., isolated from marine sediment of the coast of Jeju, Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1279–1283
Lee SD (2009) Kineococcus rhizosphaerae sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2204–2207
Leifson E (1960) Atlas of bacterial flagellation. Academic Press, London
Li WJ, Xu P, Schumann P, Zhang YQ, Pukall R, Xu LH, Stackebrandt E, Jiang CL (2007) Georgenia ruanii sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from forest soil in Yunnan (China) and emended description of the genus Georgenia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1424–1428
Liu M, Peng F, Wang Y, Zhang KD, Chen G, Fang CX (2009) Kineococcus xinjiangensis sp. nov., isolated from desert sand. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:1090–1093
MacFaddin JF (1980) Biochemical tests for identification of medical bacteria, 2nd edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Maszenan AM, Tay JH, Schumann P, Jiang HL, Tay STL (2005) Quadrisphaera granulorum gen. nov., sp. nov., a gram-positive polyphosphate-accumulating coccus in tetrads or aggregates isolated from aerobic granules. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1771–1777
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Minnikin DE, Collins MD, Goodfellow M (1979) Fatty acid and polar lipid composition in the classification of Cellulomonas, Oerskovia and related taxa. J Appl Bacteriol 47:87–95
Minnikin DE, Hutchinson IG, Caldicott AB, Goodfellow M (1980) Thin layer chromatography of methanolysates of mycolic acid-containing bacteria. J Chromatogr 188:221–233
Minnikin DE, O’Donnell AG, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Nie GX, Ming H, Li S, Zhou EM, Cheng J, Tang X, Feng HG, Tang SK, Li WJ (2012a) Amycolatopsis dongchuanensis sp. nov., a novel actinobacterium isolated from dry-hot valley in Yunnan, south-west China. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.038125-0
Nie GX, Ming H, Li S, Zhou EM, Cheng J, Yu TT, Zhang J, Feng HG, Tang SK, Li WJ (2012b) Geodermatophilus nigrescens sp. nov., isolated from a dry-hot valley. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. doi:10.1007/s10482-012-9696-0
Pagani H, Parenti F (1978) Kineosporia, a new genus of the order Actinomycetales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 28:401–406
Phillips RW, Wiegel J, Berry CJ, Filermans C, Peacock AD, White DC, Shimkets LJ (2002) Kineococcus radiotolerans sp.nov., a radiation-resistant, gram-positive bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:933–938
Saddler GS, Tavecchia P, Lociuro S, Zanol M, Colombo L, Selva E (1991) Analysis of madurose and other actinomycete whole cell sugars by gas chromatography. J Microbiol Methods 14:185–191
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl 20:16
Shirling EB, Gottlieb D (1966) Methods for characterization of Streptomyces species. Int J Syst Bacteriol 16:313–340
Stackebrandt E, Goebel BM (1994) Taxonomic note: a place for DNA–DNA reassociation and 16S rRNA sequence analysis in the present species definition in bacteriology. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:846–849
Staneck JL, Roberts GD (1974) Simplified approach to identification of aerobic actinomycetes by thin-layer chromatography. Appl Microbiol 28:226–231
Tamaoka J, Katayama-Fujimura Y, Kuraishi H (1983) Analysis of bacterial menaqui-none mixtures by high performance liquid chromatography. J Appl Bacteriol 54:31–36
Tamura T, Hayakawa M, Hatano K (1998) A new genus of the order Actinomycetales, Cryptosporangium gen. nov., with descriptions of Cryptosporangium arvum sp. nov. and Cryptosporangium japonicum sp. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:95–1005
Tamura T, Ishida Y, Otoguro M, Yamamura H, Hayakawa M, Suzuki KI (2010) Angustibacter luteus gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from subarctic forest soil. Int J Syst Bacteriol 60:2441–2445
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using a maximum likelhood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Tang SK, Tian XP, Zhi XY, Cai M, Wu JY, Yang LL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2008) Haloactinospora alba gen. nov., sp. nov., a halophilic filamentous actinomycete of the family Nocardiopsaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2075–2080
Tang SK, Wang Y, Chen Y, Lou K, Cao LL, Xu LH, Li WJ (2009) Zhihengliuella alba sp. nov., and emended description of the genus Zhihengliuella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:2025–2032
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Uchida K, Aida K (1984) An improved method for the glycolate test for simple identification of the acyl type of bacterial cell walls. J Gen Appl Microbiol 30:131–134
Waksman SA (1967) The actinomycetes. A summary of current knowledge. Ronald Press, New York
Williams ST, Goodfellow M, Alderson G (1989) Genus Streptomyces Waksman and Henrici 1943, 339AL. In: Williams ST, Sharpe ME, Holt JG (eds).s Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol. 4. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, pp 2463–2468
Yokota A, Tamura T, Nishii T, Hasegawa T (1993) Kineococcus aurantiacus gen. nov., sp. nov., a new aerobic, gram-positive, motile coccus with meso-diaminopimelic acid and arabinogalactan in the cell wall. Int J Syst Bacteriol 43:52–57
Zhi XY, Li WJ, Stackebrandt E (2009) An update of the structure and 16S rRNA gene sequence-based definition of higher ranks of the class Actinobacteria, with the proposal of two new suborders and four new families and emended descriptions of the existing higher taxa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:589–608
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by Science and Technology Innovation Talents Program in Universities of Henan Province of China (HASTIT, No. 2010HASTIT020) and Key Technologies R&D Program of Henan Province of China (112102310335, 112102210106). W-J Li was also supported by ‘Hundred Talents Program’ of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Guo-Xing Nie and Hong Ming contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nie, GX., Ming, H., Zhang, J. et al. Kineococcus glutineturens sp. nov., isolated from soil in Yunnan, south-west China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 102, 239–246 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9731-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-012-9731-1