Abstract
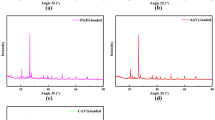
Kaolinite clay obtained from Ubulu-Ukwu, Delta state in Nigeria was modified with polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) reagent to obtain PVA-modified Kaolinite clay adsorbent. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) of the PVA-modified adsorbent suggests that Kaolinite clay particles were made more compact in nature with no definite structure. Modification of Kaolinite clay with PVA increased its adsorption capacity for 300 mg/L Pb2+ and Cd2+ by a factor of at least 6, i.e., from 4.5 mg/g to 36.23 mg/g and from 4.38 mg/g to 29.85 mg/g, respectively, at 298 K. Binary mixtures of Pb2+ and Cd2+ decreased the adsorption capacity of Unmodified Kaolinite clay for Pb2+ by 26.3% and for Cd2+ by 0.07%, respectively. In contrast, for PVA-modified Kaolinite clay, the reductions were up to 50.9% and 58.5% for Pb2+ and Cd2+, respectively.
The adsorption data of Pb2+ and Cd2+ onto both Unmodified and PVA-modified Kaolinite clay adsorbents were found to fit the Pseudo-Second Order Kinetic model (PSOM), indicating that adsorption on both surfaces was mainly by chemisorption and is concentration dependent. However, kinetic adsorption data from both adsorbent generally failed the Pseudo-First order Kinetic model (PFOM) test.
Extents of desorption of 91% Pb2+ and 94% Cd2+ were obtained, using 0.1 M HCl, for the Unmodified Kaolinite clay adsorbent. It was found that 99% Pb2+ and 97% Cd2+, were desorbed, for PVA-modified Kaolinite clay adsorbents within 3 min for 60 mg/L of the metal ions adsorbed by the adsorbents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adebowale, K.O., Unuabonah, I.E., Olu-Owolabi, B.I.: Kinetic and thermodynamic aspects of the adsorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on tripolyphosphate-modified kaolinite clay. Chem. Eng. J. 136, 99–107 (2008)
Bunzl, K., Schmidt, W., Sansoni, B.: Kinetics of ion-exchange in soil organic matter. IV. Adsorption and desorption of Pb2+, Cu2+, Cd2+, Zn2+ and Ca2+ by peat. J. Soil Sci. 27, 32–41 (1976)
Dzombak, D.A., Morel, F.M.M.: Sorption of cadmium on hydrous ferric oxide at high sorbate/sorbent ratios: equilibrium kinetics and modeling. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 112, 588–598 (1986)
Galan, E., Aparicio, P., Miras, A., Michailidis, K., Tsirambides, A.: Technical properties of compounded kaolin sample from Griva (Macedonia, Greece). Appl. Clay Sci. 10, 477–490 (1996)
Ho, Y.S., Ofomaja, A.E.: Kinetics and thermodynamics of lead ion sorption on palm kernel fiber from aqueous solution. Process Biochem. 40, 3455–3461 (2005)
Ho, Y.S., McKay, G.: Batch Lead (II) removal from aqueous solution by peat: equilibrium and kinetics. Trans. Chem. E Part B 77, 165–173 (1999)
Ho, Y.S., Ng, C.Y.J., McKay, G.: Removal of Lead (II) from effluents by sorption on peat using second-order kinetics. Sep. Sci. Technol. 36(2), 241–261 (2001)
Ikhsan, J., Johnson, B.B., Wells, J.D.: A comparative study of the adsorption of transition metals on kaolinite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 217, 403–410 (1999)
Kalavathy, M.H., Karthikeyan, T., Rajgopal, S., Miranda, L.R.: Kinetic and isotherm studies of Cu(II) adsorption onto H3PO4-activated rubber wood sawdust. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 292, 354–362 (2005)
Moore, D.M., Reynolds, Jr., R.C.: X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals, pp. 179–201. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1989)
Ramelow, U.S., Guidry, C.N., Fisk, S.D.: A kinetic study of metal ion binding by biomass immobilized in polymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 46, 37–55 (1996)
Salim, R., Al-Subu, M.M., Qashoa, S.: Removal of Lead from polluted water using decaying Leaves. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A Environ. Sci. Eng. 29, 2087–2114 (1994)
Sharma, D.C., Forster, C.F.: The treatment of chromium using sphagnum moss peat. Water Res. 27(7), 1201–1208 (1994)
Spark, K.M., Wells, J.D., Johnson, B.B.: Characterizing trace metal adsorption on kaolinite. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 46, 633–640 (1995)
Srivastava, P., Singh, B., Angove, M.: Competitive adsorption behaviour of metals on Kaolinite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 290, 28–38 (2005)
Unuabonah, E.I., Adebowale, K.O., Olu-Owolabi, B.I.: Kinetic and Thermodynamic studies of the adsorption of lead (II) ions onto phosphate-modified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 144(1–2), 386–395 (2007)
Vadivelan, V., Kumar, K.V.: Equilibrium, Kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 286(1), 90–100 (2005)
Volesky, B.: Detoxification of metal-bearing effluents: biosorption for the next century. Hydrometallurgy 59, 203–216 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unuabonah, E.I., Adebowale, K.O., Olu-Owolabi, B.I. et al. Comparison of sorption of Pb2+ and Cd2+ on Kaolinite clay and polyvinyl alcohol-modified Kaolinite clay. Adsorption 14, 791–803 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9142-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-008-9142-9